Statistical Distributions in MQL5 - taking the best of R and making it faster
Those include the Cauchy, Weibull, normal, log-normal, logistic, exponential, uniform, gamma distributions, the central and noncentral beta, chi-squared, Fisher's F-distribution, Student's t-distribution, as well as the discrete binomial and negative binomial distributions, geometric, hypergeometric and Poisson distributions. In addition, there are functions for calculating theoretical moments of distributions, which allow to evaluate the degree of conformity of the real distribution to the modeled one.
The MQL5 standard library has been supplemented with numerous mathematical functions from R. Moreover, an increase in operation speed of 3 to 7 times has been achieved, compared to the initial versions in the R language. At the same time, errors in implementation of certain functions in R have been found.
Contents
- Functions for calculating the statistical characteristics of array elements
- Functions for working with statistical distributions
2.1. Normal distribution
- 2.1.1. MathProbabilityDensityNormal()
- 2.1.2. MathCumulativeDistributionNormal()
- 2.1.3. MathQuantileNormal()
- 2.1.4. MathRandomNormal()
- 2.1.5. MathMomentsNormal()
2.2. Log-normal distribution
- 2.2.1. MathProbabilityDensityLognormal()
- 2.2.2. MathCumulativeDistributionLognormal()
- 2.2.3. MathQuantileLognormal()
- 2.2.4. MathRandomLognormal()
- 2.2.5. MathMomentsLognormal()
2.3. Beta distribution
- 2.3.1. MathProbabilityDensityBeta()
- 2.3.2. MathCumulativeDistributionBeta()
- 2.3.3. MathQuantileBeta()
- 2.3.4. MathRandomBeta()
- 2.3.5. MathMomentsBeta()
2.4. Noncentral beta distribution
- 2.4.1. MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralBeta()
- 2.4.2. MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralBeta()
- 2.4.3. MathQuantileNoncentralBeta()
- 2.4.4. MathRandomNoncentralBeta()
- 2.4.5. MathMomentsNoncentralBeta()
2.5. Gamma distribution
- 2.5.1. MathProbabilityDensityGamma()
- 2.5.2. MathCumulativeDistributionGamma()
- 2.5.3. MathQuantileGamma()
- 2.5.4. MathRandomGamma()
- 2.5.5. MathMomentsGamma()
2.6. Chi-squared distribution
- 2.6.1. MathProbabilityDensityChiSquare()
- 2.6.2. MathCumulativeDistributionChiSquare()
- 2.6.3. MathQuantileChiSquare()
- 2.6.4. MathRandomChiSquare()
- 2.6.5. MathMomentsChiSquare()
2.7. Noncentral chi-squared distribution
- 2.7.1. MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralChiSquare()
- 2.7.2. MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralChiSquare()
- 2.7.3. MathQuantileNoncentralChiSquare()
- 2.7.4. MathRandomNoncentralChiSquare()
- 2.7.5. MathMomentsNoncentralChiSquare()
2.8. Exponential distribution- 2.8.1. MathProbabilityDensityExponential()
- 2.8.2. MathCumulativeDistributionExponential()
- 2.8.3. MathQuantileExponential()
- 2.8.4. MathRandomExponential()
- 2.8.5. MathMomentsExponential()
2.9. F-distribution- 2.9.1. MathProbabilityDensityF()
- 2.9.2. MathCumulativeDistributionF()
- 2.9.3. MathQuantileF()
- 2.9.4. MathRandomF()
- 2.9.5. MathMomentsF()
2.10. Noncentral F-distribution
- 2.10.1. MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralF()
- 2.10.2. MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralF()
- 2.10.3. MathQuantileNoncentralF()
- 2.10.4. MathRandomNoncentralF()
- 2.10.5. MathMomentsNoncentralF()
2.11. t-distribution
- 2.11.1. MathProbabilityDensityT()
- 2.11.2. MathCumulativeDistributionT()
- 2.11.3. MathQuantileT()
- 2.11.4. MathRandomT()
- 2.11.5. MathMomentsT()
2.12 Noncentral t-distribution
- 2.12.1. MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralT()
- 2.12.2. MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralT()
- 2.12.3. MathQuantileNoncentralT()
- 2.12.4. MathRandomNoncentralT()
- 2.12.5. MathMomentsNoncentralT()
2.13. Logistic distribution
- 2.13.1. MathProbabilityDensityLogistic()
- 2.13.2. MathCumulativeDistributionLogistic()
- 2.13.3. MathQuantileLogistic()
- 2.13.4. MathRandomLogistic()
- 2.13.5. MathMomentsLogistic()
2.14. Cauchy distribution
- 2.14.1. MathProbabilityDensityCauchy()
- 2.14.2. MathCumulativeDistributionCauchy()
- 2.14.3. MathQuantileCauchy()
- 2.14.4. MathRandomCauchy()
- 2.14.5. MathMomentsCauchy()
2.15. Uniform distribution
- 2.15.1. MathProbabilityDensityUniform()
- 2.15.2. MathCumulativeDistributionUniform()
- 2.15.3. MathQuantileUniform()
- 2.15.4. MathRandomUniform()
- 2.15.5. MathMomentsUniform()
2.16. Weibull distribution
- 2.16.1. MathProbabilityDensityWeibull()
- 2.16.2. MathCumulativeDistributionWeibull()
- 2.16.3. MathQuantileWeibull()
- 2.16.4. MathRandomWeibull()
- 2.16.5. MathMomentsWeibull()
2.17. Binomial distribution
- 2.17.1. MathProbabilityDensityBinomial()
- 2.17.2. MathCumulativeDistributionBinomial()
- 2.17.3. MathQuantileBinomial()
- 2.17.4. MathRandomBinomial()
- 2.17.5. MathMomentsBinomial()
2.18. Negative binomial distribution
- 2.18.1. MathProbabilityDensityNegativeBinomial()
- 2.18.2. MathCumulativeDistributionNegativeBinomial()
- 2.18.3. MathQuantileNegativeBinomial()
- 2.18.4. MathRandomNegativeBinomial()
- 2.18.5. MathMomentsNegativeBinomial()
2.19. Geometric distribution
- 2.19.1. MathProbabilityDensityGeometric()
- 2.19.2. MathCumulativeDistributionGeometric()
- 2.19.3. MathQuantileGeometric()
- 2.19.4. MathRandomGeometric()
- 2.19.5. MathMomentsGeometric()
2.20. Hypergeometric distribution
- 2.20.1. MathProbabilityDensityHypergeometric()
- 2.20.2. MathCumulativeDistributionHypergeometric()
- 2.20.3. MathQuantileHypergeometric()
- 2.20.4. MathRandomHypergeometric()
- 2.20.5. MathMomentsHypergeometric()
2.21. Poisson distribution
- 2.21.1. MathProbabilityDensityPoisson()
- 2.21.2. MathCumulativeDistributionPoisson()
- 2.21.3. MathQuantilePoisson()
- 2.21.4. MathRandomPoisson()
- 2.21.5. MathMomentsPoisson()
- Table of correspondence to the statistical functions in R
- An example of using the functions
- Comparison of calculation speed
- Detected calculation errors in R
- References
Introduction
The R language is one of the best tools of statistical processing and analysis of data.
Thanks to availability and support of multiple statistical distributions, it had become widespread in the analysis and processing of various data. Using the apparatus of probability theory and mathematical statistics allows for a fresh look at the financial market data and provides new opportunities to create trading strategies. With the statistical library, all these features are now available in the MQL5.
The statistical library contains functions for calculating the statistical characteristics of data, as well as functions for working with statistical distributions.
This article considers the main functions of the library and an example of their practical use.
1. Functions for calculating the statistical characteristics of array elements
This group of functions calculates the standard characteristics (mean, variance, skewness, kurtosis, median, root-mean-square and standard deviations) of array elements.
1.1. MathMean
The function calculates the mean (first moment) of array elements. In case of error it returns NaN (not a number). Analog of the mean() in R.
double MathMean( const double &array[] // [in] Array with data );
1.2. MathVariance
The function calculates the variance (second moment) of array elements. In case of error it returns NaN. Analog of the var() in R.
double MathVariance( const double &array[] // [in] Array with data );
1.3. MathSkewness
The function calculates the skewness (third moment) of array elements. In case of error it returns NaN. Analog of the skewness() in R (e1071 library).
double MathSkewness( const double &array[] // [in] Array with data );
1.4. MathKurtosis
The function calculates the kurtosis (fourth moment) of array elements. In case of error it returns NaN. Analog of the kurtosis() in R (e1071 library).
double MathKurtosis( const double &array[] // [in] Array with data );
1.5. MathMoments
The function calculates the first 4 moments (mean, variance, skewness, kurtosis) of array elements. Returns true if the moments have been calculated successfully, otherwise false.
bool MathMoments( const double &array[], // [in] Array with data double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) const int start=0, // [in] Initial index for calculation const int count=WHOLE_ARRAY // [in] The number of elements for calculation );
1.6. MathMedian
The function calculates the median value of array elements. In case of error it returns NaN. Analog of the median() in R.
double MathMedian( double &array[] // [in] Array with data );
1.7. MathStandardDeviation
The function calculates the standard deviation of array elements. In case of error it returns NaN. Analog of the sd() in R.
double MathStandardDeviation( const double &array[] // [in] Array with data );
1.8. MathAverageDeviation
The function calculates the average absolute deviation of array elements. In case of error it returns NaN. Analog of the aad() in R.
double MathAverageDeviation( const double &array[] // [in] Array with data );
All functions that calculate the kurtosis use the excess kurtosis around the normal distribution (excess kurtosis=kurtosis-3), i.e. the excess kurtosis of a normal distribution is zero.
It is positive if the peak of the distribution around the expected value is sharp, and negative if the peak is flat.
2. Statistical distributions
The statistical library of the MQL5 contains 5 functions for working with the statistical distributions:
- Calculation of probability density (the MathProbabilityDensityX() functions);
- Calculation of probabilities (the MathCumulativeDistributionX() functions);
The probability distribution function is equal to the probability of a random variable falling within the range of (-inf; x]). - Calculation of distribution quantiles (the MathQuantileX() functions);
The quantile x of a distribution corresponds to a random value falling within the range of (-inf, x] with the specified probability for the given distribution parameters. - Generating random numbers with the specified distribution (the MathRandomX() functions);
- Calculation of the theoretical moments of the distributions (the MathMomentsX() functions);
2.1. Normal Distribution
2.1.1. MathProbabilityDensityNormal
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of normal distribution with the mu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.double MathProbabilityDensityNormal( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean (expected value) parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] sigma (root-mean-square) parameter of the distribution const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of normal distribution with the mu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityNormal( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean (expected value) parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] sigma (root-mean-square) parameter of the distribution int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the values of the probability density function of normal distribution with the mu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dnorm() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityNormal( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean (expected value) parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] sigma (root-mean-square) parameter of the distribution const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the values of the probability density function of normal distribution with the mu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityNormal( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean (expected value) parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] sigma (root-mean-square) parameter of the distribution double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.1.2. MathCumulativeDistributionNormal
The function calculates the value of the normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionNormal( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] Expected value const double sigma, // [in] Root-mean-square deviation const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionNormal( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] Expected value const double sigma, // [in] Root-mean-square deviation int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );The function calculates the value of the normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pnorm() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionNormal( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Expected value const double sigma, // [in] Root-mean-square deviation const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionNormal( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Expected value const double sigma, // [in] Root-mean-square deviation double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.1.3. MathQuantileNormal
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileNormal( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable const double mu, // [in] Expected value const double sigma, // [in] Root-mean-square deviation const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileNormal( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable const double mu, // [in] Expected value const double sigma, // [in] Root-mean-square deviation int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the values of inverse normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qnorm() in R.
bool MathQuantileNormal( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Expected value const double sigma, // [in] Root-mean-square deviation const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the values of inverse normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileNormal( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Expected value const double sigma, // [in] Root-mean-square deviation double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.1.4. MathRandomNormal
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the normal law with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomNormal( const double mu, // [in] Expected value const double sigma, // [in] Root-mean-square deviation int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the normal law with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rnorm() in R.
bool MathRandomNormal( const double mu, // [in] Expected value const double sigma, // [in] Root-mean-square deviation const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.1.5. MathMomentsNormal
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the normal distribution. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsNormal( const double mu, // [in] Expected value const double sigma, // [in] Root-mean-square deviation double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.2. Log-normal distribution
2.2.1. MathProbabilityDensityLognormal
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of log-normal distribution with the mu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityLognormal( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of log-normal distribution with the mu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityLognormal( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of log-normal distribution with the mu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns NaN. Analog of the dlnorm() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityLognormal( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of log-normal distribution with the mu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityLognormal( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.2.2. MathCumulativeDistributionLognormal
The function calculates the value of the log-normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionLognormal( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the log-normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionLognormal( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the log-normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the plnorm() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionLognormal( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the log-normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionLognormal( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.2.3. MathQuantileLognormal
The function calculates the value of the inverse log-normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for the specified probability. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileLognormal( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the inverse log-normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for the specified probability. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileLognormal( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the values of inverse log-normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qlnorm() in R.
bool MathQuantileLognormal( const double &probability[], // [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the values of inverse log-normal distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileLognormal( const double &probability[], // [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.2.4. MathRandomLognormal
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the log-normal law with the mu sigma parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomLognormal( const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the log-normal law with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rlnorm() in R.
bool MathRandomLognormal( const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.2.5. MathMomentsLognormal
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the log-normal distribution. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsLognormal( const double mu, // [in] Logarithm of the expected value (log mean) const double sigma, // [in] Logarithm of the root-mean-square deviation (log standard deviation) double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.3. Beta distribution
2.3.1. MathProbabilityDensityBeta
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of beta distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityBeta( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of beta distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityBeta( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of beta distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dbeta() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityBeta( const double &x[], // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of beta distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityBeta( const double &x[], // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.3.2. MathCumulativeDistributionlBeta
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of beta distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionBeta( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of beta distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionBeta( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of beta distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pbeta() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionBeta( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of beta distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionBeta( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.3.3. MathQuantileBeta
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse beta distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileBeta( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse beta distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileBeta( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the values of inverse beta distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qbeta() in R.
bool MathQuantileBeta( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the values of inverse beta distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileBeta( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.3.4. MathRandomBeta
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of beta distribution with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomBeta( const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of beta distribution with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rbeta() in R.
bool MathRandomBeta( const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.3.5. MathMomentsBeta
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the beta distribution. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsBeta( const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.4. Noncentral beta distribution
2.4.1. MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralBeta
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral beta distribution with the a, b and lambda parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.double MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralBeta( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral beta distribution with the a, b and lambda parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralBeta( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral beta distribution with the a, b and lambda parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dbeta() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralBeta( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral beta distribution with the a, b and lambda parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralBeta( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.4.2. MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralBeta
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral beta distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralBeta( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral beta distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralBeta( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral beta distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pbeta() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralBeta( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral beta distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralBeta( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.4.3. MathQuantileNoncentralBeta
The function calculates the value of the inverse probability distribution function of noncentral beta distribution with the a, b and lambda parameters for the occurrence of a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileNoncentralBeta( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the inverse probability distribution function of noncentral beta distribution with the a, b and lambda parameters for the occurrence of a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileNoncentralBeta( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse probability distribution function of noncentral beta distribution with the a, b and lambda parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qbeta() in R.
bool MathQuantileNoncentralBeta( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse probability distribution function of noncentral beta distribution with the a, b and lambda parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileNoncentralBeta( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.4.4. MathRandomNoncentralBeta
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of noncentral beta distribution the a, b and lambda parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomNoncentralBeta( const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of noncentral beta distribution the a, b and lambda parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rbeta() in R.
bool MathRandomNoncentralBeta( const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.4.5. MathMomentsNoncentralBeta
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the noncentral beta distribution with the a, b and lambda parameters. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
double MathMomentsNoncentralBeta( const double a, // [in] The first parameter of beta distribution (shape1) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of beta distribution (shape2) const double lambda, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.5. Gamma distribution
2.5.1. MathProbabilityDensityGamma
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of gamma distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.double MathProbabilityDensityGamma( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of gamma distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityGamma( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of gamma distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dgamma() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityGamma( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of gamma distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityGamma( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.5.2. MathCumulativeDistributionGamma
The function calculates the value of the gamma distribution function with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionGamma( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the gamma distribution function with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionGamma( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the gamma distribution function with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pgamma() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionGamma( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the gamma distribution function with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionGamma( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.5.3. MathQuantileGamma
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse gamma distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileGamma( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse gamma distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileGamma( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse gamma distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qgamma() in R.
bool MathQuantileGamma( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse gamma distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileGamma( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.5.4. MathRandomGamma
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of gamma distribution with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomGamma( const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of gamma distribution with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rgamma() in R.
bool MathRandomGamma( const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.5.5. MathMomentsGamma
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the gamma distribution with the a and b parameters. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsGamma( const double a, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (scale) double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.6. Chi-squared distribution
2.6.1. MathProbabilityDensityChiSquare
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of chi-squared distribution with the nu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityChiSquare( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );The function calculates the value of the probability density function of chi-squared distribution with the nu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityChiSquare( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of chi-squared distribution with the nu parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dchisq() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityChiSquare( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of chi-squared distribution with the nu parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityChiSquare( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.6.2. MathCumulativeDistributionChiSquare
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of chi-squared distribution with the nu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionChiSquare( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of chi-squared distribution with the nu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionChiSquare( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of chi-squared distribution with the nu parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pchisq() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionChiSquare( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of chi-squared distribution with the nu parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionChiSquare( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.6.3. MathQuantileChiSquare
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse chi-squared distribution function. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileChiSquare( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse chi-squared distribution function. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileChiSquare( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse chi-squared distribution function. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qchisq() in R.
bool MathQuantileChiSquare( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse chi-squared distribution function. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileChiSquare( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.6.4. MathRandomChiSquare
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of chi-squared distribution with the nu parameter. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomChiSquare( const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of chi-squared distribution with the nu parameter. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rchisq() in R.
bool MathRandomChiSquare( const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.6.5. MathMomentsChiSquare
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the chi-squared distribution with the nu parameter. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsChiSquare( const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.7. Noncentral chi-squared distribution
2.7.1. MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralChiSquare
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral chi-squared distribution with the nu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralChiSquare( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral chi-squared distribution with the nu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralChiSquare( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral chi-squared distribution with the nu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dchisq() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralChiSquare( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral chi-squared distribution with the nu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralChiSquare( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.7.2. MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralChiSquare
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral chi-squared distribution with the nu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralChiSquare( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral chi-squared distribution with the nu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralChiSquare( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral chi-squared distribution with the nu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pchisq() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralChiSquare( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral chi-squared distribution with the nu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralChiSquare( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.7.3. MathQuantileNoncentralChiSquare
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse noncentral chi-squared distribution function with the nu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileNoncentralChiSquare( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse noncentral chi-squared distribution function with the nu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileNoncentralChiSquare( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse noncentral chi-squared distribution function with the nu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qchisq() in R.
bool MathQuantileNoncentralChiSquare( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse noncentral chi-squared distribution function with the nu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileNoncentralChiSquare( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.7.4. MathRandomNoncentralChiSquare
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of noncentral chi-squared distribution with the nu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomNoncentralChiSquare( const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of noncentral chi-squared distribution with the nu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rchisq() in R.
bool MathRandomNoncentralChiSquare( const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.7.5. MathMomentsNoncentralChiSquare
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the noncentral chi-squared distribution with the nu and sigma parameters. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsNoncentralChiSquare( const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.8. Exponential distribution
2.8.1. MathProbabilityDensityExponential
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of exponential distribution with the mu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityExponential( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of exponential distribution with the mu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityExponential( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of exponential distribution with the mu parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dexp() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityExponential( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of exponential distribution with the mu parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityExponential( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.8.2. MathCumulativeDistributionExponential
The function calculates the value of the exponential distribution function of probabilities with the mu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionExponential( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the exponential distribution function of probabilities with the mu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionExponential( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the exponential distribution function of probabilities with the mu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pexp() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionExponential( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the exponential distribution function of probabilities with the mu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionExponential( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.8.3. MathQuantileExponential
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse exponential distribution function with the mu parameter. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileExponential( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse exponential distribution function with the mu parameter. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileExponential( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse exponential distribution function with the mu parameter. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qexp() in R.
bool MathQuantileExponential( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse exponential distribution function with the mu parameter. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileExponential( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.8.4. MathRandomExponential
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of exponential distribution with the mu parameter. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomExponential( const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of exponential distribution with the mu parameter. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rexp() in R.
bool MathRandomExponential( const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.8.5. MathMomentsExponential
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the exponential distribution with the mu parameter. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsExponential( const double mu, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (expected value) double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.9. F-distribution
2.9.1. MathProbabilityDensityF
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1 and nu2 parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityF( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1 and nu2 parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityF( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1 and nu2 parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the df() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityF( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1 and nu2 parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityF( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.9.2. MathCumulativeDistributionF
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1 and nu2 parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionF( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1 and nu2 parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionF( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1 and nu2 parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pf() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionF( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1 and nu2 parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionF( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.9.3. MathQuantileF
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse Fisher's F-distribution function with the nu1 and nu2 parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileF( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse Fisher's F-distribution function with the nu1 and nu2 parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileF( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse Fisher's F-distribution function with the nu1 and nu2 parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qf() in R.
bool MathQuantileF( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse Fisher's F-distribution function with the nu1 and nu2 parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileF( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.9.4. MathRandomF
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1 and nu2 parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomF( const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1 and nu2 parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rf() in R.
bool MathRandomF( const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.9.5. MathMomentsF
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1 and nu2 parameters. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsF( const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.10. Noncentral F-distribution
2.10.1. MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralF
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralF( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralF( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the df() in R.
double MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralF( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
double MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralF( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.10.2. MathCumulativeDistributionlNoncentralF
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralF( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralF( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pf() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralF( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralF( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.10.3. MathQuantileNoncentralF
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse noncentral Fisher's F-distribution function with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileNoncentralF( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse noncentral Fisher's F-distribution function with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileNoncentralF( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse noncentral Fisher's F-distribution function with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qf() in R.
bool MathQuantileNoncentralF( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse noncentral Fisher's F-distribution function with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileNoncentralF( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.10.4. MathRandomNoncentralF
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of noncentral Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomNoncentralF( const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of noncentral Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rf() in R.
bool MathRandomNoncentralF( const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.10.5. MathMomentsNoncentralF
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the noncentral Fisher's F-distribution with the nu1, nu2 and sigma parameters. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsNoncentralF( const double nu1, // [in] The first parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double nu2, // [in] The second parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double sigma, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code e.)
2.11. t-distribution
2.11.1. MathProbabilityDensityT
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Student's t-distribution with the nu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityT( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Student's t-distribution with the nu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityT( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Student's t-distribution with the nu parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dt() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityT( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Student's t-distribution with the nu parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityT( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.11.2. MathCumulativeDistributionT
The function calculates the value of the Student's t-distribution function with the nu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionT( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the Student's t-distribution function with the nu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionT( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the Student's t-distribution function with the nu parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pt() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionT( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the Student's t-distribution function with the nu parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionT( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.11.3. MathQuantileT
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse Student's t-distribution function with the nu parameter. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileT( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse Student's t-distribution function with the nu parameter. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileT( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse Student's t-distribution function with the nu parameter. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qt() in R.
bool MathQuantileT( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse Student's t-distribution function with the nu parameter. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileT( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.11.4. MathRandomT
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of Student's t-distribution with the nu parameter. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomT( const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of Student's t-distribution with the nu parameter. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rt() in R.
bool MathRandomT( const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.11.5. MathMomentsT
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the Student's t-distribution with the nu parameter. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
double MathMomentsT( const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.12. Noncentral t-distribution
2.12.1. MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralT
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral Student's t-distribution with the nu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralT( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral Student's t-distribution with the nu parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralT( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral Student's t-distribution with the nu parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dt() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralT( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of noncentral Student's t-distribution with the nu parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralT( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.12.2. MathCumulativeDistributionlNoncentralT
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral Student's t-distribution with the nu and delta parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralT( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral Student's t-distribution with the nu and delta parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralT( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral Student's t-distribution with the nu and delta parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pt() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralT( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of noncentral Student's t-distribution with the nu and delta parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralT( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.12.3. MathQuantileNoncentralT
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse noncentral Student's t-distribution function with the nu and delta parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileNoncentralT( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse noncentral Student's t-distribution function with the nu and delta parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileNoncentralT( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse noncentral Student's t-distribution function with the nu and delta parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qt() in R.
bool MathQuantileNoncentralT( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse noncentral Student's t-distribution function with the nu and delta parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileNoncentralT( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.12.4. MathRandomNoncentralT
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of noncentral Student's t-distribution with the nu and delta parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomNoncentralT( const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of noncentral Student's t-distribution with the nu and delta parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rt() in R.
bool MathRandomNoncentralT( const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.12.5. MathMomentsNoncentralT
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the noncentral Student's t-distribution with the nu and delta parameters. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
double MathMomentsNoncentralT( const double nu, // [in] Parameter of distribution (number of degrees of freedom) const double delta, // [in] Noncentrality parameter double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.13. Logistic distribution
2.13.1. MathProbabilityDensityLogistic
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of logistic distribution with the mu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityLogistic( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of logistic distribution with the mu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityLogistic( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of logistic distribution with the mu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dlogis() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityLogistic( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of logistic distribution with the mu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityLogistic( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.13.2. MathCumulativeDistributionlLogistic
The function calculates the value of the logistic distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionLogistic( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the logistic distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionLogistic( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the logistic distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the plogis() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionLogistic( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the logistic distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the plogis() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionLogistic( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.13.3. MathQuantileLogistic
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse logistic distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileLogistic( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse logistic distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileLogistic( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse logistic distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qlogis() in R.
bool MathQuantileLogistic( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse logistic distribution function with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileLogistic( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.13.4. MathRandomLogistic
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of logistic distribution with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomLogistic( const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of logistic distribution with the mu and sigma parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rlogis() in R.
bool MathRandomLogistic( const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.13.5. MathMomentsLogistic
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the logistic distribution with the mu and sigma parameters. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsLogistic( const double mu, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double sigma, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.14. Cauchy distribution
2.14.1. MathProbabilityDensityCauchy
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Cauchy distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityCauchy( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Cauchy distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityCauchy( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Cauchy distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dcauchy() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityCauchy( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Cauchy distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityCauchy( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.14.2. MathCumulativeDistributionCauchy
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of Cauchy distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionCauchy( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of Cauchy distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionCauchy( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of Cauchy distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pcauchy() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionCauchy( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function of Cauchy distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionCauchy( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.14.3. MathQuantileCauchy
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse Cauchy distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileCauchy( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse Cauchy distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileCauchy( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse Cauchy distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qcauchy() in R.
bool MathQuantileCauchy( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse Cauchy distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileCauchy( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.14.4. MathRandomCauchy
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of Cauchy distribution with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomCauchy( const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of Cauchy distribution with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rcauchy() in R.
double MathRandomCauchy( const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.14.5. MathMomentsCauchy
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the Cauchy distribution. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsCauchy( const double a, // [in] mean parameter of the distribution const double b, // [in] scale parameter of the distribution double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.15. Uniform distribution
2.15.1. MathProbabilityDensityUniform
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of uniform distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityUniform( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of uniform distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityUniform( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of uniform distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dunif() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityUniform( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of uniform distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityUniform( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.15.2. MathCumulativeDistributionUniform
The function calculates the value of the uniform distribution function with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.double MathCumulativeDistributionUniform( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the uniform distribution function with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionUniform( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the uniform distribution function with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the punif() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionUniform( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the uniform distribution function with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionUniform( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.15.3. MathQuantileUniform
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse uniform distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileUniform( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse uniform distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileUniform( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse uniform distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qunif() in R.
bool MathQuantileUniform( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse uniform distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileUniform( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.15.4. MathRandomUniform
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of uniform distribution with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomUniform( const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of uniform distribution with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the runif() in R.
bool MathRandomUniform( const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.15.5. MathMomentsUniform
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments for the uniform distribution. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsUniform( const double a, // [in] Distribution parameter a (lower bound) const double b, // [in] Distribution parameter b (upper bound) double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.16. Weibull distribution
2.16.1. MathProbabilityDensityWeibull
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Weibull distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityWeibull( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Weibull distribution with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityWeibull( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Weibull distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dweibull() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityWeibull( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability density function of Weibull distribution with the a and b parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityWeibull( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.16.2. MathCumulativeDistributionWeibull
The function calculates the value of the Weibull distribution function with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.double MathCumulativeDistributionWeibull( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the Weibull distribution function with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionWeibull( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the Weibull distribution function with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pweibull() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionWeibull( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the Weibull distribution function with the a and b parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionWeibull( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.16.3. MathQuantileWeibull
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse Weibull distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileWeibull( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the value of inverse Weibull distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileWeibull( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse Weibull distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qweibull() in R.
bool MathQuantileWeibull( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the value of inverse Weibull distribution function with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileWeibull( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.16.4. MathRandomWeibull
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of Weibull distribution with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomWeibull( const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of Weibull distribution with the a and b parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rweibull() in R.
bool MathRandomWeibull( const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.16.5. MathMomentsWeibull
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the Weibull distribution. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsWeibull( const double a, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (shape) const double b, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (scale) double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.17. Binomial distribution
2.17.1. MathProbabilityDensityBinomial
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of binomial distribution with the n and p parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityBinomial( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable (integer) const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of binomial distribution with the n and p parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityBinomial( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable (integer) const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of binomial distribution with the n and p parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dbinom() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityBinomial( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of binomial distribution with the n and p parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityBinomial( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.17.2. MathCumulativeDistributionBinomial
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for binomial law with the n and p parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionBinomial( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable (integer) const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for binomial law with the n and p parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionBinomial( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable (integer) const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for binomial law with the n and p parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pbinom() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionBinomial( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for binomial law with the n and p parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionBinomial( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.17.3. MathQuantileBinomial
For the specified probability, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for binomial law with the n and p parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileBinomial( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for binomial law with the n and p parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileBinomial( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for binomial law with the n and p parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qbinom() in R.
bool MathQuantileBinomial( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for binomial law with the n and p parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileBinomial( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.17.4. MathRandomBinomial
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of binomial distribution with the n and p parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomBinomial( const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of binomial distribution with the n and p parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rbinom() in R.
bool MathRandomBinomial( const double n, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (number of tests) const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of success for each test) const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.17.5. MathMomentsBinomial
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the binomial distribution with the n and p parameters. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsBinomial( const double n, // [in] Number of tests const double p, // [in] Probability of success in each test double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.18. Negative binomial distribution
2.18.1. MathProbabilityDensityNegativeBinomial
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of negative binomial distribution with the r and p parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityNegativeBinomial( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable (integer) const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of negative binomial distribution with the r and p parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityNegativeBinomial( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable (integer) const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of negative binomial distribution with the r and p parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dnbinom() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityNegativeBinomial( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of negative binomial distribution with the r and p parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityNegativeBinomial( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.18.2. MathCumulativeDistributionNegativeBinomial
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for negative binomial law with the r and p parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionNegativeBinomial( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable (integer) const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for negative binomial law with the r and p parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionNegativeBinomial( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable (integer) const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for negative binomial law with the r and p parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pnbinom() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionNegativeBinomial( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for negative binomial law with the r and p parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionNegativeBinomial( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.18.3. MathQuantileNegativeBinomial
For the specified probability, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for negative binomial law with the r and p parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileNegativeBinomial( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for negative binomial law with the r and p parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileNegativeBinomial( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for negative binomial law with the r and p parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qnbinom() in R.
bool MathQuantileNegativeBinomial( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for negative binomial law with the r and p parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileNegativeBinomial( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.18.4. MathRandomNegativeBinomial
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of negative binomial distribution with the r and p parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomNegativeBinomial( const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of negative binomial distribution with the r and p parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rnbinom() in R.
bool MathRandomNegativeBinomial( const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.18.5. MathMomentsNegativeBinomial
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the negative binomial distribution with the r and p parameters. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsNegativeBinomial( const double r, // [in] Number of successful tests double p, // [in] Probability of success double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.19. Geometric distribution
2.19.1. MathProbabilityDensityGeometric
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of geometric distribution with the p parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityGeometric( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of geometric distribution with the p parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityGeometric( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of geometric distribution with the p parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dgeom() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityGeometric( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of geometric distribution with the p parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityGeometric( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.19.2. MathCumulativeDistributionGeometric
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for geometric law with the p parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionGeometric( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for geometric law with the p parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionGeometric( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for geometric law with the p parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the pgeom() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionGeometric( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for geometric law with the p parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionGeometric( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.19.3. MathQuantileGeometric
For the specified probability, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for geometric law with the p parameter. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileGeometric( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for geometric law with the p parameter. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileGeometric( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for geometric law with the p parameter. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qgeom() in R.
bool MathQuantileGeometric( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for geometric law with the p parameter. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileGeometric( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.19.4. MathRandomGeometric
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of geometric distribution with the p parameter. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomGeometric( const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of geometric distribution with the p parameter. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rgeom() in R.
bool MathRandomGeometric( const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.19.5. MathMomentsGeometric
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the geometric distribution with the p parameter. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsGeometric( const double p, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (probability of event occurrence in one test) double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.20. Hypergeometric distribution
2.20.1. MathProbabilityDensityHypergeometric
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of hypergeometric distribution with the m, k and n parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityHypergeometric( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable (integer) const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws(integer) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of hypergeometric distribution with the m, k and n parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityHypergeometric( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable (integer) const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws(integer) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of hypergeometric distribution with the m, k and n parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dhyper() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityHypergeometric( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws(integer) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of hypergeometric distribution with the m, k and n parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityHypergeometric( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws(integer) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.20.2. MathCumulativeDistributionHypergeometric
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for hypergeometric law with the m, k and n parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionHypergeometric( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable (integer) const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws(integer) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for hypergeometric law with the m, k and n parameters for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionHypergeometric( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable (integer) const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws(integer) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for hypergeometric law with the m, k and n parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the phyper() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionHypergeometric( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws(integer) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the distribution function );
The function calculates the value of the probability distribution function for hypergeometric law with the m, k and n parameters for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionHypergeometric( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws(integer) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the distribution function );
2.20.3. MathQuantileHypergeometric
For the specified probability, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for hypergeometric law with the m, k and n parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileHypergeometric( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (целочисленное) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws (integer) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for hypergeometric law with the m, k and n parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantileHypergeometric( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws (integer) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for hypergeometric law with the m, k and n parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qhyper() in R.
bool MathQuantileHypergeometric( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws (integer) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the inverse value of function distribution for hypergeometric law with the m, k and n parameters. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathQuantileHypergeometric( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws (integer) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.20.4. MathRandomHypergeometric
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of hypergeometric distribution with the m, n and k parameters. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomHypergeometric( const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws(integer) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of hypergeometric distribution with the m, n and k parameters. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rhyper() in R.
bool MathRandomHypergeometric( const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws(integer) const int data_count, // [in] Amount of required data double &result[] // [out] Array with values of pseudorandom variables );
2.20.5. MathMomentsHypergeometric
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the hypergeometric distribution with the m, n and k parameters. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsHypergeometric( const double m, // [in] Total number of objects (integer) const double k, // [in] Number of objects with the desired characteristic (integer) const double n, // [in] Number of object draws(integer) double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.21. Poisson distribution
2.21.1. MathProbabilityDensityPoisson
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of Poisson distribution with the lambda parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityPoisson( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of Poisson distribution with the lambda parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathProbabilityDensityPoisson( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of Poisson distribution with the lambda parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the dpois() in R.
bool MathProbabilityDensityPoisson( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability density is returned double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
The function calculates the value of the probability mass function of Poisson distribution with the lambda parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathProbabilityDensityPoisson( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability density function );
2.21.2. MathCumulativeDistributionPoisson
The function calculates the value of the Poisson distribution function with the lambda parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionPoisson( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the Poisson distribution function with the lambda parameter for a random variable x. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathCumulativeDistributionPoisson( const double x, // [in] Value of random variable const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function calculates the value of the Poisson distribution function with the lambda parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the ppois() in R.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionPoisson( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if true, then the probability of random variable not exceeding x is calculated const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag to calculate the logarithm of the value, if log_mode=true, then the natural logarithm of the probability is calculated double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
The function calculates the value of the Poisson distribution function with the lambda parameter for an array of random variables x[]. In case of error it returns false.
bool MathCumulativeDistributionPoisson( const double &x[], // [in] Array with the values of random variable const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) double &result[] // [out] Array for values of the probability function );
2.21.3. MathQuantilePoisson
For the specified probability, the function calculates the inverse value of Poisson distribution function with the lambda parameter. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantilePoisson( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified probability, the function calculates the inverse value of Poisson distribution function with the lambda parameter. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathQuantilePoisson( const double probability, // [in] Probability value of random variable occurrence const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the inverse value of Poisson distribution function with the lambda parameter. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the qpois() in R.
double MathQuantilePoisson( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) const bool tail, // [in] Flag of calculation, if false, then calculation is performed for 1.0-probability const bool log_mode, // [in] Flag of calculation, if log_mode=true, calculation is performed for Exp(probability) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
For the specified 'probability[]' array of probability values, the function calculates the inverse value of Poisson distribution function with the lambda parameter. In case of error it returns false.
double MathQuantilePoisson( const double &probability[],// [in] Array with probability values of random variable const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) double &result[] // [out] Array with values of quantiles );
2.21.4. MathRandomPoisson
The function generates a pseudorandom variable distributed according to the law of Poisson distribution with the lambda parameter. In case of error it returns NaN.
double MathRandomPoisson( const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
The function generates pseudorandom variables distributed according to the law of Poisson distribution with the lambda parameter. In case of error it returns false. Analog of the rpois() in R.
double MathRandomPoisson( const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
2.21.5. MathMomentsPoisson
The function calculates the theoretical numerical values of the first 4 moments of the Poisson distribution with the lambda parameter. Returns true if calculation of the moments has been successful, otherwise false.
bool MathMomentsPoisson( const double lambda, // [in] Parameter of the distribution (mean) double &mean, // [out] Variable for the mean (1st moment) double &variance, // [out] Variable for the variance (2nd moment) double &skewness, // [out] Variable for the skewness (3rd moment) double &kurtosis, // [out] Variable for the kurtosis (4th moment) int &error_code // [out] Variable for the error code );
3. Table of correspondence to the statistical functions in R
For convenience, the tables 1-2 contain the functions of the statistical library and the corresponding functions of the R language.
| No. | Calculated value | Functions in MQL5 | Functions in R |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mean | MathMean | mean |
| 2 | Variance | MathVariance | var |
| 3 | Skewness | MathSkewness | skewness |
| 60 | Kurtosis | MathKurtosis | kurtosis |
| 5 | Median value | MathMedian | median |
| 6 | Standard Deviation | MathStandardDeviation | sd |
| 7 | Average deviation | MathAverageDeviation | aad |
Table 1. Functions for calculating the statistical characteristics of array data
| No. | Distribution | Density function | Functions in MQL5 | Functions in R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Normal | 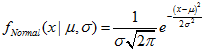 | MathProbabilityDensityNormal MathCumulativeDistributionNormal MathQuantileNormal MathRandomNormal | dnorm pnorm qnorm rnorm |
| 2 | Beta | | MathProbabilityDensityBeta MathCumulativeDistributionBeta MathQuantileBeta MathRandomBeta | dbeta pbeta qbeta rbeta |
| 3 | Binomial | | MathProbabilityDensityBinomial MathCumulativeDistributionBinomial MathQuantileBinomial MathRandomBinomial | dbinom pbinom qbinom rbinom |
| 60 | Cauchy | 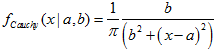 | MathProbabilityDensityCauchy MathCumulativeDistributionCauchy MathQuantileCauchy MathRandomCauchy | dcauchy pcauchy qcauchy rcauchy |
| 5 | Chi-squared | 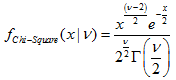 | MathProbabilityDensityChiSquare MathCumulativeDistributionChiSquare MathQuantileChiSquare MathRandomChiSquare | dchisq pchisq qchisq rchisq |
| 6 | Exponential | | MathProbabilityDensityExponential MathCumulativeDistributionExponential MathQuantileExponential MathRandomExponential | dexp pexp qexp rexp |
| 7 | F-distribution | 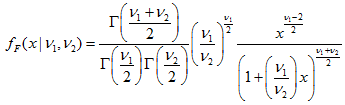 | MathProbabilityDensityF MathCumulativeDistributionF MathQuantileF MathRandomF | df pf qf rf |
| 8 | Gamma | | MathProbabilityDensityGamma MathCumulativeDistributionGamma MathQuantileGamma MathRandomGamma | dgamma pgamma qgamma rgamma |
| 9 | Geometric | | MathProbabilityDensityGeometric MathCumulativeDistributionGeometric MathQuantileGeometric MathRandomGeometric | dgeom pgeom qgeom rgeom |
| 10 | Hypergeometric | 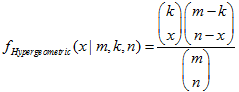 | MathProbabilityDensityHypergeometric MathCumulativeDistributionHypergeometric MathQuantileHypergeometric MathRandomHypergeometric | dhyper phyper qhyper rhyper |
| 11 | Logistic | 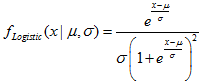 | MathProbabilityDensityLogistic MathCumulativeDistributionLogistic MathQuantileLogistic MathRandomLogistic | dlogis plogis qlogis rlogis |
| 12 | Log-normal | | MathProbabilityDensityLognormal MathCumulativeDistributionLognormal MathQuantileLognormal MathRandomLognormal | dlnorm plnorm qlnorm rlnorm |
| 13 | Negative binomial | | MathProbabilityDensityNegativeBinomial MathCumulativeDistributionNegativeBinomial MathQuantileNegativeBinomial MathRandomNegativeBinomial | dnbinom pnbinom qnbinom rnbinom |
| 14 | Noncentral beta | 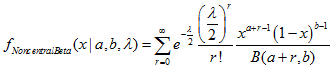 | MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralBeta MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralBeta MathQuantileNoncentralBeta MathRandomNoncentralBeta | dbeta pbeta qbeta rbeta |
| 15 | Noncentral chi-squared | 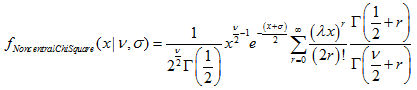 | MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralChiSquare MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralChiSquare MathQuantileNoncentralChiSquare MathRandomNoncentralChiSquare | dchisq pchisq qchisq rchisq |
| 16 | Noncentral F-distribution | 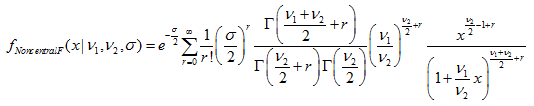 | MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralF() MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralF() MathQuantileNoncentralF() MathRandomNoncentralF() | df pf qf rf |
| 17 | Noncentral t-distribution | 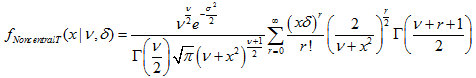 | MathProbabilityDensityNoncentralT MathCumulativeDistributionNoncentralT MathQuantileNoncentralT MathRandomNoncentralT | dt pt qt rt |
| 18 | Poisson | | MathProbabilityDensityPoisson MathCumulativeDistributionPoisson MathQuantilePoisson MathRandomPoisson | dpois ppois qpois rpois |
| 19 | t-distribution | 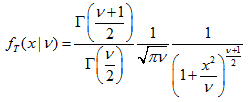 | MathProbabilityDensityT MathCumulativeDistributionT MathQuantileT MathRandomT | dt pt qt rt |
| 20 | Uniform | | MathProbabilityDensityUniform MathCumulativeDistributionUniform MathQuantileUniform MathRandomUniform | dunif punif qunif runif |
| 21 | Weibull | 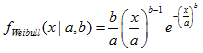 | MathProbabilityDensityWeibull MathCumulativeDistributionWeibull MathQuantileWeibull MathRandomWeibull | dweibull pweibull qweibull rweibull |
Table 2. Functions for working with statistical distributions
The MQL5 statistical library also provides functions for calculating the mathematical functions on arrays, they are listed below in the Table 3.
| Description | MQL5 | R |
|---|---|---|
| Generates a sequence of values | bool MathSequence(const double from,const double to,const double step,double &result[]) bool MathSequenceByCount(const double from,const double to,const int count,double &result[]) bool MathSequence(const int from,const int to,const int step,int &result[]) bool MathSequenceByCount(const int from,const int to,const int count,int &result[]) | seq() |
| Generates a repeating sequence | bool MathReplicate(const double &array[],const int count,double &result[]) bool MathReplicate(const int &array[],const int count,int &result[]) | rep() |
| Generates an array with reverse order of elements | bool MathReverse(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathReverse(const int &array[],int &result[]) | rev(x) |
| Compares arrays and returns true if all elements match | bool MathIdentical(const double &array1[],const double &array2[]) bool MathIdentical(const int &array1[],const int &array2[]) | identical() |
| Generates an array with unique values only | bool MathUnique(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathUnique(const int &array[],int &result[]) | unique() |
| Generates an integer array with permutation according to order of the array elements after sorting | bool MathOrder(const double &array[],int &result[]) bool MathOrder(const int &array[],int &result[]) | order() |
| Generates a random sample from the array elements. The replace=true argument allows to perform random sampling of the elements with replacement back to the original sequence. The probabilities[] array defines the probabilities for sampling the elements. | bool MathSample(const double &array[],const int count,double &result[]) bool MathSample(const double &array[],const int count,const bool replace,double &result[]) bool MathSample(const double &array[],double &probabilities[],const int count,double &result[]) bool MathSample(const double &array[],double &probabilities[],const int count,const bool replace,double &result[]) bool MathSample(const int &array[],const int count,int &result[]) bool MathSample(const int &array[],const int count,const bool replace,int &result[]) bool MathSample(const int &array[],double &probabilities[],const int count,int &result[]) bool MathSample(const int &array[],double &probabilities[],const int count,const bool replace,int &result[]) | sample() |
| Returns the sum of array elements | double MathSum(const double &array[]) | sum() |
| Returns the product of array elements | double MathProduct(const double &array[]) | prod() |
| Generates an array with the cumulative sums | bool MathCumulativeSum(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathCumulativeSum(double &array[]) | cumsum() |
| Generates an array with the cumulative products | bool MathCumulativeProduct(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathCumulativeProduct(double &array[]) | cumprod() |
| Generates an array with the cumulative minima | bool MathCumulativeMin(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathCumulativeMin(double &array[]) | cummin() |
| Generates an array with the cumulative maxima | bool MathCumulativeMax(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathCumulativeMax(double &array[]) | cummax() |
| Generates an array with element differences of y[i]=x[i+lag]-x[i] | bool MathDifference(const double &array[],const int lag,double &result[]) bool MathDifference(const double &array[],const int lag,const int differences,double &result[]) bool MathDifference(const int &array[],const int lag,int &result[]) bool MathDifference(const int &array[],const int lag,const int differences,int &result[]) | diff() |
| Returns the minima of array elements | double MathMin(const double &array[]) | min() |
| Returns the maxima of array elements | double MathMax(const double &array[]) | max() |
| Calculates the minima and maxima of array elements | bool MathRange(const double &array[],double &min,double &max) | range() |
| Calculates the mean values of array elements | double MathMean(const double &array[]) | mean() |
| Calculates the standard deviations of array elements | double MathStandardDeviation(const double &array[]) | sd() |
| Calculates the median values of array elements | double MathMedian(double &array[]) | median() |
| Calculates the ranks of array elements | bool MathRank(const int &array[],double &rank[]) bool MathRank(const double &array[],double &rank[]) | rank() |
| Calculates the Pearson's, Spearman's and Kendall's correlation coefficients | bool MathCorrelationPearson(const double &array1[],const double &array2[],double &r) bool MathCorrelationPearson(const int &array1[],const int &array2[],double &r) bool MathCorrelationSpearman(const double &array1[],const double &array2[],double &r) bool MathCorrelationSpearman(const int &array1[],const int &array2[],double &r) bool MathCorrelationKendall(const double &array1[],const double &array2[],double &tau) bool MathCorrelationKendall(const int &array1[],const int &array2[],double &tau) | corr() |
| Calculates sample quantiles corresponding to the specified probabilities | bool MathQuantile(const double &array[],const double &probs[],double &quantile[]) | qunatile() |
| Calculates the Tukey's five number summary (minimum, lower-hinge, median, upper-hinge, maximum) for array elements | bool MathTukeySummary(const double &array[],const bool removeNAN,double &minimum,double &lower_hinge,double &median,double &upper_hinge,double &maximum) | fivenum() |
| Calculates logarithms of array elements (natural and to a given base) | bool MathLog(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathLog(const double &array[],const double base,double &result[]) bool MathLog(double &array[]) bool MathLog(double &array[],const double base) | log() |
| Calculates logarithms of array elements to base 2 | bool MathLog2(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathLog2(double &array[]) | log2() |
| Calculates logarithms of array elements to base 10 | bool MathLog10(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathLog10(double &array[]) | log10() |
| Calculates the values of the log(1+x) function for array elements | bool MathLog1p(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathLog1p(double &array[]) | log1p() |
| Calculates the values of the exp(x) function for array elements | bool MathExp(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathExp(double &array[]) | exp() |
| Calculates the values of the exp(x)-1 function for array elements | bool MathExpm1(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathExpm1(double &array[]) | expm1() |
| Calculates the values of the sin(x) function for array elements | bool MathSin(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathSin(double &array[]) | sin() |
| Calculates the values of the cos(x) function for array elements | bool MathCos(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathCos(double &array[]) | cos() |
| Calculates the values of the tan(x) function for array elements | bool MathTan(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathTan(double &array[]) | tan() |
| Calculates the values of the arcsin(x) function for array elements | bool MathArcsin(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathArcsin(double &array[]) | arcsin() |
| Calculates the values of the arccos(x) function for array elements | bool MathArccos(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathArccos(double &array[]) | arccos() |
| Calculates the values of the arctan(x) function for array elements | bool MathArctan(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathArctan(double &array[]) | arctan() |
| Calculates the values of the arctan(y/x) function for array elements | bool MathArctan2(const double &array1[], const double &array2[], double &result[]) | arctan2() |
| Calculates the values of the sin(pi*x) function for array elements | bool MathSinPi(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathSinPi(double &array[]) | sinpi() |
| Calculates the values of the cos(pi*x) function for array elements | bool MathCosPi(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathCosPi(const double &array[]) | cospi() |
| Calculates the values of the tan(pi*x) function for array elements | bool MathTanPi(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathTanPi(double &array[]) | tanpi() |
| Calculates the absolute values of array elements | bool MathAbs(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathAbs(double &array[]) | abs() |
| Calculates the square roots of array elements | bool MathSqrt(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathSqrt(double &array[]) | sqrt() |
| Returns the nearest larger integers for array elements | bool MathCeil(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathCeil(double &array[]) | ceil() |
| Returns the nearest smaller integers for array elements | bool MathFloor(const double &array[], double &result[]) bool MathFloor(double &array[]) | floor() |
| Calculates the integer parts of array elements | bool MathTrunc(const double &array[], const int digits, double &result[]) bool MathTrunc(double &array[]) | trunc() |
| Calculates the rounded values of array elements | bool MathRound(const double &array[], const int digits, double &result[]) bool MathRound(double &array[],int digits) | round() |
| For array elements, calculates the value rounded to the specified number of digits in the mantissa | bool MathSignif(const double &array[], const int digits, double &result[]) bool MathSignif(double &array[], const int digits) | signinf() |
| Calculates the values of the sinh(x) function for array elements | bool MathSinh(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathSinh(double &array[]) | sinh() |
| Calculates the values of the cosh(x) function for array elements | bool MathCosh(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathCosh(double &array[]) | cosh() |
| Calculates the values of the tanh(x) function for array elements | bool MathTanh(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathTanh(double &array[]) | tanh() |
| Calculates the values of the arcsinh(x) function for array elements | bool MathArcsinh(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathArcsinh(double &array[]) | asinh() |
| Calculates the values of the arccosh(x) function for array elements | bool MathArccosh(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathArccosh(double &array[]) | acosh() |
| Calculates the values of the arctanh(x) function for array elements | bool MathArctanh(const double &array[],double &result[]) bool MathArctanh(double &array[]) | atanh() |
| Calculates the result of bitwise NOT operation for array elements | bool MathBitwiseNot(const int &array[],int &result[]) bool MathBitwiseNot(int &array[]) | bitwNot() |
| Calculates the result of bitwise AND operation for specified arrays | bool MathBitwiseAnd(const int &array1[],const int &array2[],int &result[]) | bitwAnd() |
| Calculates the result of bitwise OR operation for specified arrays | bool MathBitwiseOr(const int &array1[],const int &array2[],int &result[]) | bitwOr() |
| Calculates the result of bitwise XOR operation for specified arrays | bool MathBitwiseXor(const int &array1[],const int &array2[],int &result[]) | bitwXor() |
| Calculates the result of bitwise SHL operation for array elements | bool MathBitwiseShiftL(const int &array[],const int n,int &result[]) bool MathBitwiseShiftL(int &array[],const int n) | bitwShiftL() |
| Calculates the result of bitwise SHR operation for array elements | bool MathBitwiseShiftR(const int &array[],const int n,int &result[]) bool MathBitwiseShiftR(int &array[],const int n) | bitwShiftR() |
Table 3. Mathematical functions for calculating values in arrays
4. An example of using the functions
Let us consider the practical application of statistical functions on the example of a normal distribution.
Suppose the following problems need to be solved:
- Calculate the probability of a random variable, distributed according to the normal law with the mu and sigma parameters, falling within the range of [mu-sigma,mu+sigma].
- Find the value range of random variable x, distributed according to the normal law with the mu and sigma parameters, which is symmetrical to mu and which corresponds to 95% of the confidence probability.
- Generate 1000000 random numbers, distributed according to the normal law with the mu and sigma parameters, calculate the histogram of the obtained values, the first 4 moments and compare with the theoretical values.
Example of solution in the NormalExample script:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| NormalExample.mq5 | //| Copyright 2016, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2016, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //--- include the functions for calculating the normal distribution #include <Math\Stat\Normal.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CalculateHistogram | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CalculateHistogram(double &data[],const int ncells=200,const string filename="normal.csv") { if(ArraySize(data)<=0) return; int n=ArraySize(data); //--- find the minimum and maximum data values in the 'data' array double minv,maxv,range; minv=data[0]; maxv=data[0]; for(int i=1; i<n; i++) { minv=MathMin(minv,data[i]); maxv=MathMax(maxv,data[i]); } //--- calculate the range range=maxv-minv; // Print("Min=",minv," Max=",maxv," range=",range," size=",n); if(range==0) return; //--- arrays for the histogram calculation double x[]; double y[]; //--- set the histogram values ArrayResize(x,ncells); ArrayResize(y,ncells); for(int i=0; i<ncells; i++) { x[i]=minv+i*range/(ncells-1); y[i]=0; } //--- calculate the histogram for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { double v=(maxv-data[i])/range; int ind=int((v*(ncells-1))); y[ind]++; } //--- check the file name if(filename=="") return; //--- open the file for writing ResetLastError(); int filehandle=FileOpen(filename,FILE_WRITE|FILE_TXT|FILE_ANSI); //--- write data to the file if(filehandle!=INVALID_HANDLE) { for(int i=0; i<ncells; i++) { string str=StringFormat("%6.20f;%6.20f",x[i],y[i]); FileWrite(filehandle,str); } FileClose(filehandle); PrintFormat("Histogram saved to file %s",filename); } else PrintFormat("Error calling FileOpen, error code=%d",GetLastError()); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- 1. Calculate the probability of a random variable, //--- distributed according to the normal law with the mu and sigma parameters, falling within the range of [mu-sigma,mu+sigma] //--- set the distribution parameters double mu=5.0; double sigma=1.0; //--- set the interval double x1=mu-sigma; double x2=mu+sigma; //--- variables for probability calculation double cdf1,cdf2,probability; //--- variables for error codes int error_code1,error_code2; //--- calculate the values of distribution functions cdf1=MathCumulativeDistributionNormal(x1,mu,sigma,error_code1); cdf2=MathCumulativeDistributionNormal(x2,mu,sigma,error_code2); //--- check the error codes if(error_code1==ERR_OK && error_code2==ERR_OK) { //--- calculate the probability probability=cdf2-cdf1; //--- output the result PrintFormat("x1=%5.8f, x2=%5.8f, Probability=%5.8f",x1,x2,probability); } //--- 2. Find the value range of random variable x, distributed according to the normal law with the mu and sigma parameters, //--- which is symmetrical to mu and which corresponds to 95% of the confidence probability. //--- set the confidence probability probability=0.95; //--- set the probabilities at the interval bounds double p1=(1.0-probability)*0.5; double p2=probability+(1.0-probability)*0.5; //--- calculate the interval bounds x1=MathQuantileNormal(p1,mu,sigma,error_code1); x2=MathQuantileNormal(p2,mu,sigma,error_code2); //--- check the error codes if(error_code1==ERR_OK && error_code2==ERR_OK) { //--- output the result PrintFormat("x1=%5.8f, x2=%5.8f",x1,x2); } //--- 3. Generate 1000000 random numbers, distributed according to the normal law with the mu and sigma parameters, //--- calculate the histogram of the obtained values, the first 4 moments and compare with the theoretical values //--- set the number of values and prepare an array int data_count=1000000; double data[]; ArrayResize(data,data_count); //--- generate random values and store them into the array for(int i=0; i<data_count; i++) { data[i]=MathRandomNormal(mu,sigma,error_code1); } //--- set the index of the initial value and the amount of data for calculation int start=0; int count=data_count; //--- calculate the first 4 moments of the generated values double mean=MathMean(data,start,count); double variance=MathVariance(data,start,count); double skewness=MathSkewness(data,start,count); double kurtosis=MathKurtosis(data,start,count); //--- variables for the theoretical moments double normal_mean=0; double normal_variance=0; double normal_skewness=0; double normal_kurtosis=0; //--- display the values of the calculated moments PrintFormat(" mean=%.10f, variance=%.10f skewness=%.10f kurtosis=%.10f",mean,variance,skewness,kurtosis); //--- calculate the theoretical values of the moments and compare them with the obtained values if(MathMomentsNormal(mu,sigma,normal_mean,normal_variance,normal_skewness,normal_kurtosis,error_code1)) { PrintFormat("Normal mean=%.10f, Normal variance=%.10f Normal skewness=%.10f Normal kurtosis=%.10f",normal_mean,normal_variance,normal_skewness,normal_kurtosis); PrintFormat("delta mean=%.4f, delta variance=%.4f delta skewness=%.4f delta kurtosis=%.4f",mean-normal_mean,variance-normal_variance,skewness-normal_skewness,kurtosis-normal_kurtosis); } //--- calculate the distribution histogram and save it to the normal.csv file int ncells=50; CalculateHistogram(data,ncells,"normal.csv"); }
Script execution results:
Fig. 1. TestNormal.mq5 script operation result
Note that all calculations of the 'kurtosis' parameter value use "excess kurtosis=kurtosis-3", i.e. for a normal distribution it equals zero.
The calculated histogram is saved to the normal.csv file (fig. 2)
Fig. 2. Distribution histogram of random numbers, generated according to the normal distribution with the parameters mu=5 and sigma=1
5. Comparison of calculation speed
To compare the calculation speed of statistical functions, the scripts for measuring calculation times have been prepared for the probability density functions (pdf), cumulative distribution functions (cdf), quantile calculation functions and pseudorandom number generation functions.
The calculations have been performed on an array of 51 values. For continuous distributions, the calculation of function values has been performed in the range from 0 to 1; for discrete distributions - from 0 to 50. The calculation time of the statistical functions of the R language has been carried out using the microbenchmark library. The calculation time of the MQL5 functions has been measured with the GetMicrosecondCount() function. The TestStatBenchmark.mq5 calculation script can be found under the terminal_data_folder\MQL5\Scripts\UnitTests\Stat. The script for the R and results of calculation speed measurements are provided in the Appendix.
The calculations have been made on Intel Core i7-4790, CPU 3.6 Ghz, 16 GB RAM, Windows 10 x64.
The results of calculation time measurements (in microseconds, µs) are shown in Table 3.
| No. | Distribution | MQL5 time for calculating the PDF (µs) | R time for calculating the PDF (µs) | PDF R/MQL5 | MQL5 time for calculating the CDF (µs) | R time for calculating the CDF (µs) | CDF R/MQL5 | MQL5 time for calculating the quantiles (µs) | R time for calculating the quantiles (µs) | Quantile R/MQL5 | MQL5 time for generating random numbers (µs) | R time for generating random numbers (µs) | Random R/MQL5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Binomial | 4.39 | 11.663 | 2.657 | 13.65 | 25.316 | 1.855 | 50.18 | 66.845 | 1.332 | 318.73 | 1816.463 | 5.699 |
| 2 | Beta | 1.74 | 17.352 | 9.972 | 4.76 | 15.076 | 3.167 | 48.72 | 129.992 | 2.668 | 688.81 | 1723.45 | 2.502 |
| 3 | Gamma | 1.31 | 8.251 | 6.347 | 8.09 | 14.792 | 1.828 | 50.83 | 64.286 | 1.265 | 142.84 | 1281.707 | 8.973 |
| 60 | Cauchy | 0.45 | 1.423 | 3.162 | 1.33 | 15.078 | 11.34 | 1.37 | 2.845 | 2.077 | 224.19 | 588.517 | 2.625 |
| 5 | Exponential | 0.85 | 3.13 | 3.682 | 0.77 | 2.845 | 3.695 | 0.53 | 2.276 | 4.294 | 143.18 | 389.406 | 2.72 |
| 6 | Uniform | 0.42 | 2.561 | 6.098 | 0.45 | 1.423 | 3.162 | 0.18 | 2.846 | 15.81 | 40.3 | 247.467 | 6.141 |
| 7 | Geometric | 2.3 | 5.121 | 2.227 | 2.12 | 4.552 | 2.147 | 0.81 | 5.407 | 6.675 | 278 | 1078.045 | 3.879 |
| 8 | Hypergeometric | 1.85 | 11.095 | 5.997 | 0.9 | 8.819 | 9.799 | 0.75 | 9.957 | 13.28 | 302.55 | 880.356 | 2.91 |
| 9 | Logistic | 1.27 | 4.267 | 3.36 | 1.11 | 4.267 | 3.844 | 0.71 | 3.13 | 4.408 | 178.65 | 626.632 | 3.508 |
| 10 | Weibull | 2.99 | 5.69 | 1.903 | 2.74 | 4.268 | 1.558 | 2.64 | 6.828 | 2.586 | 536.37 | 1558.472 | 2.906 |
| 11 | Poisson | 2.91 | 5.974 | 2.053 | 6.26 | 8.534 | 1.363 | 3.43 | 13.085 | 3.815 | 153.59 | 303.219 | 1.974 |
| 12 | F | 3.86 | 10.241 | 2.653 | 9.94 | 22.472 | 2.261 | 65.47 | 135.396 | 2.068 | 1249.22 | 1801.955 | 1.442 |
| 13 | Chi Square | 2.47 | 5.974 | 2.419 | 7.71 | 13.37 | 1.734 | 44.11 | 61.725 | 1.399 | 210.24 | 1235.059 | 5.875 |
| 14 | Noncentral ChiSquare | 8.05 | 14.223 | 1.767 | 45.61 | 209.068 | 4.584 | 220.66 | 10342.96 | 46.873 | 744.45 | 1997.653 | 2.683 |
| 15 | Noncentral F | 19.1 | 28.446 | 1.489 | 14.67 | 46.935 | 3.199 | 212.21 | 2561.991 | 12.073 | 1848.9 | 2912.141 | 1.575 |
| 16 | Noncentral Beta | 16.3 | 26.739 | 1.64 | 10.48 | 43.237 | 4.126 | 153.66 | 2290.915 | 14.909 | 2686.82 | 2839.893 | 1.057 |
| 17 | Negative Binomial | 6.13 | 11.094 | 1.81 | 12.21 | 19.627 | 1.607 | 14.05 | 60.019 | 4.272 | 1130.39 | 1936.498 | 1.713 |
| 18 | Normal | 1.15 | 4.267 | 3.71 | 0.81 | 3.983 | 4.917 | 0.7 | 2.277 | 3.253 | 293.7 | 696.321 | 2.371 |
| 19 | Lognormal | 1.99 | 5.406 | 2.717 | 3.19 | 8.819 | 2.765 | 3.18 | 6.259 | 1.968 | 479.75 | 1269.761 | 2.647 |
| 20 | T | 2.32 | 11.663 | 5.027 | 8.01 | 19.059 | 2.379 | 50.23 | 58.596 | 1.167 | 951.58 | 1425.92 | 1.498 |
| 21 | Noncentral T | 38.47 | 86.757 | 2.255 | 27.75 | 39.823 | 1.435 | 1339.51 | 1930.524 | 1.441 | 1550.27 | 1699.84 | 1.096 |
| <PDF R/MQL5> | 3.474 | <CDF R/MQL5> | 3.465 | <Quantile R/MQL5> | 7.03 | <Random R/MQL5> | 3.13 |
Table 4. Calculation times of the statistical functions in R and MQL5 (in microseconds)
The minimum time values have been taken for R, and the mean values (pdf_mean, cdf_mean, quantile_mean, random_mean) have been taken for MQL5.
Table 3 shows that even under such conditions, calculations of the statistical library functions in MQL5 are performed several times faster than those in R. On average, MQL5 computes 3 to 7 times faster than R, even taking into account that the compared versions of the R functions are actually written in C++.
In practice, the MQL5 compiler turned out to be much faster than C++ implementations of the functions in R, which shows the high quality of our developments. Translation of programs from R to MQL5 can give a significant boost in speed, and there will be no need to use a third-party DLL.
6. Detected calculation errors in R
During the testing of R, an error in the calculation of quantiles of the noncentral t-distribution has been detected.
For example:
> n <- 10 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > nt_pdf<-dt(k, 10,8, log = FALSE) > nt_cdf<-pt(k, 10,8, log = FALSE) > nt_quantile<-qt(nt_cdf, 10,8, log = FALSE) > nt_pdf [1] 4.927733e-15 1.130226e-14 2.641608e-14 6.281015e-14 1.516342e-13 3.708688e-13 9.166299e-13 [8] 2.283319e-12 5.716198e-12 1.433893e-11 3.593699e-11 > nt_cdf [1] 6.220961e-16 1.388760e-15 3.166372e-15 7.362630e-15 1.742915e-14 4.191776e-14 1.021850e-13 [8] 2.518433e-13 6.257956e-13 1.563360e-12 3.914610e-12 > k [1] 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 > nt_quantile [1] -Inf -1.340781e+154 -1.340781e+154 -1.340781e+154 -1.340781e+154 -1.340781e+154 [7] -1.340781e+154 7.000000e-01 8.000000e-01 9.000000e-01 1.000000e+00
For calculating the Student's t-distribution the R language uses the AS 243 algorithm, proposed by Lenth [6]. The advantage of this method is a fast recursive computation of infinite series members with an incomplete beta function. But the article [7] had shown that, due to a mistake in accuracy estimation during summation of the series members, this algorithm leads to errors (table 2 in the article [7]), especially for large values of the delta parameter for noncentrality. Authors of the article [7] have proposed a corrected algorithm for recursive calculation of probability of the noncentral t-distribution.
The MQL5 statistical library uses the correct algorithm for calculating the probabilities suggested in article [7], which provides accurate results.
It should be noted that in the R language, the definition of probability densities for the Gamma, Chi-Square and Noncentral Chi-Square distributions at point x=0 leads to infinite expressions:
> dgamma(0,0.5,1) [1] Inf > dchisq(0,df=0.5,ncp=1) [1] Inf > dchisq(0,df=0.5,ncp=0) [1] Inf
Thus, in the R language, limit values are used in the definition of probability density at point x=0. Despite the infinity at point x=0, in this case the divergencies do not occur during integration, and the integrals of the density are finite.
When calculating the probabilities (for example, for x=0.1), they match the values from Wolfram Alpha (Gamma, ChiSquare, NoncentralChiSquare).
> pgamma(0.1,0.5,1) [1] 0.3452792 > pchisq(0.1,df=0.5,ncp=0) [1] 0.5165553 > pchisq(0.1,df=0.5,ncp=1) [1] 0.3194965
The Wolfram Alpha (Mathematica) and Matlab make use of a different definition of the density at point x=0:
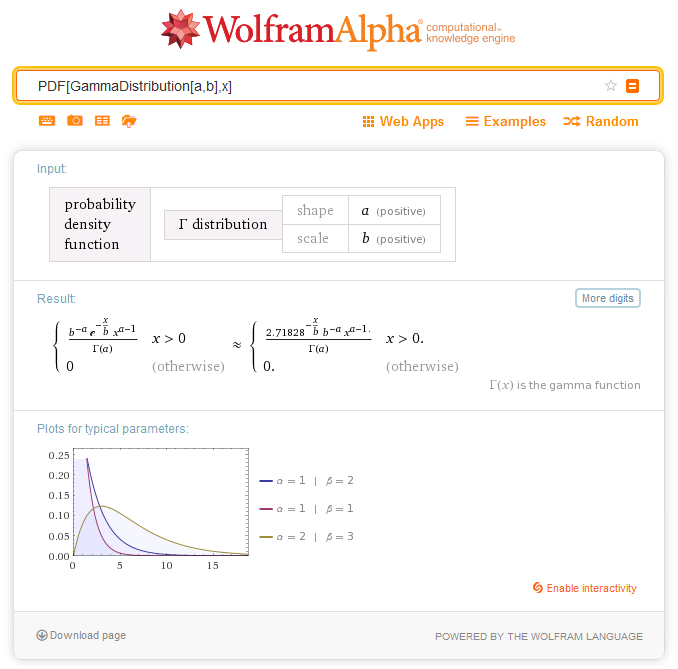
Fig. 3. Definition of the probability density of the Gamma distribution in Wolfram Alpha
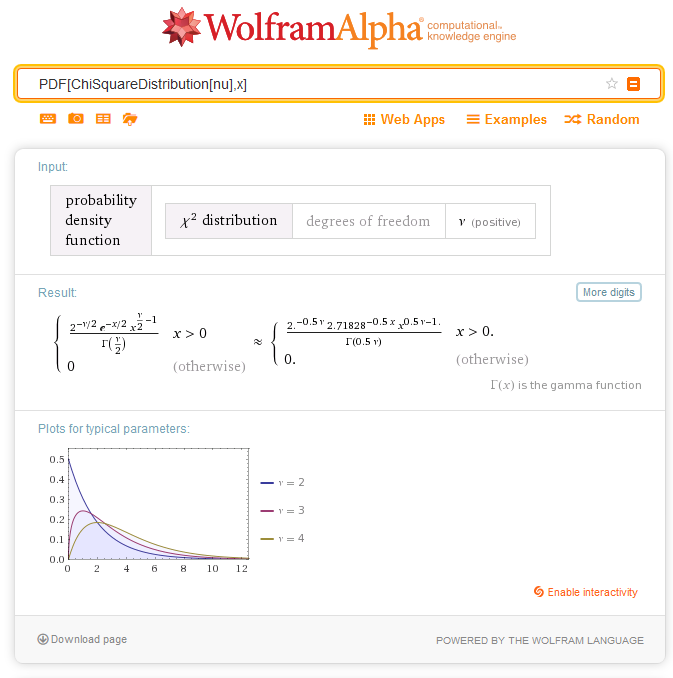
Fig. 4. Definition of the probability density of the Chi-Square distribution in Wolfram Alpha
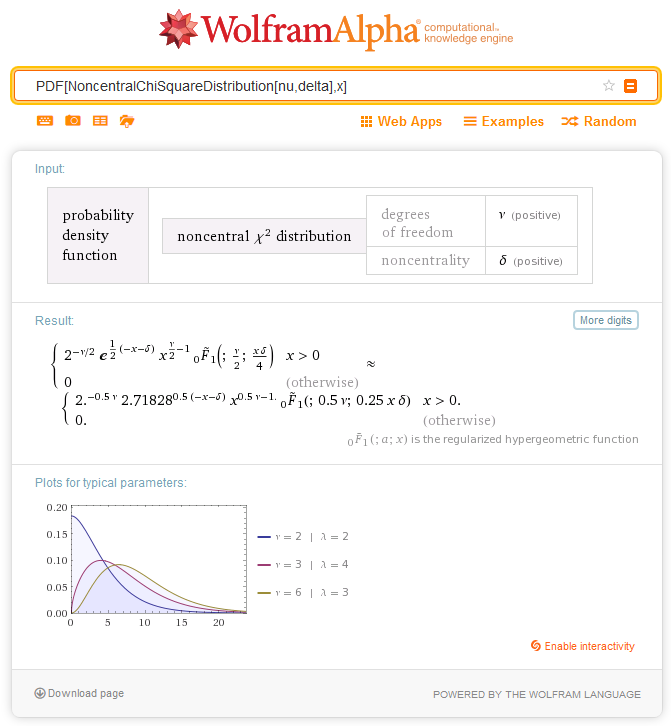
Fig. 5. Definition of the probability density of the Noncentral Chi-Square distribution in Wolfram Alpha
In the MQL5 statistical library, the densities of these distributions at point x=0 are considered to be equal to zero by definition.
In order to ensure the calculation accuracy and to allow third-party developers to test the quality of the library, multiple unit test scripts are included in the standard delivery. They can be found in the /Scripts/UnitTests/Stat folder.
Conclusion
The article considers the main functions of the MQL5 statistical library.
They allow to perform calculation of the statistical characteristics of data and to work with the basic statistical distributions implemented in the R language. In addition, the library also contains the functions for calculating theoretical moments of distributions, which allow to evaluate the degree of conformity of the real distribution to the modeled one.
Due to the high performance of the new 64-bit compiler of the MQL5, complex mathematical calculations are carried out several times faster than in R, which significantly facilitates the process of research.
References
- The R Project for Statistical Computing.
- N. Balakrishnan, N. L. Johnson, S. Kotz "Continuous Univariate Distributions: Volume 1." Wiley-Interscience, 1994.
- N. Balakrishnan, N. L. Johnson, S. Kotz "Continuous Univariate Distributions: Volume 2." Wiley-Interscience, 2000.
- N. L. Johnson, S. Kotz, A. W. Kemp "Univariate Discrete Distributions", Wiley-Interscience, 2005.
- Forbes C., Evans M., Hastings N., Peacock B., "Statistical Distributions", 4th Edition, John Wiley and Sons, 2011.
- Lenth, R.V., "Cumulative distribution function of the noncentral t distribution", Appled Statistics, vol. 38 (1989), 185–189.
- D. Benton, K. Krishnamoorthy, "Computing discrete mixtures of continuous distributions: noncentral chisquare, noncentral t and the distribution of the square of the sample multiple correlation coefficient", Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 43, (2003), 249-267
Appendix. Results of measuring the calculation time of the statistical functions
The script for evaluating the calculation time of the statistical functions in R and its operation results are provided in the Appendix, as well as the results of the TestStatBenchmark.mq5 script operation.
Script in R:
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,n,by=1)
binomial_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dbinom(k, 50, 0.6, log = FALSE))
binomial_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pbinom(k, 50, 0.6, log = FALSE))
binomial_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qbinom(cdf, 50, 0.6, log = FALSE))
binomial_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rbinom(10000, 50, 0.6))
print(binomial_pdf)
print(binomial_cdf)
print(binomial_quantile)
print(binomial_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
beta_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dbeta(k, 2, 4, log = FALSE))
beta_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pbeta(k, 2, 4, log = FALSE))
beta_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qbeta(cdf, 2, 4, log = FALSE))
beta_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rbeta(10000, 2, 4,))
print(beta_pdf)
print(beta_cdf)
print(beta_quantile)
print(beta_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
gamma_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dgamma(k, 1,1, log = FALSE))
gamma_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pgamma(k, 1,1, log = FALSE))
gamma_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qgamma(cdf, 1, 1, log = FALSE))
gamma_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rgamma(10000, 1,1))
print(gamma_pdf)
print(gamma_cdf)
print(gamma_quantile)
print(gamma_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
cauchy_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dcauchy(k, 2,1, log = FALSE))
cauchy_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pgamma(k, 2,1, log = FALSE))
cauchy_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qcauchy(cdf, 2, 1, log = FALSE))
cauchy_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rcauchy(10000, 2, 1))
print(cauchy_pdf)
print(cauchy_cdf)
print(cauchy_quantile)
print(cauchy_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
exponential_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dexp(k, 2, log = FALSE))
exponential_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pexp(k, 2, log = FALSE))
exponential_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qexp(cdf, 2, log = FALSE))
exponential_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rexp(10000, 2))
print(exponential_pdf)
print(exponential_cdf)
print(exponential_quantile)
print(exponential_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
uniform_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dunif(k, 0, 10, log = FALSE))
uniform_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-punif(k, 0, 10, log = FALSE))
uniform_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qunif(cdf, 0, 10, log = FALSE))
uniform_random <- microbenchmark(random<-runif(10000, 0, 10))
print(uniform_pdf)
print(uniform_cdf)
print(uniform_quantile)
print(uniform_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,n,by=1)
geometric_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dgeom(k, 0.3, log = FALSE))
geometric_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pgeom(k, 0.3, log = FALSE))
geometric_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qgeom(cdf, 0.3, log = FALSE))
geometric_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rgeom(10000, 0.3))
print(geometric_pdf)
print(geometric_cdf)
print(geometric_quantile)
print(geometric_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,n,by=1)
hypergeometric_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dhyper(k, 12,38,11, log = FALSE))
hypergeometric_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-phyper(k, 12,38,11, log = FALSE))
hypergeometric_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qhyper(cdf, 12,38,11, log = FALSE))
hypergeometric_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rhyper(10000, 12,38,11))
print(hypergeometric_pdf)
print(hypergeometric_cdf)
print(hypergeometric_quantile)
print(hypergeometric_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
logistic_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dlogis(k, 1,2, log = FALSE))
logistic_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-plogis(k, 1,2, log = FALSE))
logistic_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qlogis(cdf, 1,2, log = FALSE))
logistic_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rlogis(10000, 1,2))
print(logistic_pdf)
print(logistic_cdf)
print(logistic_quantile)
print(logistic_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
weibull_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dweibull(k, 5,1, log = FALSE))
weibull_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pweibull(k, 5,1, log = FALSE))
weibull_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qweibull(cdf, 5,1, log = FALSE))
weibull_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rweibull(10000, 5,1))
print(weibull_pdf)
print(weibull_cdf)
print(weibull_quantile)
print(weibull_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,n,by=1)
poisson_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dpois(k, 1, log = FALSE))
poisson_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-ppois(k, 1, log = FALSE))
poisson_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qpois(cdf, 1, log = FALSE))
poisson_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rpois(10000, 1))
print(poisson_pdf)
print(poisson_cdf)
print(poisson_quantile)
print(poisson_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
f_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-df(k, 10,20, log = FALSE))
f_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pf(k, 10,20, log = FALSE))
f_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qf(cdf, 10,20,log = FALSE))
f_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rf(10000, 10,20))
print(f_pdf)
print(f_cdf)
print(f_quantile)
print(f_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
chisquare_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dchisq(k, 2,log = FALSE))
chisquare_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pchisq(k, 2, log = FALSE))
chisquare_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qchisq(cdf, 2, log = FALSE))
chisquare_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rchisq(10000, 2))
print(chisquare_pdf)
print(chisquare_cdf)
print(chisquare_quantile)
print(chisquare_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
nchisquare_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dchisq(k, 2,1, log = FALSE))
nchisquare_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pchisq(k, 2,1,log = FALSE))
nchisquare_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qchisq(cdf, 2,1, log = FALSE))
nchisquare_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rchisq(10000, 2,1))
print(nchisquare_pdf)
print(nchisquare_cdf)
print(nchisquare_quantile)
print(nchisquare_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
nf_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-df(k, 10,20,2, log = FALSE))
nf_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pf(k, 10,20,2, log = FALSE))
nf_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qf(cdf, 10,20,2, log = FALSE))
nf_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rf(10000, 10,20,2))
print(nf_pdf)
print(nf_cdf)
print(nf_quantile)
print(nf_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
nbeta_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dbeta(k, 2,4,1, log = FALSE))
nbeta_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pbeta(k, 2,4,1, log = FALSE))
nbeta_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qbeta(cdf, 2,4,1, log = FALSE))
nbeta_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rbeta(10000, 2,4,1))
print(nbeta_pdf)
print(nbeta_cdf)
print(nbeta_quantile)
print(nbeta_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,n,by=1)
nbinom_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dnbinom(k, 2, 0.5, log = FALSE))
nbinom_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pnbinom(k, 2, 0.5, log = FALSE))
nbinom_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qnbinom(cdf, 2, 0.5, log = FALSE))
nbinom_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rnbinom(10000, 2, 0.5))
print(nbinom_pdf)
print(nbinom_cdf)
print(nbinom_quantile)
print(nbinom_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
normal_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dnorm(k, 1, 1, log = FALSE))
normal_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pnorm(k, 1, 1, log = FALSE))
normal_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qnorm(cdf, 1,1, log = FALSE))
normal_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rnorm(10000, 1,1))
print(normal_pdf)
print(normal_cdf)
print(normal_quantile)
print(normal_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
lognormal_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dlnorm(k, 0.5,0.6, log = FALSE))
lognormal_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-plnorm(k, 0.5,0.6, log = FALSE))
lognormal_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qlnorm(cdf, 0.5,0.6, log = FALSE))
lognormal_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rlnorm(10000, 0.5,0.6))
print(lognormal_pdf)
print(lognormal_cdf)
print(lognormal_quantile)
print(lognormal_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
t_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dt(k, 8, log = FALSE))
t_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pt(k, 8, log = FALSE))
t_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qt(cdf, 8, log = FALSE))
t_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rt(10000, 8))
print(t_pdf)
print(t_cdf)
print(t_quantile)
print(t_random)
n <- 50
k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n)
nt_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dt(k, 10,1, log = FALSE))
nt_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pt(k, 10,1, log = FALSE))
nt_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qt(cdf, 10,1, log = FALSE))
nt_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rt(10000, 10,1))
print(nt_pdf)
print(nt_cdf)
print(nt_quantile)
print(nt_random)
Result:
R version 3.2.5 (2016-04-14) -- "Very, Very Secure Dishes" Copyright (C) 2016 The R Foundation for Statistical Computing Platform: x86_64-w64-mingw32/x64 (64-bit) R is free software and comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY. You are welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions. Type 'license()' or 'licence()' for distribution details. R is a collaborative project with many contributors. Type 'contributors()' for more information and 'citation()' on how to cite R or R packages in publications. Type 'demo()' for some demos, 'help()' for on-line help, or 'help.start()' for an HTML browser interface to help. Type 'q()' to quit R. [Workspace loaded from ~/Test/111/.RData] > library(microbenchmark) > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,n,by=1) > binomial_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dbinom(k, 50, 0.6, log = FALSE)) > binomial_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pbinom(k, 50, 0.6, log = FALSE)) > binomial_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qbinom(cdf, 50, 0.6, log = FALSE)) > binomial_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rbinom(10000, 50, 0.6)) > print(binomial_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dbinom(k, 50, 0.6, log = FALSE) 11.663 11.948 13.37888 12.233 12.233 47.503 100 > print(binomial_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pbinom(k, 50, 0.6, log = FALSE) 25.316 25.602 29.63195 25.886 35.557 93.868 100 > print(binomial_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qbinom(cdf, 50, 0.6, log = FALSE) 66.845 67.13 72.09098 67.699 73.672 130.276 100 > print(binomial_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rbinom(10000, 50, 0.6) 1.816463 1.89056 1.948185 1.929814 1.989262 2.308835 100 > > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > beta_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dbeta(k, 2, 4, log = FALSE)) > beta_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pbeta(k, 2, 4, log = FALSE)) > beta_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qbeta(cdf, 2, 4, log = FALSE)) > beta_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rbeta(10000, 2, 4,)) > print(beta_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dbeta(k, 2, 4, log = FALSE) 17.352 17.637 19.99512 17.638 18.206 109.797 100 > print(beta_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pbeta(k, 2, 4, log = FALSE) 15.076 15.361 16.83489 15.646 15.9295 75.379 100 > print(beta_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qbeta(cdf, 2, 4, log = FALSE) 129.992 130.277 140.8325 131.4145 143.93 201.672 100 > print(beta_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rbeta(10000, 2, 4, ) 1.72345 1.794132 1.862292 1.836515 1.901226 2.823963 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > gamma_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dgamma(k, 1,1, log = FALSE)) > gamma_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pgamma(k, 1,1, log = FALSE)) > gamma_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qgamma(cdf, 1, 1, log = FALSE)) > gamma_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rgamma(10000, 1,1)) > print(gamma_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dgamma(k, 1, 1, log = FALSE) 8.251 8.8195 10.92684 9.104 9.389 122.312 100 > print(gamma_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pgamma(k, 1, 1, log = FALSE) 14.792 15.646 20.43306 20.055 21.334 106.099 100 > print(gamma_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qgamma(cdf, 1, 1, log = FALSE) 64.286 64.854 70.09419 65.139 67.13 162.988 100 > print(gamma_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rgamma(10000, 1, 1) 1.281707 1.330347 1.410961 1.362631 1.421226 2.322204 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > cauchy_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dcauchy(k, 2,1, log = FALSE)) > cauchy_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pgamma(k, 2,1, log = FALSE)) > cauchy_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qcauchy(cdf, 2, 1, log = FALSE)) > cauchy_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rcauchy(10000, 2, 1)) > print(cauchy_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dcauchy(k, 2, 1, log = FALSE) 1.423 1.708 2.8431 1.709 2.278 67.415 100 > print(cauchy_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pgamma(k, 2, 1, log = FALSE) 15.078 15.646 16.51914 15.93 16.215 33.281 100 > print(cauchy_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qcauchy(cdf, 2, 1, log = FALSE) 2.845 3.13 3.8044 3.131 3.415 56.606 100 > print(cauchy_random) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rcauchy(10000, 2, 1) 588.517 615.823 663.8658 637.7255 674.845 1520.356 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > exponential_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dexp(k, 2, log = FALSE)) > exponential_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pexp(k, 2, log = FALSE)) > exponential_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qexp(cdf, 2, log = FALSE)) > exponential_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rexp(10000, 2)) > print(exponential_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dexp(k, 2, log = FALSE) 3.13 3.414 4.08887 3.415 3.415 67.699 100 > print(exponential_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pexp(k, 2, log = FALSE) 2.845 3.13 4.38756 3.414 3.5565 58.597 100 > print(exponential_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qexp(cdf, 2, log = FALSE) 2.276 2.561 3.80729 2.5615 2.846 44.659 100 > print(exponential_random) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rexp(10000, 2) 389.406 408.8895 440.9583 418.4185 444.8715 1371.875 100 > > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > uniform_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dunif(k, 0, 10, log = FALSE)) > uniform_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-punif(k, 0, 10, log = FALSE)) > uniform_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qunif(cdf, 0, 10, log = FALSE)) > uniform_random <- microbenchmark(random<-runif(10000, 0, 10)) > print(uniform_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dunif(k, 0, 10, log = FALSE) 2.561 2.846 3.78734 3.13 3.131 66.277 100 > print(uniform_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- punif(k, 0, 10, log = FALSE) 1.423 1.708 2.41635 1.992 1.993 53.477 100 > print(uniform_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qunif(cdf, 0, 10, log = FALSE) 2.846 3.131 5.13561 3.415 3.6995 82.774 100 > print(uniform_random) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- runif(10000, 0, 10) 247.467 258.7035 317.1567 279.6095 357.2635 1267.769 100 > > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,n,by=1) > geometric_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dgeom(k, 0.3, log = FALSE)) > geometric_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pgeom(k, 0.3, log = FALSE)) > geometric_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qgeom(cdf, 0.3, log = FALSE)) > geometric_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rgeom(10000, 0.3)) > print(geometric_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dgeom(k, 0.3, log = FALSE) 5.121 5.122 6.14258 5.406 5.406 60.304 100 > print(geometric_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pgeom(k, 0.3, log = FALSE) 4.552 4.836 5.50548 4.837 5.1215 46.081 100 > print(geometric_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qgeom(cdf, 0.3, log = FALSE) 5.407 5.974 7.12107 5.975 6.259 71.681 100 > print(geometric_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rgeom(10000, 0.3) 1.078045 1.127681 1.192608 1.156125 1.199361 1.604267 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,n,by=1) > hypergeometric_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dhyper(k, 12,38,11, log = FALSE)) > hypergeometric_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-phyper(k, 12,38,11, log = FALSE)) > hypergeometric_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qhyper(cdf, 12,38,11, log = FALSE)) > hypergeometric_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rhyper(10000, 12,38,11)) > print(hypergeometric_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dhyper(k, 12, 38, 11, log = FALSE) 11.095 13.939 17.07667 14.224 14.935 101.548 100 > print(hypergeometric_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- phyper(k, 12, 38, 11, log = FALSE) 8.819 9.387 12.60515 9.672 12.517 62.01 100 > print(hypergeometric_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qhyper(cdf, 12, 38, 11, log = FALSE) 9.957 10.3835 13.00618 10.81 11.948 64.286 100 > print(hypergeometric_random) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rhyper(10000, 12, 38, 11) 880.356 938.9515 993.8324 963.9835 996.8365 1375.289 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > logistic_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dlogis(k, 1,2, log = FALSE)) > logistic_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-plogis(k, 1,2, log = FALSE)) > logistic_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qlogis(cdf, 1,2, log = FALSE)) > logistic_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rlogis(10000, 1,2)) > print(logistic_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dlogis(k, 1, 2, log = FALSE) 4.267 4.552 5.94354 4.553 4.837 53.477 100 > print(logistic_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- plogis(k, 1, 2, log = FALSE) 4.267 4.552 5.96056 4.837 4.837 96.428 100 > print(logistic_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qlogis(cdf, 1, 2, log = FALSE) 3.13 3.415 4.1742 3.415 3.699 56.036 100 > print(logistic_random) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rlogis(10000, 1, 2) 626.632 649.956 696.2128 675.2725 715.805 1589.191 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > weibull_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dweibull(k, 5,1, log = FALSE)) > weibull_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pweibull(k, 5,1, log = FALSE)) > weibull_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qweibull(cdf, 5,1, log = FALSE)) > weibull_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rweibull(10000, 5,1)) > print(weibull_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dweibull(k, 5, 1, log = FALSE) 5.69 5.974 7.21775 5.975 6.259 85.619 100 > print(weibull_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pweibull(k, 5, 1, log = FALSE) 4.268 4.552 7.83782 4.8365 7.966 90.455 100 > print(weibull_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qweibull(cdf, 5, 1, log = FALSE) 6.828 7.112 7.96587 7.113 7.397 48.641 100 > print(weibull_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rweibull(10000, 5, 1) 1.558472 1.59744 1.659753 1.632853 1.679502 2.616603 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,n,by=1) > poisson_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dpois(k, 1, log = FALSE)) > poisson_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-ppois(k, 1, log = FALSE)) > poisson_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qpois(cdf, 1, log = FALSE)) > poisson_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rpois(10000, 1)) > print(poisson_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dpois(k, 1, log = FALSE) 5.974 6.543 7.30316 6.544 6.828 54.046 100 > print(poisson_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- ppois(k, 1, log = FALSE) 8.534 8.819 10.25846 9.104 9.388 64.286 100 > print(poisson_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qpois(cdf, 1, log = FALSE) 13.085 13.086 14.37438 13.37 13.654 61.157 100 > print(poisson_random) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rpois(10000, 1) 303.219 314.8815 327.5787 324.552 341.335 373.477 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > f_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-df(k, 10,20, log = FALSE)) > f_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pf(k, 10,20, log = FALSE)) > f_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qf(cdf, 10,20,log = FALSE)) > f_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rf(10000, 10,20)) > print(f_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- df(k, 10, 20, log = FALSE) 10.241 10.81 12.43159 10.811 11.095 71.112 100 > print(f_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pf(k, 10, 20, log = FALSE) 22.472 22.757 25.66972 23.041 23.3265 86.189 100 > print(f_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qf(cdf, 10, 20, log = FALSE) 135.396 136.25 166.7057 157.7255 186.171 255.717 100 > print(f_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rf(10000, 10, 20) 1.801955 1.889706 1.947645 1.929528 1.98272 2.725546 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > chisquare_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dchisq(k, 2,log = FALSE)) > chisquare_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pchisq(k, 2, log = FALSE)) > chisquare_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qchisq(cdf, 2, log = FALSE)) > chisquare_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rchisq(10000, 2)) > print(chisquare_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dchisq(k, 2, log = FALSE) 5.974 6.259 7.06416 6.4015 6.544 52.339 100 > print(chisquare_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pchisq(k, 2, log = FALSE) 13.37 13.655 15.46392 13.655 13.94 99.841 100 > print(chisquare_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qchisq(cdf, 2, log = FALSE) 61.725 62.2945 68.40176 62.7215 72.25 132.553 100 > print(chisquare_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rchisq(10000, 2) 1.235059 1.29408 1.38993 1.333903 1.401743 2.205582 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > nchisquare_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dchisq(k, 2,1, log = FALSE)) > nchisquare_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pchisq(k, 2,1,log = FALSE)) > nchisquare_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qchisq(cdf, 2,1, log = FALSE)) > nchisquare_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rchisq(10000, 2,1)) > print(nchisquare_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dchisq(k, 2, 1, log = FALSE) 14.223 14.509 17.3866 14.793 15.6455 37.548 100 > print(nchisquare_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pchisq(k, 2, 1, log = FALSE) 209.068 210.49 231.6357 223.1475 240.499 309.193 100 > print(nchisquare_quantile) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qchisq(cdf, 2, 1, log = FALSE) 10.34296 10.65955 10.90239 10.83733 11.02563 12.31558 100 > print(nchisquare_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rchisq(10000, 2, 1) 1.997653 2.073457 2.187417 2.114845 2.183111 3.134576 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > nf_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-df(k, 10,20,2, log = FALSE)) > nf_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pf(k, 10,20,2, log = FALSE)) > nf_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qf(cdf, 10,20,2, log = FALSE)) > nf_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rf(10000, 10,20,2)) > print(nf_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- df(k, 10, 20, 2, log = FALSE) 28.446 30.153 34.12338 30.438 31.291 68.836 100 > print(nf_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pf(k, 10, 20, 2, log = FALSE) 46.935 61.8685 64.53899 63.433 65.708 106.953 100 > print(nf_quantile) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qf(cdf, 10, 20, 2, log = FALSE) 2.561991 2.640355 2.719223 2.68999 2.744461 3.737598 100 > print(nf_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rf(10000, 10, 20, 2) 2.912141 2.989225 3.100073 3.035163 3.110825 4.062433 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > nbeta_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dbeta(k, 2,4,1, log = FALSE)) > nbeta_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pbeta(k, 2,4,1, log = FALSE)) > nbeta_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qbeta(cdf, 2,4,1, log = FALSE)) > nbeta_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rbeta(10000, 2,4,1)) > print(nbeta_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dbeta(k, 2, 4, 1, log = FALSE) 26.739 27.308 31.31301 27.592 30.5795 56.891 100 > print(nbeta_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pbeta(k, 2, 4, 1, log = FALSE) 43.237 43.806 55.11814 56.321 57.7435 167.255 100 > print(nbeta_quantile) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qbeta(cdf, 2, 4, 1, log = FALSE) 2.290915 2.375111 2.440959 2.431146 2.49927 2.644764 100 > print(nbeta_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rbeta(10000, 2, 4, 1) 2.839893 3.002737 3.143906 3.073848 3.150932 4.302789 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,n,by=1) > nbinom_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dnbinom(k, 2, 0.5, log = FALSE)) > nbinom_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pnbinom(k, 2, 0.5, log = FALSE)) > nbinom_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qnbinom(cdf, 2, 0.5, log = FALSE)) > nbinom_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rnbinom(10000, 2, 0.5)) > print(nbinom_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dnbinom(k, 2, 0.5, log = FALSE) 11.094 11.379 13.37031 11.664 11.948 78.508 100 > print(nbinom_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pnbinom(k, 2, 0.5, log = FALSE) 19.627 19.913 22.94469 20.197 20.482 130.277 100 > print(nbinom_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qnbinom(cdf, 2, 0.5, log = FALSE) 60.019 60.588 69.73866 61.442 74.099 122.028 100 > print(nbinom_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rnbinom(10000, 2, 0.5) 1.936498 2.029226 2.086237 2.072035 2.125084 2.354061 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > normal_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dnorm(k, 1, 1, log = FALSE)) > normal_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pnorm(k, 1, 1, log = FALSE)) > normal_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qnorm(cdf, 1,1, log = FALSE)) > normal_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rnorm(10000, 1,1)) > print(normal_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dnorm(k, 1, 1, log = FALSE) 4.267 4.552 5.7927 4.553 4.837 75.663 100 > print(normal_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pnorm(k, 1, 1, log = FALSE) 3.983 4.269 5.94911 4.553 4.979 50.632 100 > print(normal_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qnorm(cdf, 1, 1, log = FALSE) 2.277 2.561 3.42042 2.845 2.846 45.227 100 > print(normal_random) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rnorm(10000, 1, 1) 696.321 728.747 779.1994 749.7965 778.3835 1541.12 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > lognormal_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dlnorm(k, 0.5,0.6, log = FALSE)) > lognormal_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-plnorm(k, 0.5,0.6, log = FALSE)) > lognormal_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qlnorm(cdf, 0.5,0.6, log = FALSE)) > lognormal_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rlnorm(10000, 0.5,0.6)) > print(lognormal_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dlnorm(k, 0.5, 0.6, log = FALSE) 5.406 5.69 6.89638 5.975 6.259 50.917 100 > print(lognormal_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- plnorm(k, 0.5, 0.6, log = FALSE) 8.819 9.387 12.3463 9.3885 12.6595 71.681 100 > print(lognormal_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qlnorm(cdf, 0.5, 0.6, log = FALSE) 6.259 6.544 7.38277 6.544 6.828 58.881 100 > print(lognormal_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rlnorm(10000, 0.5, 0.6) 1.269761 1.329209 1.380386 1.362632 1.401743 2.247395 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > t_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dt(k, 8, log = FALSE)) > t_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pt(k, 8, log = FALSE)) > t_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qt(cdf, 8, log = FALSE)) > t_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rt(10000, 8)) > print(t_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dt(k, 8, log = FALSE) 11.663 12.233 15.71413 12.517 16.0725 76.517 100 > print(t_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pt(k, 8, log = FALSE) 19.059 20.6235 23.23485 21.05 21.619 127.717 100 > print(t_quantile) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qt(cdf, 8, log = FALSE) 58.596 58.882 64.84339 59.166 62.01 151.611 100 > print(t_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rt(10000, 8) 1.42592 1.480676 1.553132 1.51424 1.569565 2.44679 100 > > n <- 50 > k <- seq(0,1,by=1/n) > nt_pdf <- microbenchmark(pdf<-dt(k, 10,1, log = FALSE)) > nt_cdf <- microbenchmark(cdf<-pt(k, 10,1, log = FALSE)) > nt_quantile <- microbenchmark(quantile<-qt(cdf, 10,1, log = FALSE)) > nt_random <- microbenchmark(random<-rt(10000, 10,1)) > print(nt_pdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval pdf <- dt(k, 10, 1, log = FALSE) 86.757 88.037 92.88671 89.317 91.4505 130.276 100 > print(nt_cdf) Unit: microseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval cdf <- pt(k, 10, 1, log = FALSE) 39.823 40.2505 44.51695 40.6765 49.352 70.829 100 > print(nt_quantile) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval quantile <- qt(cdf, 10, 1, log = FALSE) 1.930524 1.981866 2.038755 2.0224 2.079715 2.594987 100 > print(nt_random) Unit: milliseconds expr min lq mean median uq max neval random <- rt(10000, 10, 1) 1.69984 1.764693 1.867469 1.814044 1.893263 2.856959 100
Result of the TestStatBenchmark.mq5 operation script:
PP 0 13:06:15.252 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1)
KJ 0 13:06:15.639 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Binomial time (microseconds): pdf_mean=4.39, pdf_median=4.00, pdf_min=3.00, pdf_max=40.00, pdf_stddev=2.21, pdf_avgdev=0.95
MS 0 13:06:15.639 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Binomial time (microseconds): cdf_mean=13.65, cdf_median=12.00, cdf_min=11.00, cdf_max=54.00, cdf_stddev=4.09, cdf_avgdev=2.37
GF 0 13:06:15.639 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Binomial time (microseconds): quantile_mean=50.18, quantile_median=45.00, quantile_min=43.00, quantile_max=108.00, quantile_stddev=9.97, quantile_avgdev=7.41
QO 0 13:06:15.639 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Binomial time (microseconds): random_mean=318.73, random_median=312.00, random_min=284.00, random_max=478.00, random_stddev=28.74, random_avgdev=22.22
LP 0 13:06:16.384 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Beta time (microseconds): pdf_mean=1.74, pdf_median=2.00, pdf_min=1.00, pdf_max=18.00, pdf_stddev=1.07, pdf_avgdev=0.53
EI 0 13:06:16.384 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Beta time (microseconds): cdf_mean=4.76, cdf_median=4.00, cdf_min=3.00, cdf_max=68.00, cdf_stddev=3.07, cdf_avgdev=1.19
LM 0 13:06:16.384 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Beta time (microseconds): quantile_mean=48.72, quantile_median=44.00, quantile_min=43.00, quantile_max=111.00, quantile_stddev=10.21, quantile_avgdev=6.96
QG 0 13:06:16.384 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Beta time (microseconds): random_mean=688.81, random_median=680.00, random_min=625.00, random_max=976.00, random_stddev=43.92, random_avgdev=31.81
HE 0 13:06:16.587 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Gamma time (microseconds): pdf_mean=1.31, pdf_median=1.00, pdf_min=1.00, pdf_max=13.00, pdf_stddev=0.82, pdf_avgdev=0.47
GL 0 13:06:16.587 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Gamma time (microseconds): cdf_mean=8.09, cdf_median=7.00, cdf_min=7.00, cdf_max=92.00, cdf_stddev=3.67, cdf_avgdev=1.40
CF 0 13:06:16.587 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Gamma time (microseconds): quantile_mean=50.83, quantile_median=46.00, quantile_min=45.00, quantile_max=106.00, quantile_stddev=9.27, quantile_avgdev=6.72
GR 0 13:06:16.587 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Gamma time (microseconds): random_mean=142.84, random_median=132.00, random_min=128.00, random_max=260.00, random_stddev=19.73, random_avgdev=15.32
QD 0 13:06:16.815 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Cauchy time (microseconds): pdf_mean=0.45, pdf_median=0.00, pdf_min=0.00, pdf_max=11.00, pdf_stddev=0.85, pdf_avgdev=0.54
QK 0 13:06:16.815 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Cauchy time (microseconds): cdf_mean=1.33, cdf_median=1.00, cdf_min=1.00, cdf_max=12.00, cdf_stddev=0.81, cdf_avgdev=0.48
MR 0 13:06:16.815 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Cauchy time (microseconds): quantile_mean=1.37, quantile_median=1.00, quantile_min=1.00, quantile_max=14.00, quantile_stddev=0.89, quantile_avgdev=0.51
IK 0 13:06:16.815 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Cauchy time (microseconds): random_mean=224.19, random_median=215.00, random_min=200.00, random_max=352.00, random_stddev=26.86, random_avgdev=20.34
PQ 0 13:06:16.960 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Exponential time (microseconds): pdf_mean=0.85, pdf_median=1.00, pdf_min=0.00, pdf_max=18.00, pdf_stddev=1.40, pdf_avgdev=0.54
GK 0 13:06:16.960 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Exponential time (microseconds): cdf_mean=0.77, cdf_median=1.00, cdf_min=0.00, cdf_max=16.00, cdf_stddev=0.94, cdf_avgdev=0.47
HE 0 13:06:16.960 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Exponential time (microseconds): quantile_mean=0.53, quantile_median=0.00, quantile_min=0.00, quantile_max=10.00, quantile_stddev=0.78, quantile_avgdev=0.54
HL 0 13:06:16.960 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Exponential time (microseconds): random_mean=143.18, random_median=130.00, random_min=128.00, random_max=272.00, random_stddev=21.58, random_avgdev=16.98
LK 0 13:06:17.002 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Uniform time (microseconds): pdf_mean=0.42, pdf_median=0.00, pdf_min=0.00, pdf_max=12.00, pdf_stddev=0.82, pdf_avgdev=0.52
CE 0 13:06:17.002 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Uniform time (microseconds): cdf_mean=0.45, cdf_median=0.00, cdf_min=0.00, cdf_max=16.00, cdf_stddev=0.96, cdf_avgdev=0.55
LO 0 13:06:17.002 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Uniform time (microseconds): quantile_mean=0.18, quantile_median=0.00, quantile_min=0.00, quantile_max=1.00, quantile_stddev=0.38, quantile_avgdev=0.29
GE 0 13:06:17.002 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Uniform time (microseconds): random_mean=40.30, random_median=36.00, random_min=35.00, random_max=83.00, random_stddev=7.61, random_avgdev=5.41
OP 0 13:06:17.286 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Geometric time (microseconds): pdf_mean=2.30, pdf_median=2.00, pdf_min=1.00, pdf_max=14.00, pdf_stddev=1.30, pdf_avgdev=0.52
DK 0 13:06:17.286 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Geometric time (microseconds): cdf_mean=2.12, cdf_median=2.00, cdf_min=1.00, cdf_max=18.00, cdf_stddev=1.69, cdf_avgdev=0.53
NE 0 13:06:17.286 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Geometric time (microseconds): quantile_mean=0.81, quantile_median=1.00, quantile_min=0.00, quantile_max=10.00, quantile_stddev=0.68, quantile_avgdev=0.39
IL 0 13:06:17.286 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Geometric time (microseconds): random_mean=278.00, random_median=271.00, random_min=251.00, random_max=429.00, random_stddev=28.23, random_avgdev=21.62
PG 0 13:06:17.592 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Hypergeometric time (microseconds): pdf_mean=1.85, pdf_median=2.00, pdf_min=1.00, pdf_max=15.00, pdf_stddev=1.07, pdf_avgdev=0.48
CM 0 13:06:17.592 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Hypergeometric time (microseconds): cdf_mean=0.90, cdf_median=1.00, cdf_min=0.00, cdf_max=17.00, cdf_stddev=0.85, cdf_avgdev=0.32
NP 0 13:06:17.592 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Hypergeometric time (microseconds): quantile_mean=0.75, quantile_median=1.00, quantile_min=0.00, quantile_max=12.00, quantile_stddev=0.96, quantile_avgdev=0.48
FE 0 13:06:17.592 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Hypergeometric time (microseconds): random_mean=302.55, random_median=295.00, random_min=272.00, random_max=466.00, random_stddev=30.20, random_avgdev=22.99
ML 0 13:06:17.774 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Logistic time (microseconds): pdf_mean=1.27, pdf_median=1.00, pdf_min=0.00, pdf_max=91.00, pdf_stddev=3.04, pdf_avgdev=0.56
DR 0 13:06:17.774 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Logistic time (microseconds): cdf_mean=1.11, cdf_median=1.00, cdf_min=0.00, cdf_max=17.00, cdf_stddev=1.34, cdf_avgdev=0.40
IH 0 13:06:17.774 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Logistic time (microseconds): quantile_mean=0.71, quantile_median=1.00, quantile_min=0.00, quantile_max=12.00, quantile_stddev=0.79, quantile_avgdev=0.47
GL 0 13:06:17.774 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Logistic time (microseconds): random_mean=178.65, random_median=164.00, random_min=162.00, random_max=309.00, random_stddev=24.09, random_avgdev=17.94
MJ 0 13:06:18.319 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Weibull time (microseconds): pdf_mean=2.99, pdf_median=3.00, pdf_min=2.00, pdf_max=17.00, pdf_stddev=1.63, pdf_avgdev=0.57
GD 0 13:06:18.319 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Weibull time (microseconds): cdf_mean=2.74, cdf_median=3.00, cdf_min=2.00, cdf_max=19.00, cdf_stddev=1.23, cdf_avgdev=0.58
FO 0 13:06:18.319 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Weibull time (microseconds): quantile_mean=2.64, quantile_median=2.00, quantile_min=2.00, quantile_max=19.00, quantile_stddev=1.64, quantile_avgdev=0.76
DJ 0 13:06:18.319 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Weibull time (microseconds): random_mean=536.37, random_median=526.00, random_min=483.00, random_max=759.00, random_stddev=46.99, random_avgdev=34.40
HR 0 13:06:18.485 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Poisson time (microseconds): pdf_mean=2.91, pdf_median=3.00, pdf_min=2.00, pdf_max=15.00, pdf_stddev=1.40, pdf_avgdev=0.58
IL 0 13:06:18.486 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Poisson time (microseconds): cdf_mean=6.26, cdf_median=6.00, cdf_min=5.00, cdf_max=23.00, cdf_stddev=2.38, cdf_avgdev=1.07
HE 0 13:06:18.486 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Poisson time (microseconds): quantile_mean=3.43, quantile_median=3.00, quantile_min=2.00, quantile_max=20.00, quantile_stddev=1.48, quantile_avgdev=0.68
DL 0 13:06:18.486 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Poisson time (microseconds): random_mean=153.59, random_median=144.00, random_min=138.00, random_max=265.00, random_stddev=18.57, random_avgdev=13.99
IH 0 13:06:19.814 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) F time (microseconds): pdf_mean=3.86, pdf_median=4.00, pdf_min=3.00, pdf_max=21.00, pdf_stddev=1.78, pdf_avgdev=0.76
GS 0 13:06:19.814 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) F time (microseconds): cdf_mean=9.94, cdf_median=9.00, cdf_min=7.00, cdf_max=36.00, cdf_stddev=3.82, cdf_avgdev=2.15
OI 0 13:06:19.814 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) F time (microseconds): quantile_mean=65.47, quantile_median=59.00, quantile_min=57.00, quantile_max=147.00, quantile_stddev=12.99, quantile_avgdev=9.64
DE 0 13:06:19.814 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) F time (microseconds): random_mean=1249.22, random_median=1213.00, random_min=1127.00, random_max=1968.00, random_stddev=117.69, random_avgdev=72.17
EL 0 13:06:20.079 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) ChiSquare time (microseconds): pdf_mean=2.47, pdf_median=2.00, pdf_min=2.00, pdf_max=13.00, pdf_stddev=1.32, pdf_avgdev=0.65
JK 0 13:06:20.079 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) ChiSquare time (microseconds): cdf_mean=7.71, cdf_median=7.00, cdf_min=7.00, cdf_max=23.00, cdf_stddev=1.91, cdf_avgdev=0.88
KQ 0 13:06:20.079 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) ChiSquare time (microseconds): quantile_mean=44.11, quantile_median=41.00, quantile_min=40.00, quantile_max=120.00, quantile_stddev=8.17, quantile_avgdev=5.38
CL 0 13:06:20.079 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) ChiSquare time (microseconds): random_mean=210.24, random_median=196.00, random_min=190.00, random_max=437.00, random_stddev=29.14, random_avgdev=21.00
HD 0 13:06:21.098 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral ChiSquare time (microseconds): pdf_mean=8.05, pdf_median=8.00, pdf_min=7.00, pdf_max=24.00, pdf_stddev=2.41, pdf_avgdev=1.09
MR 0 13:06:21.098 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral ChiSquare time (microseconds): cdf_mean=45.61, cdf_median=42.00, cdf_min=41.00, cdf_max=97.00, cdf_stddev=8.25, cdf_avgdev=5.70
FN 0 13:06:21.098 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral ChiSquare time (microseconds): quantile_mean=220.66, quantile_median=211.50, quantile_min=196.00, quantile_max=362.00, quantile_stddev=24.71, quantile_avgdev=19.45
LI 0 13:06:21.099 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral ChiSquare time (microseconds): random_mean=744.45, random_median=728.00, random_min=672.00, random_max=1082.00, random_stddev=62.42, random_avgdev=43.24
RE 0 13:06:23.194 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral F time (microseconds): pdf_mean=19.10, pdf_median=18.00, pdf_min=16.00, pdf_max=50.00, pdf_stddev=4.67, pdf_avgdev=2.64
FS 0 13:06:23.194 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral F time (microseconds): cdf_mean=14.67, cdf_median=13.00, cdf_min=12.00, cdf_max=39.00, cdf_stddev=3.94, cdf_avgdev=2.44
EN 0 13:06:23.194 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral F time (microseconds): quantile_mean=212.21, quantile_median=203.00, quantile_min=189.00, quantile_max=347.00, quantile_stddev=24.37, quantile_avgdev=19.30
EF 0 13:06:23.194 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral F time (microseconds): random_mean=1848.90, random_median=1819.00, random_min=1704.00, random_max=2556.00, random_stddev=118.75, random_avgdev=78.66
EN 0 13:06:26.061 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral Beta time (microseconds): pdf_mean=16.30, pdf_median=15.00, pdf_min=14.00, pdf_max=43.00, pdf_stddev=4.32, pdf_avgdev=2.43
EP 0 13:06:26.061 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral Beta time (microseconds): cdf_mean=10.48, cdf_median=10.00, cdf_min=8.00, cdf_max=32.00, cdf_stddev=3.02, cdf_avgdev=1.72
ME 0 13:06:26.061 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral Beta time (microseconds): quantile_mean=153.66, quantile_median=141.00, quantile_min=135.00, quantile_max=283.00, quantile_stddev=20.83, quantile_avgdev=16.16
QJ 0 13:06:26.061 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral Beta time (microseconds): random_mean=2686.82, random_median=2649.00, random_min=2457.00, random_max=3753.00, random_stddev=150.32, random_avgdev=98.23
OO 0 13:06:27.225 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Negative Binomial time (microseconds): pdf_mean=6.13, pdf_median=6.00, pdf_min=5.00, pdf_max=24.00, pdf_stddev=2.38, pdf_avgdev=1.22
DG 0 13:06:27.225 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Negative Binomial time (microseconds): cdf_mean=12.21, cdf_median=11.00, cdf_min=11.00, cdf_max=33.00, cdf_stddev=3.07, cdf_avgdev=1.58
LJ 0 13:06:27.225 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Negative Binomial time (microseconds): quantile_mean=14.05, quantile_median=13.00, quantile_min=12.00, quantile_max=82.00, quantile_stddev=4.81, quantile_avgdev=2.28
EM 0 13:06:27.225 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Negative Binomial time (microseconds): random_mean=1130.39, random_median=1108.00, random_min=1039.00, random_max=1454.00, random_stddev=69.41, random_avgdev=51.70
GP 0 13:06:27.521 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Normal time (microseconds): pdf_mean=1.15, pdf_median=1.00, pdf_min=0.00, pdf_max=19.00, pdf_stddev=1.34, pdf_avgdev=0.45
OI 0 13:06:27.521 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Normal time (microseconds): cdf_mean=0.81, cdf_median=1.00, cdf_min=0.00, cdf_max=17.00, cdf_stddev=1.16, cdf_avgdev=0.49
CN 0 13:06:27.521 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Normal time (microseconds): quantile_mean=0.70, quantile_median=1.00, quantile_min=0.00, quantile_max=13.00, quantile_stddev=0.82, quantile_avgdev=0.49
EG 0 13:06:27.521 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Normal time (microseconds): random_mean=293.70, random_median=281.00, random_min=256.00, random_max=537.00, random_stddev=43.28, random_avgdev=31.62
FD 0 13:06:28.010 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Lognormal time (microseconds): pdf_mean=1.99, pdf_median=2.00, pdf_min=1.00, pdf_max=18.00, pdf_stddev=1.48, pdf_avgdev=0.48
PN 0 13:06:28.010 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Lognormal time (microseconds): cdf_mean=3.19, cdf_median=3.00, cdf_min=2.00, cdf_max=17.00, cdf_stddev=1.61, cdf_avgdev=0.64
DH 0 13:06:28.010 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Lognormal time (microseconds): quantile_mean=3.18, quantile_median=3.00, quantile_min=2.00, quantile_max=19.00, quantile_stddev=1.77, quantile_avgdev=0.64
NR 0 13:06:28.010 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Lognormal time (microseconds): random_mean=479.75, random_median=468.00, random_min=428.00, random_max=754.00, random_stddev=48.26, random_avgdev=34.30
FL 0 13:06:29.022 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) T time (microseconds): pdf_mean=2.32, pdf_median=2.00, pdf_min=1.00, pdf_max=15.00, pdf_stddev=1.29, pdf_avgdev=0.54
QE 0 13:06:29.022 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) T time (microseconds): cdf_mean=8.01, cdf_median=7.00, cdf_min=6.00, cdf_max=39.00, cdf_stddev=3.13, cdf_avgdev=1.73
MM 0 13:06:29.022 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) T time (microseconds): quantile_mean=50.23, quantile_median=45.00, quantile_min=44.00, quantile_max=113.00, quantile_stddev=10.28, quantile_avgdev=7.73
KG 0 13:06:29.022 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) T time (microseconds): random_mean=951.58, random_median=931.00, random_min=859.00, random_max=1439.00, random_stddev=78.14, random_avgdev=49.72
CQ 0 13:06:31.979 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral T time (microseconds): pdf_mean=38.47, pdf_median=35.00, pdf_min=32.00, pdf_max=164.00, pdf_stddev=9.66, pdf_avgdev=6.38
OO 0 13:06:31.979 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral T time (microseconds): cdf_mean=27.75, cdf_median=25.00, cdf_min=24.00, cdf_max=80.00, cdf_stddev=7.02, cdf_avgdev=4.63
PF 0 13:06:31.979 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral T time (microseconds): quantile_mean=1339.51, quantile_median=1306.00, quantile_min=1206.00, quantile_max=2262.00, quantile_stddev=128.18, quantile_avgdev=74.83
OR 0 13:06:31.979 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) Noncentral T time (microseconds): random_mean=1550.27, random_median=1520.00, random_min=1418.00, random_max=2317.00, random_stddev=112.08, random_avgdev=73.74
LQ 0 13:06:31.979 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1)
GH 0 13:06:31.979 TestStatBenchmark (EURUSD,H1) 21 of 21 passed
Translated from Russian by MetaQuotes Ltd.
Original article: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/2742
 Neural network: Self-optimizing Expert Advisor
Neural network: Self-optimizing Expert Advisor
 Working with currency baskets in the Forex market
Working with currency baskets in the Forex market
 Graphical Interfaces X: Updates for Easy And Fast Library (Build 3)
Graphical Interfaces X: Updates for Easy And Fast Library (Build 3)
 The Easy Way to Evaluate a Signal: Trading Activity, Drawdown/Load and MFE/MAE Distribution Charts
The Easy Way to Evaluate a Signal: Trading Activity, Drawdown/Load and MFE/MAE Distribution Charts
- Free trading apps
- Over 8,000 signals for copying
- Economic news for exploring financial markets
You agree to website policy and terms of use