
重塑经典策略(第二部分):布林带突破
概述
布林带是交易策略中的多功能工具,既可用于趋势跟踪,也可用于识别潜在的转折点或反转点。从技术上讲,该指标由一条指数移动平均线(EMA)组成,用于平滑证券的收盘价。这条中线被两条附加线包裹,这两条线通常位于 EMA 的上下两侧,距离为两个标准差。
在本文中,我们旨在从头开始对策略进行实证分析,帮助那些可能考虑使用布林带的读者决定这种策略是否更适合他们。此外,我们将展示如何利用技术指标指导人工智能模型,希望开发出更稳定的交易策略。
我们通过训练两个等价的人工智能模型来实现这一点,这些模型使用线性判别分析算法,并通过时间序列交叉验证对模型进行比较,测试中仅依赖 scikit-learn 库。第一个模型被训练用于简单预测价格是上涨还是下跌,而第二个模型则学习预测价格在布林带划分的四个区域之间的移动。遗憾的是,对于布林带的粉丝来说,我们通过实证观察得出结论:直接预测价格可能比预测布林带创建的四个区域之间的转换更有效。然而,值得注意的是,我们没有使用任何优化技术来设置指标的参数。
本文旨在展示:
- 如何分析比较两种可能的交易策略。
- 如何从零开始在MQL5中实现线性判别分析。
- 如何构建结合人工智能的稳定交易策略。
策略概述及我们的目标
“人工智能”(AI)这个词可能是历史上最具误导性的命名惯例之一。读完本文后,你可能会同意AI是一个误称。作为作者,我对“智能”这个词有疑问。人工智能模型并非以人类意义上的智能存在。相反,它们是优化算法的智能应用。
人工智能模型的主要目标是在一个系统内最小化误差或最大化回报。然而,这些模型得出的解决方案并不总是实用的。例如,一个旨在最小化交易账户损失的人工智能系统可能会得出结论:不进行任何交易是最好的解决方案,因为这样可以保证没有损失。尽管从数学方面来看满足了问题本身,但这种解决方案对交易来说是不切实际的。
作为智能的人工智能实践者,我们必须用精心设计的约束条件来引导我们的模型。在本文中,我们将使用布林带来指导我们的人工智能模型。我们将识别出价格可能处于的四个区域。请注意,在任何给定时间价格只能处于以下这四个区域中的一个。
- 区域1:价格完全高于布林带。
- 区域2:价格高于中带但低于上带。
- 区域3:价格高于下带但低于中带。
- 区域4:价格低于下带。
我们将训练一个模型,用以理解价格在这四个区域之间的转换,并预测价格将移动到的下一个区域。每当价格从一个区域转移到另一个区域时,就会生成交易信号。例如,如果我们的模型预测价格将从区域2移动到区域1,我们将此解释为向上移动,并发起买入订单。我们的模型和EA将完全用原生MQL5实现。
布林带可以在多种交易策略中使用,从趋势跟踪到识别转折点或反转点。从技术上讲,该指标由一条指数移动平均线(EMA)组成,通常用于平滑证券的收盘价。它由两条附加带包围:一条位于EMA的上方,另一条位于下方,每条通常设置为两个标准差。
传统上,布林带用于识别超买和超卖的价格水平。当价格达到上布林带时,它们倾向于回落到中值,这种行为通常也适用于下布林带。这可以被解释为,当证券价格触及下布林带时,其价格被低估了两个标准差,可能会吸引投资者以有吸引力的折扣买入该资产。然而,有时价格可能会猛烈突破布林带并继续强劲趋势。不幸的是,我们的统计分析显示,预测布林带突破可能比预测价格变化更具挑战性。从我们的MetaTrader 5终端获取数据
首先,打开您的MetaTrader5终端,单击上下文菜单中的符号图标,您应该会看到终端上可用的符号列表。
图1:准备从我们的MetaTrader5交易平台获取数据。
然后点击“条形图”窗口,搜索您想要建模的交易品种,选择您希望使用的时间框架。在我们的例子中,我将对GBPUSD的日汇率进行建模。

图2:准备导出我们的数据。
然后点击“导出条形图”按钮,接下来我们将在Python中继续进行分析。
探索性数据分析
让我们可视化布林带与价格水平变化之间的相互作用。
我们将首先导入所需的库。
#Import libraries import pandas as pd import numpy as np import seaborn as sns import pandas_ta as ta然后,我们将读取为实证测试生成的csv文件。请注意,我们传递了参数sep="\t"来表示我们的csv文件是以制表符分隔的。这是MetaTrader5终端的标准输出格式。
#Read in the csv file csv = pd.read_csv("/home/volatily/market_data/GBPUSD_Daily_20160103_20240131.csv",sep="\t")现在让我们定义预测范围。
#Define how far into the future we should forecast look_ahead = 20现在,我们将使用pandas ta库计算数据的布林带。
#Add the Bollinger bands csv.ta.bbands(length=30,std=2,append=True)接下来,我们需要一个列来存储未来的收盘价。
#Add a column to show the future price csv["Future Close"] = csv["Close"].shift(-look_ahead)
现在我们将对数据进行标记。我们将使用两个标签,一个表示价格的变化,另一个表示价格在布林带区域之间的变化。价格的变化将用1表示上涨,用0表示下跌。布林带标签已经在之前定义过了。
#Add the normal target, predicting changes in the close price csv["Price Target"] = 0 csv["Price State"] = 0 #Label the data our conditions #If price depreciated, our label is 0 csv.loc[csv["Close"] < csv["Close"].shift(look_ahead),"Price State"] = 0 csv.loc[csv["Close"] > csv["Future Close"], "Price Target"] = 0 #If price appreciated, our label is 1 csv.loc[csv["Close"] > csv["Close"].shift(look_ahead),"Price State"] = 1 csv.loc[csv["Close"] < csv["Future Close"], "Price Target"] = 1 #Label the Bollinger bands #The label to store the current state of the market csv["Current State"] = -1 #If price is above the upper-band, our label is 1 csv.loc[csv["Close"] > csv["BBU_30_2.0"], "Current State"] = 1 #If price is below the upper-band and still above the mid-band,our label is 2 csv.loc[(csv["Close"] < csv["BBU_30_2.0"]) & (csv["Close"] > csv["BBM_30_2.0"]),"Current State"] = 2 #If price is below the mid-band and still above the low-band,our label is 3 csv.loc[(csv["Close"] < csv["BBM_30_2.0"]) & (csv["Close"] > csv["BBL_30_2.0"]),"Current State"] = 3 #Finally, if price is beneath the low-band our label is 4 csv.loc[csv["Close"] < csv["BBL_30_2.0"], "Current State"] = 4 #Now we can add a column to denote the future state the market will be in csv["State Target"] = csv["Current State"].shift(-look_ahead)
让我们删除所有空条目。
#Let's drop any NaN values csv.dropna(inplace=True)
现在我们已经准备好开始可视化我们的数据,首先使用箱线图来展示价格水平的变化。在y轴上,将显示收盘价,而在x轴上,将有两个值。x轴上的第一个值表示数据中价格下跌的情况,标记为 0。在0值内,您会看到两个箱线图。第一个蓝色的箱线图表示价格下跌了20个K线,并且在接下来的20个K线中会延续下跌的情况。橙色的箱线图表示价格下跌了20个K线,但在接下来的20个K线中会开始上涨的情况。请注意,在我们收集的数据中,似乎只要价格水平跌破1.1,就总会反弹。相反,x 轴上的1值上方也有两个箱线图。第一个蓝色的箱线图总结了价格上涨后下跌的情况,而第二个橙色的箱线图总结了价格持续上涨的情况。
请注意,对于1值(换句话说,当价格上涨20个K线时),蓝色箱线图的尾部比橙色箱线图的尾部更长。这可能表明,每当英镑兑美元汇率上涨接近1.5水平时,它倾向于下跌;而在0列中,当汇率下跌到接近1.1水平时,价格似乎有反转并开始上涨的倾向。
#Notice that the tails of the box plots have regions where they stop overlapping these zones may guide us as boundaries sns.boxplot(data=csv,x="Price State",y="Close",hue="Price Target")

图3:可视化价格水平的变化。
我们也可以使用布林带定义的状态来进行类似的可视化。与之前一样,收盘价将显示在y轴上,而价格在布林带内的当前位置将通过x轴上的四个值来标记。请注意,箱线图的尾部有一些自然不重叠的区域。这些区域可能可以作为潜在的分类边界。例如,观察到当价格处于状态4(即完全低于布林带)且接近1.1水平时,价格似乎总是会反弹。
#Notice that the tails of the box plots have regions where they stop overlapping these zones may guide us as boundaries sns.boxplot(data=csv,x="Current State",y="Close",hue="Price Target")
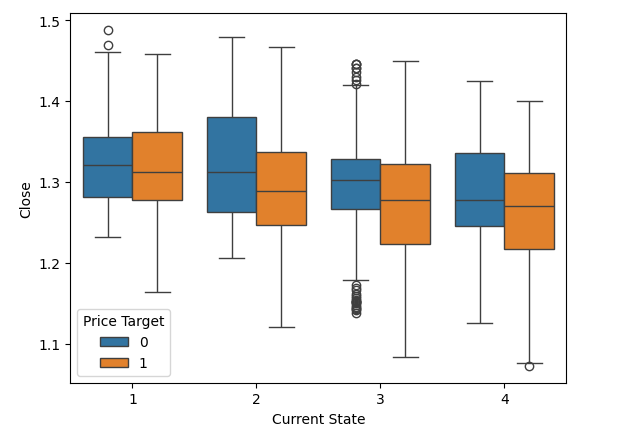
图 4:可视化布林带四个区域的价格行为。
此外,我们还可以使用箱线图来可视化价格在布林带四个状态之间的转换。例如,下面的箱线图以收盘价为y轴,x轴上有四个值,分别表示布林带划分的四个区域。每个箱线图总结了价格在出现于该区域后转换到的下一个区域。让我们一起解读这些数据。请注意,第一个值(状态1)只有三个箱线图。这意味着从状态1出发,价格只会转换到三个可能的状态:它要么保持在状态1,要么转换到状态2或状态3。
#Notice that the tails of the box plots have regions where they stop overlapping these zones may guide us as boundaries sns.boxplot(data=csv,x="Current State",y="Close",hue="State Target")
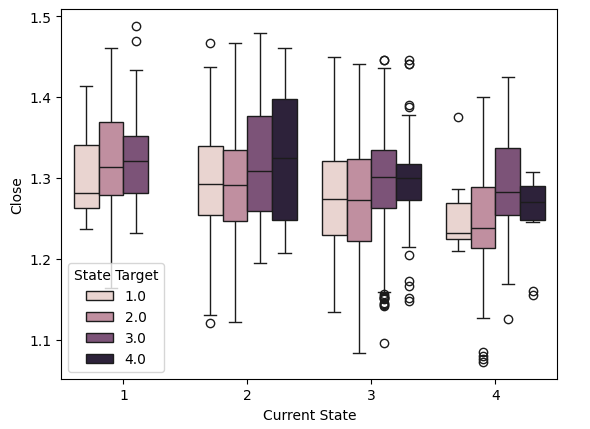
图 5:可视化四个区域的价格行为。
#we have very poor separation in the data sns.catplot(data=csv,x="Price State",y="Close",hue="Price Target")
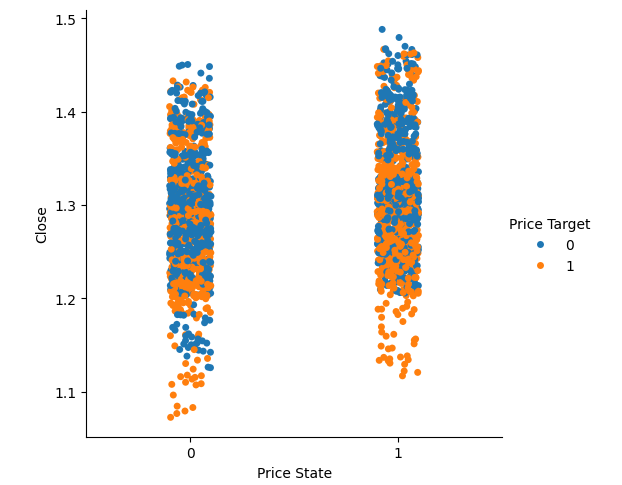
图 6:可视化数据集中的分离情况。
我们也可以使用布林带定义的四个状态来进行类似的可视化。同样地,我们观察到蓝色和橙色的点在极端价格水平时分离得最为明显。
#Visualizing the separation of data in the Bollinger band zones sns.catplot(data=csv,x="Current State",y="Close",hue="Price Target")
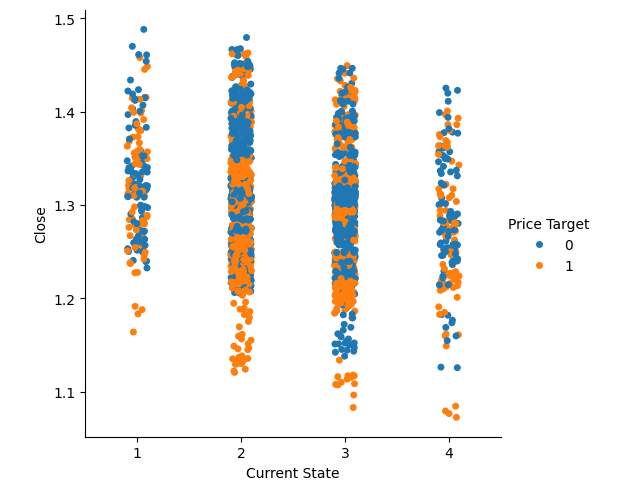
图 7:可视化布林带区域数据的分离情况。
现在我们可以创建一个散点图,以收盘价为x轴,未来的收盘价为y轴。我们将根据价格在过去20个K线期间是上涨还是下跌,将点涂成橙色或蓝色。想象一下从图表的左下角到右上角画一条金色的线。所有位于这条金色线以上的点都表示价格在未来20个K线期间最终上涨的情况,无论它在过去20个K线期间是下跌(蓝色)还是上涨(橙色)。请注意,金色线的两侧都有蓝色和橙色的点混合在一起。
此外,观察到如果我们假设在收盘价为1.3的位置画一条红色的线,会有很多蓝色和橙色的点触及这条线。这意味着除了当前收盘价之外,还有其他变量会影响未来的收盘价。另一种解释这些观察结果的方式是,由于相同的输入值可能会导致不同的输出值,这表明我们的数据集存在噪声!
#Notice that using the price target gives us beautiful separation in the data set sns.scatterplot(data=csv,x="Close",y="Future Close",hue="Price Target")
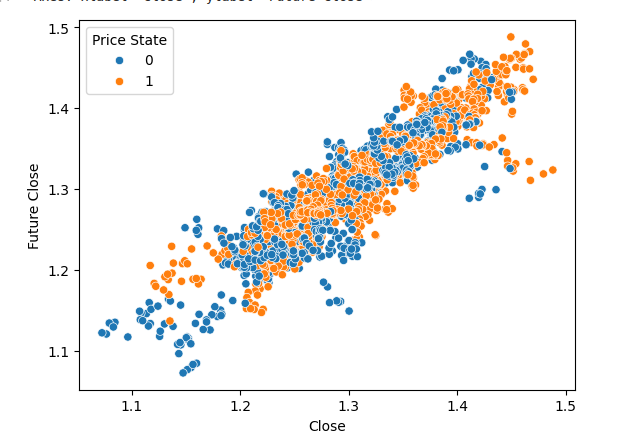
图 8:我们的数据集几乎没有自然分离。
现在我们将使用布林带的目标状态来为散点图上色,进行相同的可视化。请注意,当我们使用布林带时,在我们的数据集中的分离效果非常差。从视觉效果来看,甚至比我们仅使用价格本身时获得的分离效果还要糟糕。
#Using the Bollinger bands to define states, however, gives us rather mixed separation sns.scatterplot(data=csv,x="Close",y="Future Close",hue="Current State")
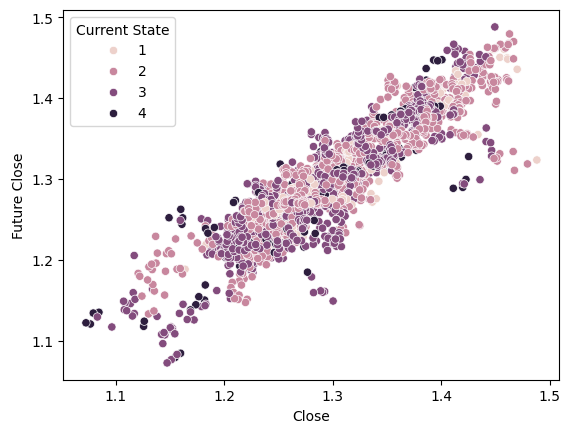
图 9:可视化布林带区域所创建的数据集的分离情况。
现在,让我们进行分析测试,以确定我们在预测价格水平的变化与预测布林带状态的变化之间,哪一个能获得更高的准确性。首先,我们需要导入必要的库。
#Now let us compare our accuracy forecasting the original price target and the new Bollinger bands target from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis from sklearn.model_selection import TimeSeriesSplit from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
接下来,我们将定义我们的时间序列交叉验证参数。第一个参数splits,指定了从我们的数据中创建的分区数量。第二个参数gap,决定了每个分区之间的间隔大小。这个间隔至少应该和我们的预测范围一样大。
#Now let us define the cross validation parameters splits = 10 gap = look_ahead
现在我们可以创建时间序列对象,它将为我们提供训练集和测试集的适当索引。在我们的实例中,将生成10对索引,用于训练和评估我们的模型。
#Now create the cross validation object
tscv = TimeSeriesSplit(n_splits=splits,gap=gap)
接下来,我们将创建一个数据框(DataFrame),用于存储我们模型在预测每个目标时的准确性。
#We need a dataframe to store the accuracy associated with each target target_accuracy = pd.DataFrame(index=np.arange(0,splits),columns=["Price Target Accuracy","New Target Accuracy"])
现在我们将定义模型输入。
#Define the inputs predictors = ["Open","High","Low","Close"] target = "Price Target"
现在我们将执行交叉验证测试。
#Now let us perform the cross validation for i,(train,test) in enumerate(tscv.split(csv)): #First initialize the model model = LinearDiscriminantAnalysis() #Now train the model model.fit(csv.loc[train[0]:train[-1],predictors],csv.loc[train[0]:train[-1],target]) #Now record the accuracy target_accuracy.iloc[i,0] = accuracy_score(csv.loc[test[0]:test[-1],target],model.predict(csv.loc[test[0]:test[-1],predictors]))
现在我们终于可以分析测试结果了。
target_accuracy

图 10:我们的模型在直接预测价格变化时的表现更好。
正如之前提到的,我们的测试显示,我们的模型在预测价格水平方面比预测布林带转换更有效。然而,需要注意的是,平均而言,这两种策略并没有显著差异。
接下来,我们将把这种策略用MQL5代码实现,并对其进行回测,看看它在真实市场数据上的表现如何。
实施该策略
首先,我们将导入我们在整个程序中将要使用的必要库。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Target Engineering.mq5 | //| Gamuchirai Zororo Ndawana | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Gamuchirai Zororo Ndawana" #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Libraries we need | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ /* This Expert Advisor will implement the Linear Discriminant Anlysis algorithm to help us successfully trade Bollinger Band Breakouts. Gamuchirai Zororo Ndawana Selebi Phikwe Botswana Wednesday 10 July 2024 15:42 */ #include <Trade/Trade.mqh>//Trade class CTrade Trade;
接下来,我们将定义用户可配置的输入,如布林带周期和标准差。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Input variables | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ input double bband_deviation = 2.0;//Bollinger Bands standard deviation input int bband_period = 60; //Bollinger Bands Period input int look_ahead = 10; //How far into the future should we forecast? int input lot_multiple = 1; //How many times bigger than minimum lot? int input fetch = 200;//How much data should we fetch? input double stop_loss_values = 1;//Stop loss values
随后,我们将定义会在应用程序中使用的全局变量。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Global variables | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int bband_handler;//Technical Indicator Handlers vector bband_high_reading = vector::Ones(fetch);//Bollinger band high reading vector bband_mid_reading = vector::Ones(fetch);//Bollinger band mid reading vector bband_low_reading = vector::Ones(fetch);//Bollinger band low reading double minimum_volume;//The smallest contract size allowed double ask_price;//Ask double bid_price;//Bid vector input_data = vector::Zeros(fetch);//All our input data will be kept in vectors int training_output_array[];//Our output data will be stored in a vector vector output_data = vector::Zeros(fetch); double variance;//This is the variance of our input data int classes = 4;//The total number of output classes we have vector mean_values = vector::Zeros(classes);//This vector will store the mean value for each class vector probability_values = vector::Zeros(classes);//This vector will store the prior probability the target will belong each class vector total_class_count = vector::Zeros(classes);//This vector will count the number of times each class was the target bool model_trained = false;//Has our model been trained? bool training_procedure_running = false;//Have we started the training process? int forecast = 0;//Our model's forecast double discriminant_values[4];//The discriminant function int current_state = 0;//The current state of the system
接下来,我们需要定义EA的初始化函数。在该函数中,我们将初始化布林带指标并获取重要的市场数据。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- Initialize the bollinger bands bband_handler = iBands(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,bband_period,0,bband_deviation,PRICE_CLOSE); //--- Market data minimum_volume = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,SYMBOL_VOLUME_MIN); //--- End of initilization return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
下面,我们将定义基本的辅助函数,将代码分解为更小、更易于管理的片段。我们将创建的第一个函数用于更新我们的市场数据。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|This function will update the price and other technical data | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void update_technical_data(void) { //--- Update the bid and ask prices ask_price = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,SYMBOL_ASK); bid_price = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,SYMBOL_BID); }
随后,我们需要实现一个协调初始化过程的函数。这个函数将确保我们按正确的顺序获取训练数据、拟合我们的模型,并开始进行预测。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|This function will start training our model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void model_initialize(void) { //--- First we have to fetch the input and output data Print("Initializing the model"); int input_start = 1 + (look_ahead * 2); int output_start = 1+ look_ahead; fetch_input_data(input_start,fetch); fetch_output_data(output_start,fetch); //--- Fit the model fit_lda_model(); }
接下来,我们将定义负责获取输入数据以训练我们模型的函数。需要注意的是,模型的输入将包括市场的当前状态——具体来说,就是市场当前所处的区域。然后,模型将预测市场会移动到的下一个区域。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|This function will fetch the inputs for our model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void fetch_input_data(int f_start,int f_fetch) { //--- This function will fetch input data for our model Print("Fetching input data"); //--- The input for our model will be the current state of the market //--- To know the current state of the market, we have to first update our indicator readings bband_mid_reading.CopyIndicatorBuffer(bband_handler,0,f_start,f_fetch); bband_high_reading.CopyIndicatorBuffer(bband_handler,1,f_start,f_fetch); bband_low_reading.CopyIndicatorBuffer(bband_handler,2,f_start,f_fetch); vector historical_prices; historical_prices.CopyRates(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,f_start,f_fetch); //--- Reshape the input data input_data.Resize(f_fetch); //--- Now we will input the state of the market for(int i = 0; i < f_fetch;i++) { //--- Are we above the bollinger bands entirely? if(historical_prices[i] > bband_high_reading[i]) { input_data[i] = 1; } //--- Are we between the upper and mid band? else if((historical_prices[i] < bband_high_reading[i]) && (historical_prices[i] > bband_mid_reading[i])) { input_data[i] = 2; } //--- Are we between the mid and lower band? else if((historical_prices[i] < bband_mid_reading[i]) && (historical_prices[i] > bband_low_reading[i])) { input_data[i] = 3; } //--- Are we below the bollinger bands entirely? else if(historical_prices[i] < bband_low_reading[i]) { input_data[i] = 4; } } //--- Show the input data Print(input_data); }
接下来,我们需要一个函数来获取我们模型的输出数据。这项任务比获取输入数据要复杂得多。我们不仅要记录价格最终所在的区域,还要跟踪每个区域作为输出的次数。这个计数对于后续估计我们的线性判别分析(LDA)模型的参数至关重要。
从这一点开始,我们已经准备好拟合我们的LDA模型。拟合模型有多种方法可供选择;现在,我们将专注于其中一种特定的方法。
//+---------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|Fetch the output data for our model | //+---------------------------------------------------------------------+ void fetch_output_data(int f_start,int f_fetch) { //--- The output for our model will be the state of the market //--- To know the state of the market, we have to first update our indicator readings Print("Fetching output data"); bband_mid_reading.CopyIndicatorBuffer(bband_handler,0,f_start,(f_fetch)); bband_high_reading.CopyIndicatorBuffer(bband_handler,1,f_start,(f_fetch)); bband_low_reading.CopyIndicatorBuffer(bband_handler,2,f_start,(f_fetch)); vector historical_prices; historical_prices.CopyRates(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,f_start,f_fetch); //--- First we have to ensure that the class count has been reset total_class_count[0] = 0; total_class_count[1] = 0; total_class_count[2] = 0; total_class_count[3] = 0; //--- Now we need to resize the matrix ArrayResize(training_output_array,f_fetch); //--- Now we will input the state of the market to our output vector for(int i =0 ; i < f_fetch;i++) { //--- Are we above the bollinger bands entirely? if(historical_prices[i] > bband_high_reading[i]) { training_output_array[i] = 1; total_class_count[0] += 1; } //--- Are we between the upper and mid band? else if((historical_prices[i] < bband_high_reading[i]) && (historical_prices[i] > bband_mid_reading[i])) { training_output_array[i] = 2; total_class_count[1] += 1; } //--- Are we between the mid and lower band? else if((historical_prices[i] < bband_mid_reading[i]) && (historical_prices[i] > bband_low_reading[i])) { training_output_array[i] = 3; total_class_count[2] += 1; } //--- Are we below the bollinger bands entirely? else if(historical_prices[i] < bband_low_reading[i]) { training_output_array[i] = 4; total_class_count[3] += 1; } } //--- Show the output data Print("Final state of output vector"); ArrayPrint(training_output_array); //--- Show the total number of times each class appeared as the target. Print(total_class_count); }
这个过程有些复杂,需要详细解释。一开始,我们计算每个输出类别对应的输入值的总和。例如,对于目标值为1的每一个实例,我们计算所有映射到输出值为1的输入值的总和,以此类推,为每个输出类别分别计算。随后,我们计算每个类别的输入值X的均值。如果有多个输入,我们会计算每个输入的均值。接下来,我们根据训练集数据确定每个类别作为实际目标出现的概率。接下来,我们计算每个类别y的输入值X的方差。最后,我们更新标识以表明训练过程已经完成。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|Fit the LDA model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void fit_lda_model(void) { //--- To fit the LDA model, we first need to know the mean value for each our inputs for each of our 4 classes double sum_class_one = 0; double sum_class_two = 0; double sum_class_three = 0; double sum_class_four = 0; //--- In this case we only have 1 input for(int i = 0; i < fetch;i++) { //--- Class 1 if(training_output_array[i] == 1) { sum_class_one += input_data[i]; } //--- Class 2 else if(training_output_array[i] == 2) { sum_class_two += input_data[i]; } //--- Class 3 else if(training_output_array[i] == 3) { sum_class_three += input_data[i]; } //--- Class 4 else if(training_output_array[i] == 4) { sum_class_four += input_data[i]; } } //--- Show the sums Print("Class 1: ",sum_class_one," Class 2: ",sum_class_two," Class 3: ",sum_class_three," Class 4: ",sum_class_four); //--- Calculate the mean value for each class mean_values[0] = sum_class_one / fetch; mean_values[1] = sum_class_two / fetch; mean_values[2] = sum_class_three / fetch; mean_values[3] = sum_class_four / fetch; Print("Mean values"); Print(mean_values); //--- Now we need to calculate class probabilities for(int i=0;i<classes;i++) { probability_values[i] = total_class_count[i] / fetch; } Print("Class probability values"); Print(probability_values); //--- Calculating the variance Print("Calculating the variance"); //--- Next we need to calculate the variance of the inputs within each class of y. //--- This process can be simplified into 2 steps //--- First we calculate the difference of each instance of x from the group mean. double squared_difference[4]; for(int i =0; i < fetch;i++) { //--- If the output value was 1, find the input value that created the output //--- Calculate how far that value is from it's group mean and square the difference if(training_output_array[i] == 1) { squared_difference[0] = MathPow((input_data[i]-mean_values[0]),2); } else if(training_output_array[i] == 2) { squared_difference[1] = MathPow((input_data[i]-mean_values[1]),2); } else if(training_output_array[i] == 3) { squared_difference[2] = MathPow((input_data[i]-mean_values[2]),2); } else if(training_output_array[i] == 4) { squared_difference[3] = MathPow((input_data[i]-mean_values[3]),2); } } //--- Show the squared difference values Print("Squared difference value for each output value of y"); ArrayPrint(squared_difference); //--- Next we calculate the variance as the average squared difference from the mean variance = (1.0/(fetch - 4.0)) * (squared_difference[0] + squared_difference[1] + squared_difference[2] + squared_difference[3]); Print("Variance: ",variance); //--- Update our flags to denote the model has been trained model_trained = true; training_procedure_running = false; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
为了用我们的模型进行预测,我们首先从市场获取最新的输入数据。利用这些输入数据,我们为每个可能的类别计算判别函数。判别函数值最高的类别将是我们的预测类别。
在MQL5中,数组提供了一个名为ArrayMaximum() 的有用函数,它返回一维数组中最大值的索引。由于数组是从0开始索引的,所以我们将ArrayMaximum() 的结果加1,以获得预测的类别。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|This function will obtain forecasts from our model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int model_forecast(void) { //--- First we need to fetch the most recent input data fetch_input_data(0,1); //--- Update the current state of the system current_state = input_data[0]; //--- We need to calculate the discriminant function for each class //--- The predicted class is the one with the largest discriminant function Print("Calculating discriminant values."); for(int i = 0; i < classes; i++) { discriminant_values[i] = (input_data[0] * (mean_values[i]/variance) - (MathPow(mean_values[i],2)/(2*variance)) + (MathLog(probability_values[i]))); } ArrayPrint(discriminant_values); return(ArrayMaximum(discriminant_values) + 1); }
在从我们的模型获得预测之后,下一步是对其进行解释并据此做出决策。正如前面提到的,我们的交易信号是在模型预测价格将移动到不同区域时生成的:
- 如果预测显示价格将从区域1移动到区域2,这将触发一个卖出信号。
- 相反,预测显示价格将从区域4移动到区域3,则代表一个买入信号。
- 然而,如果预测表明价格将保持在同一个区域(例如,从区域1到区域1),这不会产生入场信号。
//+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|This function will interpret out model's forecast and execute trades| //+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ void find_entry(void) { //--- If the model's forecast is not equal to the current state then we are interested //--- Otherwise whenever the model forecasts that the state will remain the same //--- We are uncertain whether price levels will rise or fall if(forecast != current_state) { //--- If the model forecasts that we will move from a small state to a greater state //--- That is from 1 to 2 or from 2 to 4 then that is a down move if(forecast > current_state) { Trade.Sell(minimum_volume * lot_multiple,_Symbol,bid_price,(bid_price + stop_loss_values),(bid_price - stop_loss_values)); } //--- Otherwise we have a buy setup else { Trade.Buy(minimum_volume * lot_multiple,_Symbol,ask_price,(ask_price - stop_loss_values),(ask_price +stop_loss_values)); } } //--- Otherwise we do not have an entry signal from our model }
最后,我们的OnTick()事件处理程序负责管理事件流程,并确保只有在我们的模型已经完成训练,并且满足其他的交易条件时,才会进行交易。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { //--- We must always update market data update_technical_data(); //--- First we must ensure our model has been trained switch(model_trained) { //--- Our model has been trained case(true): //--- If we have no open positions, let's obtain a forecast from our model if(PositionsTotal() == 0) { //--- Obtaining a forecast forecast = model_forecast(); Comment("Model forecast: ",forecast); //--- Find an entry setup find_entry(); } break; //--- End of case 1 //--- Our model has not been trained default: //--- We haven't started the training procedure! if(!training_procedure_running) { Print("Our model has not been trained, starting the training procedure now."); //--- Initialize the model model_initialize(); } break; //--- End of default case } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
图 11:我们的交易系统正在运行。
局限性
到目前为止,我们的策略面临一个显著的局限性:其难以解释。当我们的模型预测价格将保持在同一个区域时,我们无法明确价格是会上涨还是下跌。这种权衡源于我们决定将市场状态划分为四个不同的区域,这提高了准确性,但与直接预测价格走势相比,牺牲了透明度。此外,这种方法产生的交易信号较少,因为我们必须等待模型预测区域变化后才能采取行动。
结论
总而言之,我们的策略利用了机器学习的优势,特别是线性判别分析(LDA),结合布林带来生成交易信号。尽管这种方法提高了准确性,但牺牲了一些透明度。概括而言,交易者可能更适合预测价格的变化,而不是预测布林带的突破。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/15336
 自定义指标:为净额结算账户绘制部分入场、出场和反转交易
自定义指标:为净额结算账户绘制部分入场、出场和反转交易
 从基础到中级:变量(II)
从基础到中级:变量(II)
 神经网络变得简单(第 92 部分):频域和时域中的自适应预测
神经网络变得简单(第 92 部分):频域和时域中的自适应预测
 结合基本面和技术分析策略在MQL5中的实现(适合初学者)
结合基本面和技术分析策略在MQL5中的实现(适合初学者)