GMDH (The Group Method of Data Handling):MQL5で組合せアルゴリズムを実装する
はじめに
GMDHの組合せアルゴリズム(しばしばCOMBIと呼ばれる)はGMDHの基本形であり、ファミリー内のより複雑なアルゴリズムの基礎として機能します。多層反復アルゴリズム(MIA)と同じように、変数のセットに対する観測を含む行列として表現される入力データサンプルで動作します。データサンプルは訓練サンプルとテストサンプルの2つに分けられます。訓練サブサンプルは多項式の係数を推定するために使用され、テストサブサンプルは選択された基準の最小値に基づいて最適モデルの構造を選択するために使用されます。この記事では、COMBIアルゴリズムの計算について説明します。また、前回の記事で紹介したGmdhModelクラスを拡張することで、MQL5での実装を紹介します。後ほど、密接に関連する組合せ選択アルゴリズムとそのMQL5実装についても説明します。そして最後に、ビットコインの日次価格の予測モデルを構築することで、GMDHアルゴリズムの実用的なアプリケーションを提供することで締めくくります。
COMBIアルゴリズム
MIAとCOMBIの根本的な違いは、そのネットワーク構造にあります。MIAが多層構造であるのとは対照的に、COMBIは単層構造です。
この層のノード数は入力数によって決まります。ここで、各ノードは、すべての入力の1つ以上によって定義されるモデル候補を表します。説明のために、2つの入力変数で定義される、モデル化したいシステムの例を考えてみましょう。COMBIアルゴリズムを適用し、これらの変数のすべての可能な組合わせを使用して候補モデルを構築します。可能な組合わせの数は次の式で与えられます。
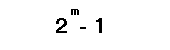
ここで
- m:入力変数の数
これらの組合わせのそれぞれについて、候補モデルが生成されます。第1層のノードで評価されるモデル候補は以下で与えられます。
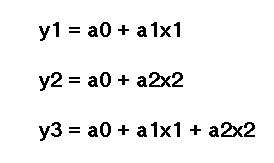
ここで
- a:係数(a1:1番目の係数、a2:2番目の係数)
- x:入力変数(x1:1番目の入力変数または予測変数、x2:2番目の入力変数)
このプロセスでは、連立一次方程式を解いて、候補モデルの係数の推定値を導き出します。各モデルの性能基準は、データを最もよく記述する最終モデルを選択するために使用されます。
COMBI MQL5の実装
COMBIアルゴリズムを実装するコードは、前回の記事で説明したGmdhModel基本クラスに依存しています。また、linearmodel.mqhで宣言されている中間クラスLinearModelにも依存しています。COMBIメソッドの最も基本的な特徴は、COMBIモデルの線形性であることだと要約されます。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| linearmodel.mqh | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #include "gmdh.mqh" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class implementing the general logic of GMDH linear algorithms | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class LinearModel:public GmdhModel { protected: vector calculatePrediction(vector& x) { if(x.Size()<ulong(inputColsNumber)) return vector::Zeros(ulong(inputColsNumber)); matrix modifiedX(1,x.Size()+ 1); modifiedX.Row(x,0); modifiedX[0][x.Size()] = 1.0; vector comb = bestCombinations[0][0].combination(); matrix xx(1,comb.Size()); for(ulong i = 0; i<xx.Cols(); ++i) xx[0][i] = modifiedX[0][ulong(comb[i])]; vector c,b; c = bestCombinations[0][0].bestCoeffs(); b = xx.MatMul(c); return b; } virtual matrix xDataForCombination(matrix& x, vector& comb) override { matrix out(x.Rows(), comb.Size()); for(ulong i = 0; i<out.Cols(); i++) out.Col(x.Col(int(comb[i])),i); return out; } virtual string getPolynomialPrefix(int levelIndex, int combIndex) override { return "y="; } virtual string getPolynomialVariable(int levelIndex, int coeffIndex, int coeffsNumber, vector& bestColsIndexes) override { return ((coeffIndex != coeffsNumber - 1) ? "x" + string(int(bestColsIndexes[coeffIndex]) + 1) : ""); } public: LinearModel(void) { } vector predict(vector& x, int lags) override { if(lags <= 0) { Print(__FUNCTION__," lags value must be a positive integer"); return vector::Zeros(1); } if(!training_complete) { Print(__FUNCTION__," model was not successfully trained"); return vector::Zeros(1); } vector expandedX = vector::Zeros(x.Size() + ulong(lags)); for(ulong i = 0; i<x.Size(); i++) expandedX[i]=x[i]; for(int i = 0; i < lags; ++i) { vector vect(x.Size(),slice,expandedX,ulong(i),x.Size()+ulong(i)-1); vector res = calculatePrediction(vect); expandedX[x.Size() + i] = res[0]; } vector vect(ulong(lags),slice,expandedX,x.Size()); return vect; } }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
combi.mqhファイルにはCOMBIクラスの定義が含まれています。LinearModelを継承し、モデルをフィッティングするためのfit()メソッドを定義しています。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| combi.mqh | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #include "linearmodel.mqh" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class implementing combinatorial COMBI algorithm | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class COMBI:public LinearModel { private: Combination getBest(CVector &combinations) { double proxys[]; int best[]; ArrayResize(best,combinations.size()); ArrayResize(proxys,combinations.size()); for(int k = 0; k<combinations.size(); k++) { best[k]=k; proxys[k]=combinations[k].evaluation(); } MathQuickSortAscending(proxys,best,0,int(proxys.Size()-1)); return combinations[best[0]]; } protected: virtual void removeExtraCombinations(void) override { CVector2d realBestCombinations; CVector n; Combination top; for(int i = 0 ; i<bestCombinations.size(); i++) { top = getBest(bestCombinations[i]); n.push_back(top); } top = getBest(n); CVector sorted; sorted.push_back(top); realBestCombinations.push_back(sorted); bestCombinations = realBestCombinations; } virtual bool preparations(SplittedData &data, CVector &_bestCombinations) override { lastLevelEvaluation = DBL_MAX; return (bestCombinations.push_back(_bestCombinations) && ulong(level+1) < data.xTrain.Cols()); } void generateCombinations(int n_cols,vector &out[]) override { GmdhModel::nChooseK(n_cols,level,out); return; } public: COMBI(void):LinearModel() { modelName = "COMBI"; } bool fit(vector &time_series,int lags,double testsize=0.5,CriterionType criterion=stab) { if(lags < 1) { Print(__FUNCTION__," lags must be >= 1"); return false; } PairMVXd transformed = timeSeriesTransformation(time_series,lags); SplittedData splited = splitData(transformed.first,transformed.second,testsize); Criterion criter(criterion); int pAverage = 1; double limit = 0; int kBest = pAverage; if(validateInputData(testsize, pAverage, limit, kBest)) return false; return GmdhModel::gmdhFit(splited.xTrain, splited.yTrain, criter, kBest, testsize, pAverage, limit); } bool fit(matrix &vars,vector &targets,double testsize=0.5,CriterionType criterion=stab) { if(vars.Cols() < 1) { Print(__FUNCTION__," columns in vars must be >= 1"); return false; } if(vars.Rows() != targets.Size()) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " vars dimensions donot correspond with targets"); return false; } SplittedData splited = splitData(vars,targets,testsize); Criterion criter(criterion); int pAverage = 1; double limit = 0; int kBest = pAverage; if(validateInputData(testsize, pAverage, limit, kBest)) return false; return GmdhModel::gmdhFit(splited.xTrain, splited.yTrain, criter, kBest, testsize, pAverage, limit); } }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
COMBIクラスの使用
COMBIクラスを使用したデータセットへのモデルのフィッティングは、MIAクラスの適用とまったく同じです。インスタンスを作成し、fit()メソッドを呼び出します。これはスクリプトCOMBI_test.mq5と COMBI_Multivariable_test.mq5で示されています。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| COMBI_test.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #property script_show_inputs #include <GMDH\combi.mqh> input int NumLags = 2; input int NumPredictions = 6; input CriterionType critType = stab; input double DataSplitSize = 0.33; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- vector tms = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12}; if(NumPredictions<1) { Alert("Invalid setting for NumPredictions, has to be larger than 0"); return; } COMBI combi; if(!combi.fit(tms,NumLags,DataSplitSize,critType)) return; string modelname = combi.getModelName()+"_"+EnumToString(critType)+"_"+string(DataSplitSize); combi.save(modelname+".json"); vector in(ulong(NumLags),slice,tms,tms.Size()-ulong(NumLags)); vector out = combi.predict(in,NumPredictions); Print(modelname, " predictions ", out); Print(combi.getBestPolynomial()); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
どちらも、以前の記事で紹介したMIAアルゴリズムの適用方法を示すスクリプト例で使用したのと同じデータセットにCOMBIアルゴリズムを適用します。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| COMBI_Multivariable_test.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #property script_show_inputs #include <GMDH\combi.mqh> input CriterionType critType = stab; input double DataSplitSize = 0.33; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- matrix independent = {{1,2,3},{3,2,1},{1,4,2},{1,1,3},{5,3,1},{3,1,9}}; vector dependent = {6,6,7,5,9,13}; COMBI combi; if(!combi.fit(independent,dependent,DataSplitSize,critType)) return; string modelname = combi.getModelName()+"_"+EnumToString(critType)+"_"+string(DataSplitSize)+"_multivars"; combi.save(modelname+".json"); matrix unseen = {{8,6,4},{1,5,3},{9,-5,3}}; for(ulong row = 0; row<unseen.Rows(); row++) { vector in = unseen.Row(row); Print("inputs ", in, " prediction ", combi.predict(in,1)); } Print(combi.getBestPolynomial()); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
COMBI_test.mq5の出力を見ると、フィッティングされた多項式の複雑さをMIAアルゴリズムで生成されたものと比較することができます。以下は、時系列データセットと多変量データセットそれぞれの多項式です。
LR 0 14:54:15.354 COMBI_test (BTCUSD,D1) COMBI_stab_0.33 predictions [13,14,15,16,17,18.00000000000001] PN 0 14:54:15.355 COMBI_test (BTCUSD,D1) y= 1.000000e+00*x1 + 2.000000e+00 CI 0 14:54:29.864 COMBI_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) inputs [8,6,4] prediction [18.00000000000001] QD 0 14:54:29.864 COMBI_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) inputs [1,5,3] prediction [9] QQ 0 14:54:29.864 COMBI_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) inputs [9,-5,3] prediction [7.00000000000001] MM 0 14:54:29.864 COMBI_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) y= 1.000000e+00*x1 + 1.000000e+00*x2 + 1.000000e+00*x3 - 7.330836e-15
次に、MIA法によって明らかになった多項式です。
JQ 0 14:43:07.969 MIA_Test (Step Index 500,M1) MIA_stab_0.33_1_0.0 predictions [13.00000000000001,14.00000000000002,15.00000000000004,16.00000000000005,17.0000000000001,18.0000000000001] IP 0 14:43:07.969 MIA_Test (Step Index 500,M1) y = - 9.340179e-01*x1 + 1.934018e+00*x2 + 3.865363e-16*x1*x2 + 1.065982e+00 II 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) inputs [1,2,4] prediction [6.999999999999998] CF 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) inputs [1,5,3] prediction [8.999999999999998] JR 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) inputs [9,1,3] prediction [13.00000000000001] NP 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) f1_1 = 1.071429e-01*x1 + 6.428571e-01*x2 + 4.392857e+00 LR 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) f1_2 = 6.086957e-01*x2 - 8.695652e-02*x3 + 4.826087e+00 ME 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) f1_3 = - 1.250000e+00*x1 - 1.500000e+00*x3 + 1.125000e+01 DJ 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) IP 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) f2_1 = 1.555556e+00*f1_1 - 6.666667e-01*f1_3 + 6.666667e-01 ER 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) f2_2 = 1.620805e+00*f1_2 - 7.382550e-01*f1_3 + 7.046980e-01 ES 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) f2_3 = 3.019608e+00*f1_1 - 2.029412e+00*f1_2 + 5.882353e-02 NH 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) CN 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) f3_1 = 1.000000e+00*f2_1 - 3.731079e-15*f2_3 + 1.155175e-14 GP 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) f3_2 = 8.342665e-01*f2_2 + 1.713326e-01*f2_3 - 3.359462e-02 DO 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) OG 0 14:52:59.698 MIA_Multivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) y = 1.000000e+00*f3_1 + 3.122149e-16*f3_2 - 1.899249e-15
MIAモデルが複雑なのに対し、COMBIモデルはこのシリーズと同じように複雑ではありません。この方法の線形的な性質の反映です。これは、スクリプトCOMBI_Multivariable_test.mq5の出力からも確認できます。このスクリプトは、入力変数と対応する出力例を提供することで、3つの数値を合計するモデルを構築する試みです。ここでは、COMBIアルゴリズムがシステムの基本的な特性をうまく推測することができました。
COMBIアルゴリズムの徹底的な探索は、長所であると同時に短所でもあります。肯定的な面では、すべての入力の組合わせを評価することで、データを記述する最適な多項式を確実に見つけることができます。しかし、入力変数が多数ある場合、この広範な探索には計算コストがかかります。訓練時間が長くなる可能性もあります。候補モデルの数は2のm乗から1を引いた数で表され、mが大きいほど、評価する必要がある候補モデルの数が多くなります。この問題に対処するために開発されたのが、組合せ選択アルゴリズムです。
組合せ選択アルゴリズム
組合せ選択アルゴリズム(以下、MULTIと呼ぶ)は、COMBI法を効率の面で改良したものとされています。GMDHの多層アルゴリズムで使用されているものと同様の手順を採用することで、網羅的な探索を回避しています。従って、COMBIアルゴリズムの単層的な性質に対する多層的なアプローチとみなすことができます。
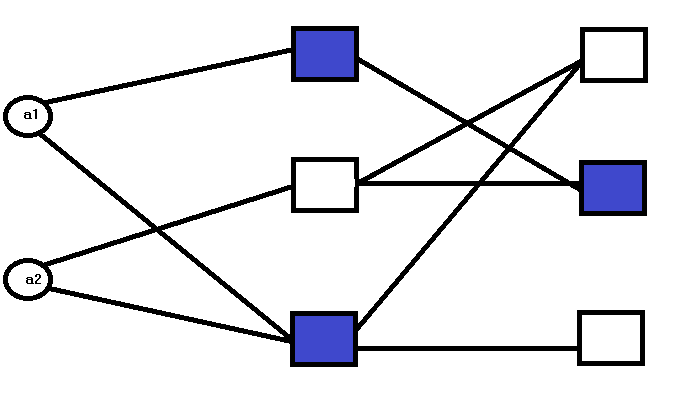
最初の層では、入力変数のいずれかを含むすべてのモデルが推定され、外部基準に従って最適なものが選択され、次の層に渡されます。続く層では、異なる入力変数が選択され、これらの候補モデルに追加されます。このようにして新しい層が追加されるのは、出力の推定精度が向上するかどうかやまだ候補モデルの一部になっていない入力変数が利用可能かどうかによります。これは、可能な層の最大数が入力変数の総数と一致することを意味します。
この方法で候補モデルを評価することは、多くの場合、網羅的な探索を避けることにつながりますが、同時に問題も生じます。アルゴリズムが、データセットを最もよく記述する最適な多項式を見つけられない可能性があります。これは、訓練の段階で、より多くの候補モデルを検討すべきだったことを示します。最適な多項式を導き出すには、ハイパーパラメータを注意深く調整する必要があります。特に、各層で評価される候補モデルの数です。
組合せ選択アルゴリズムの実装
組合せ選択アルゴリズムの実装はmulti.mqhで提供されます。LinearModel を継承したMULTIクラスの定義が含まれています。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| multi.mqh | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #include "linearmodel.mqh" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class implementing combinatorial selection MULTI algorithm | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class MULTI : public LinearModel { protected: virtual void removeExtraCombinations(void) override { CVector2d realBestCombinations; CVector n; n.push_back(bestCombinations[0][0]); realBestCombinations.push_back(n); bestCombinations = realBestCombinations; } virtual bool preparations(SplittedData &data, CVector &_bestCombinations) override { return (bestCombinations.setAt(0,_bestCombinations) && ulong(level+1) < data.xTrain.Cols()); } void generateCombinations(int n_cols,vector &out[]) override { if(level == 1) { nChooseK(n_cols,level,out); return; } for(int i = 0; i<bestCombinations[0].size(); i++) { for(int z = 0; z<n_cols; z++) { vector comb = bestCombinations[0][i].combination(); double array[]; vecToArray(comb,array); int found = ArrayBsearch(array,double(z)); if(int(array[found])!=z) { array.Push(double(z)); ArraySort(array); comb.Assign(array); ulong dif = 1; for(uint row = 0; row<out.Size(); row++) { dif = comb.Compare(out[row],1e0); if(!dif) break; } if(dif) { ArrayResize(out,out.Size()+1,100); out[out.Size()-1] = comb; } } } } } public: MULTI(void):LinearModel() { CVector members; bestCombinations.push_back(members); modelName = "MULTI"; } bool fit(vector &time_series,int lags,double testsize=0.5,CriterionType criterion=stab,int kBest = 3,int pAverage = 1,double limit = 0.0) { if(lags < 1) { Print(__FUNCTION__," lags must be >= 1"); return false; } PairMVXd transformed = timeSeriesTransformation(time_series,lags); SplittedData splited = splitData(transformed.first,transformed.second,testsize); Criterion criter(criterion); if(validateInputData(testsize, pAverage, limit, kBest)) return false; return GmdhModel::gmdhFit(splited.xTrain, splited.yTrain, criter, kBest, testsize, pAverage, limit); } bool fit(matrix &vars,vector &targets,double testsize=0.5,CriterionType criterion=stab,int kBest = 3,int pAverage = 1,double limit = 0.0) { if(vars.Cols() < 1) { Print(__FUNCTION__," columns in vars must be >= 1"); return false; } if(vars.Rows() != targets.Size()) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " vars dimensions donot correspond with targets"); return false; } SplittedData splited = splitData(vars,targets,testsize); Criterion criter(criterion); if(validateInputData(testsize, pAverage, limit, kBest)) return false; return GmdhModel::gmdhFit(splited.xTrain, splited.yTrain, criter, kBest, testsize, pAverage, limit); } }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
MULTIクラスは、おなじみのfit()メソッドでCOMBIクラスと同様に動作します。COMBIクラスと比較して、読者はfit()メソッドのハイパーパラメータがより多くあることに注意する必要があります。kBestとpAverageは、MULTIクラスを適用する際に慎重な調整が必要な2つのパラメータです。データセットへのモデルのフィッティングは、スクリプトMULTI_test.mq5とMULTI_Multivariable_test.mq5で実演されています。コードを以下に示します。
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| MULTI_test.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+----------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #property script_show_inputs #include <GMDH\multi.mqh> input int NumLags = 2; input int NumPredictions = 6; input CriterionType critType = stab; input int Average = 1; input int NumBest = 3; input double DataSplitSize = 0.33; input double critLimit = 0; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- vector tms = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12}; if(NumPredictions<1) { Alert("Invalid setting for NumPredictions, has to be larger than 0"); return; } MULTI multi; if(!multi.fit(tms,NumLags,DataSplitSize,critType,NumBest,Average,critLimit)) return; vector in(ulong(NumLags),slice,tms,tms.Size()-ulong(NumLags)); vector out = multi.predict(in,NumPredictions); Print(" predictions ", out); Print(multi.getBestPolynomial()); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| MULTI_Mulitivariable_test.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #property script_show_inputs #include <GMDH\multi.mqh> input CriterionType critType = stab; input double DataSplitSize = 0.33; input int Average = 1; input int NumBest = 3; input double critLimit = 0; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- matrix independent = {{1,2,3},{3,2,1},{1,4,2},{1,1,3},{5,3,1},{3,1,9}}; vector dependent = {6,6,7,5,9,13}; MULTI multi; if(!multi.fit(independent,dependent,DataSplitSize,critType,NumBest,Average,critLimit)) return; matrix unseen = {{1,2,4},{1,5,3},{9,1,3}}; for(ulong row = 0; row<unseen.Rows(); row++) { vector in = unseen.Row(row); Print("inputs ", in, " prediction ", multi.predict(in,1)); } Print(multi.getBestPolynomial()); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
スクリプトを実行することにより、単純なデータセットから誘導された多項式は、COMBIアルゴリズムを適用して得られたものと全く同じであることがわかります。
IG 0 18:24:28.811 MULTI_Mulitivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) inputs [1,2,4] prediction [7.000000000000002] HI 0 18:24:28.812 MULTI_Mulitivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) inputs [1,5,3] prediction [9] NO 0 18:24:28.812 MULTI_Mulitivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) inputs [9,1,3] prediction [13.00000000000001] PP 0 18:24:28.812 MULTI_Mulitivariable_test (BTCUSD,D1) y= 1.000000e+00*x1 + 1.000000e+00*x2 + 1.000000e+00*x3 - 7.330836e-15 DP 0 18:25:04.454 MULTI_test (BTCUSD,D1) predictions [13,14,15,16,17,18.00000000000001] MH 0 18:25:04.454 MULTI_test (BTCUSD,D1) y= 1.000000e+00*x1 + 2.000000e+00
ビットコイン価格のGMDHモデル
本セクションでは、GMDH法を適用して、日次のビットコイン終値の予測モデルを構築します。これは記事の最後に添付したスクリプトGMDH_Price_Model.mq5で実現されています。デモでは特にビットコインという銘柄を扱っていますが、スクリプトはどのような銘柄や時間枠にも適用できます。スクリプトには、プログラムのさまざまな側面を制御する、ユーザー変更可能なパラメータがいくつかあります。
//--- input parameters input string SetSymbol=""; input ENUM_GMDH_MODEL modelType = Combi; input datetime TrainingSampleStartDate=D'2019.12.31'; input datetime TrainingSampleStopDate=D'2022.12.31'; input datetime TestSampleStartDate = D'2023.01.01'; input datetime TestSampleStopDate = D'2023.12.31'; input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES tf=PERIOD_D1; //time frame input int Numlags = 3; input CriterionType critType = stab; input PolynomialType polyType = linear_cov; input int Average = 10; input int NumBest = 10; input double DataSplitSize = 0.2; input double critLimit = 0; input ulong NumTestSamplesPlot = 20;
これらは以下の表で説明されています。
| 入力パラメータ名 | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| SetSymbol | 訓練データとして使用される終値の銘柄名(空白の場合、スクリプトが適用されるチャートの銘柄が想定される) |
| modeltype | GMDHアルゴリズムの選択を表す列挙 |
| TrainingSampleStartDate | 終値サンプル期間開始日 |
| TrainingSampleStopDate | サンプルの終値の期間の終了日 |
| TestSampleStartDate | サンプル価格外期間の開始日 |
| TestSampleStopDate | サンプル価格外期間の終了日 |
| tf | 適用期間 |
| Numlags | 次の終値を予測するために使用されるラグ値の数 |
| critType | モデル構築プロセスの外部基準 |
| polyType | 訓練中に既存の変数から新しい変数を構成するために使用する多項式タイプ |
| Average | 停止基準の計算で考慮される最良の部分モデルの数 |
| Numbest | 後続層の新しい入力を構築するための、最適な部分モデルの数(MIAモデルの場合) 各層で選択される候補モデルの数(COMBIモデルの場合) |
| DataSplitSize | モデルの評価に使用すべき入力データの割合 |
| critLimit | 訓練を継続するために外部基準を改善すべき最小値 |
| NumTestSamplePlot | 対応する予測値とともに可視化される、サンプル外データセットからのサンプル数 |
スクリプトは、訓練データとして使用する観測の適切なサンプルの選択から始まります。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //get relative shift of IS and OOS sets int trainstart,trainstop, teststart, teststop; trainstart=iBarShift(SetSymbol!=""?SetSymbol:NULL,tf,TrainingSampleStartDate); trainstop=iBarShift(SetSymbol!=""?SetSymbol:NULL,tf,TrainingSampleStopDate); teststart=iBarShift(SetSymbol!=""?SetSymbol:NULL,tf,TestSampleStartDate); teststop=iBarShift(SetSymbol!=""?SetSymbol:NULL,tf,TestSampleStopDate); //check for errors from ibarshift calls if(trainstart<0 || trainstop<0 || teststart<0 || teststop<0) { Print(ErrorDescription(GetLastError())); return; } //---set the size of the sample sets size_observations=(trainstart - trainstop) + 1 ; size_outsample = (teststart - teststop) + 1; //---check for input errors if(size_observations <= 0 || size_outsample<=0) { Print("Invalid inputs "); return; } //---download insample prices for training int try = 10; while(!prices.CopyRates(SetSymbol,tf,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,TrainingSampleStartDate,TrainingSampleStopDate) && try) { try --; if(!try) { Print("error copying to prices ",GetLastError()); return; } Sleep(5000);
終値の別のサンプルがダウンロードされ、予測終値と実際の終値のプロットでモデルのパフォーマンスを可視化するために使用されます。
//---download out of sample prices testing try = 10; while(!testprices.CopyRates(SetSymbol,tf,COPY_RATES_CLOSE|COPY_RATES_TIME|COPY_RATES_VERTICAL,TestSampleStartDate,TestSampleStopDate) && try) { try --; if(!try) { Print("error copying to testprices ",GetLastError()); return; } Sleep(5000); }
スクリプトのユーザー定義パラメータにより、これまで説明し実装してきた3つのGMDHモデルのいずれかを適用することができます。
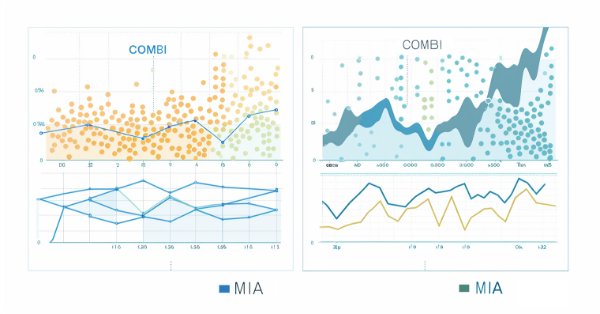
//--- train and make predictions switch(modelType) { case Combi: { COMBI combi; if(!combi.fit(prices,Numlags,DataSplitSize,critType)) return; Print("Model ", combi.getBestPolynomial()); MakePredictions(combi,testprices.Col(0),predictions); } break; case Mia: { MIA mia; if(!mia.fit(prices,Numlags,DataSplitSize,polyType,critType,NumBest,Average,critLimit)) return; Print("Model ", mia.getBestPolynomial()); MakePredictions(mia,testprices.Col(0),predictions); } break; case Multi: { MULTI multi; if(!multi.fit(prices,Numlags,DataSplitSize,critType,NumBest,Average,critLimit)) return; Print("Model ", multi.getBestPolynomial()); MakePredictions(multi,testprices.Col(0),predictions); } break; default: Print("Invalid GMDH model type "); return; } //---
このプログラムは、予測された終値と、サンプル外のデータセットから得られた実際の値をプロットして表示することで終了します。
//--- ulong TestSamplesPlot = (NumTestSamplesPlot>0)?NumTestSamplesPlot:20; //--- if(NumTestSamplesPlot>=testprices.Rows()) TestSamplesPlot = testprices.Rows()-Numlags; //--- vector testsample(100,slice,testprices.Col(0),Numlags,Numlags+TestSamplesPlot-1); vector testpredictions(100,slice,predictions,0,TestSamplesPlot-1); vector dates(100,slice,testprices.Col(1),Numlags,Numlags+TestSamplesPlot-1); //--- //Print(testpredictions.Size(), ":", testsample.Size()); //--- double y[], y_hat[]; //--- if(vecToArray(testpredictions,y_hat) && vecToArray(testsample,y) && vecToArray(dates,xaxis)) { PlotPrices(y_hat,y); } //--- ChartRedraw(); }
以下は、組合せアルゴリズムとマルチ層反復アルゴリズムをそれぞれ使用した予測からのプロットです。
結論
GMDHの組合せアルゴリズムは、複雑なシステムをモデリングするための枠組みを提供し、特にデータ駆動型の帰納的アプローチが有利な分野で強みを発揮すると結論づけることができます。大規模なデータセットを扱う場合、アルゴリズムが非効率であるため、実用的な応用は限られています。組合せ選択的アルゴリズムは、この欠点をある程度までしか緩和できません。アルゴリズムを最大限に活用するために調整する必要のあるハイパーパラメータがさらに導入されるため、速度の向上が抑制されます。金融時系列分析におけるGMDH法の応用は、価値ある洞察を提供する可能性を示しています。
| ファイル | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| Mql5\include\VectorMatrixTools.mqh | ベクトルや行列の操作に使われる関数定義のヘッダーファイル |
| Mql5\include\JAson.mqh | JSONオブジェクトの解析と生成に使用されるカスタム型の定義 |
| Mql5\include\GMDH\gmdh_internal.mqh | gmdhライブラリで使用されるカスタム型の定義を含むヘッダファイル |
| Mql5\include\GMDH\gmdh.mqh | 基本クラスGmdhModelの定義を含むインクルードファイル |
| Mql5\include\GMDH\linearmodel.mqh | COMBIクラスとMULTIクラスの基礎となる中間クラスLinearModelの定義を含むインクルードファイル |
| Mql5\include\GMDH\combi.mqh | COMBIクラスの定義を含むインクルードファイル |
| Mql5\include\GMDH\multi.mqh | MULTIクラスの定義を含むインクルードファイル |
| Mql5\include\GMDH\mia.mqh | 多層反復アルゴリズムを実装したクラスMIA |
| Mql5\script\COMBI_test.mq5 | 単純な時系列のモデルを構築することで、COMBIクラスの使用を示すスクリプト |
| Mql5\script\COMBI_Multivariable_test.mq5 | 多変数データセットのモデルを構築するためのCOMBIクラスの適用を示すスクリプト |
| Mql5\script\MULTI_test.mq5 | 単純な時系列のモデルを構築することでMULTIクラスの使用を示すスクリプト |
| Mql5\script\MULTI_Multivariable_test.mq5 | 多変数データ集合のモデルを構築するためのMULTIクラスの適用を示すスクリプト |
| Mql5\script\GMDH_Price_Model.mqh | 価格系列のGMDHモデルを示すスクリプト |
MetaQuotes Ltdにより英語から翻訳されました。
元の記事: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/14804
警告: これらの資料についてのすべての権利はMetaQuotes Ltd.が保有しています。これらの資料の全部または一部の複製や再プリントは禁じられています。
この記事はサイトのユーザーによって執筆されたものであり、著者の個人的な見解を反映しています。MetaQuotes Ltdは、提示された情報の正確性や、記載されているソリューション、戦略、または推奨事項の使用によって生じたいかなる結果についても責任を負いません。
 知っておくべきMQL5ウィザードのテクニック(第17回):多通貨取引
知っておくべきMQL5ウィザードのテクニック(第17回):多通貨取引
 ボラティリティベースの取引システムの構築と最適化の方法(チャイキンボラティリティ - CHV)
ボラティリティベースの取引システムの構築と最適化の方法(チャイキンボラティリティ - CHV)
 カスタム指標(第1回):MQL5でシンプルなカスタム指標を開発するためのステップバイステップ入門ガイド
カスタム指標(第1回):MQL5でシンプルなカスタム指標を開発するためのステップバイステップ入門ガイド
 Candlestick Trend Constraintモデルの構築(第1回):EAとテクニカル指標について
Candlestick Trend Constraintモデルの構築(第1回):EAとテクニカル指標について
- 無料取引アプリ
- 8千を超えるシグナルをコピー
- 金融ニュースで金融マーケットを探索