
Price Action. Automatización de la estrategia del patrón envolvente (Engulfing)
Introducción
Todos los traders en Forex habrán utilizado la técnica Price Action (Comportamiento del precio) en algún momento. Esto no es una simple técnica de análisis de gráficos, sino todo un sistema para determinar la posible dirección del movimiento del precio en el futuro. En este artículo, vamos a analizar el patrón envolvente (Engulfing) y crear un Asesor Experto que hará el seguimiento de este patrón y tomar las decisiones pertinentes en base a él.
Ya hemos descrito el trading automatizado con los patrones Price Action en el artículo Price Action. Automatización de la estrategia de la barra interna.
Reglas del patrón envolvente
Tenemos un patrón envolvente si el cuerpo y las sombras de una vela envuelve por completo el cuerpo y las sombras de la vela anterior. Hay dos tipos de patrones envolventes:
- BUOVB — Bullish Outside Vertical Bar (barra vertical externa alcista);
- BEOVB — Bearish Outside Vertical Bar (barra vertical externa bajista).
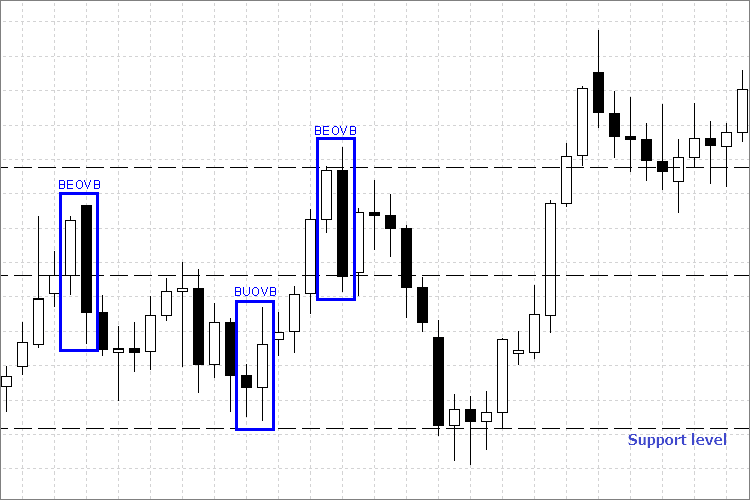
Fig. 1 Tipos de patrones en el gráfico
BUOVB. Se puede observar en el gráfico que el máximo de la barra externa es superior al máximo de la barra anterior y el mínimo de la barra externa es inferior al mínimo de la barra anterior.
BEOVB. Este patrón también es fácil de identificar en el gráfico. El máximo de la barra externa es superior al máximo de la barra anterior y el mínimo de la barra externa es inferior al mínimo de la barra anterior.
Cada patrón da una idea clara sobre las posibles tendencias del mercado.
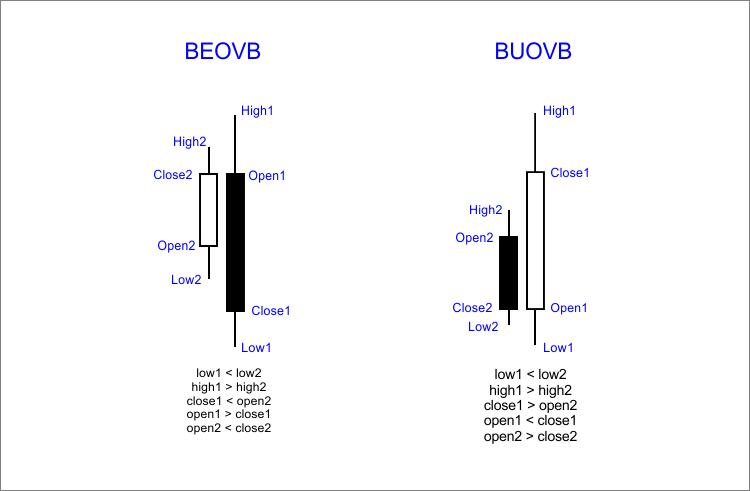
Fig. 2 Estructura del patrón
Reglas del patrón envolvente:- Para trabajar con este patrón hay que utilizar períodos de tiempo mayores: H4, D1.
- Para encontrar el punto de entrada más óptimo, hay que utilizar otros elementos de análisis gráfico, como líneas de tendencia, niveles de soporte y resistencia, niveles de Fibonacci, otros patrones Price Action, etc.
- Para evitar las entradas prematuras o erróneas al mercado, hay que utilizar las órdenes pendientes.
- Los patrones que se repiten en una zona plana no se deben utilizar como señales para entrar al mercado.
Establecer los puntos de entrada para "BUOVB" y colocar las órdenes Stop
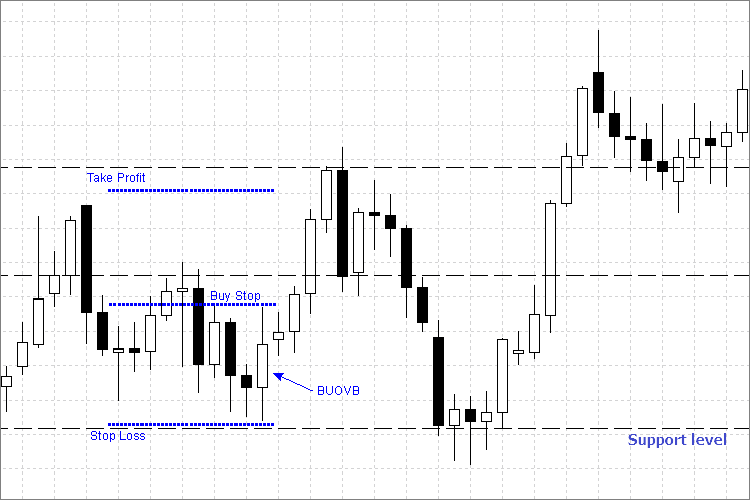
Fig. 3 Establecimiento de las órdenes Buy Stop y Stop Loss
Vamos a analizar las reglas de entrada y colocación de las órdenes Stop para BUOVB (barra vertical externa alcista) mediante el siguiente ejemplo:
- Colocamos una orden Buy Stop pendiente en un precio ligeramente por encima del máximo (pocos puntos, para asegurarnos) de la barra externa.
- Establecemos el nivel Stop Loss por debajo del mínimo de la barra externa.
- Establecemos el nivel Take Profit justo antes del siguiente nivel de resistencia.
Establecer los puntos de entrada para "BEOVB" y colocar las órdenes Stop
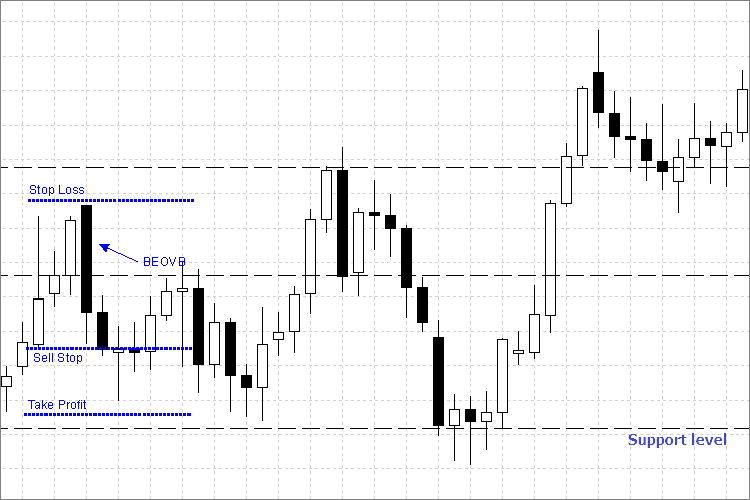
Fig. 4 Establecimiento de las órdenes Sell Stop y Stop Loss
Vamos a analizar las reglas de entrada y colocación de las órdenes Stop para BEOVB (barra vertical externa bajista) mediante el ejemplo anterior:
- Colocamos una orden Sell Stop pendiente en un precio ligeramente por debajo del mínimo (pocos puntos, para asegurarnos) de la barra externa.
- Establecemos el nivel Stop Loss por encima del máximo de la barra externa.
- Establecemos el nivel Take Profit justo antes del siguiente nivel de soporte.
Crear un Asesor Experto para el trading con el patrón envolvente
Hemos repasado el patrón envolvente y aprendido cómo entrar al mercado de forma segura, así como determinar los niveles de las órdenes Stop para limitar las pérdidas o garantizar las ganancias.
A continuación vamos a tratar de implementar los algoritmos del Asesor Experto y automatizar el trading con el patrón envolvente.
Abrimos MetaEditor desde el terminal de MetaTrader 4 y creamos un nuevo Asesor Experto (no voy a entrar en los detalles de cómo crear Asesores Expertos, ya que hay bastante información sobre este tema en el sitio web). De momento, dejamos todos los parámetros en blanco. Puede poner el nombre que quiera. Al final, obtenemos el siguiente resultado:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| BEOVB_BUOVB_Bar.mq4 | //| Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry. | //| cjdmitri@gmail.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry." #property link "cjdmitri@gmail.com" #property version "1.00" #property strict //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { //--- } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { //--- } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Convertir el patrón en un algoritmo MQL4
Una vez creado el Asesor Experto hay que definir el patrón envolvente después del cierre de una vela. Para ello, introducimos nuevas variables y les asignamos unos valores. Véase el siguiente código:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| BEOVB_BUOVB_Bar.mq4 | //| Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry. | //| cjdmitri@gmail.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry." #property link "cjdmitri@gmail.com" #property version "1.00" #property strict double open1,//first candle Open price open2, //second candle Open price close1, //first candle Close price close2, //second candle Close price low1, //first candle Low price low2, //second candle Low price high1, //first candle High price high2; //second candle High price //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { //--- define prices of necessary bars open1 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); open2 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); close1 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); close2 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); low1 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); low2 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); high1 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); high2 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Encontramos dos tipo de patrones envolventes:
void OnTick() { //--- define prices of necessary bars open1 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); open2 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); close1 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); close2 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); low1 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); low2 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); high1 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); high2 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); //--- Finding bearish pattern BEOVB if(low1 < low2 &&// First bar's Low is below second bar's Low high1 > high2 &&// First bar's High is above second bar's High close1 < open2 && //First bar's Close price is below second bar's Open open1 > close1 && //First bar is a bearish bar open2 < close2) //Second bar is a bullish bar { //--- we have described all conditions indicating that the first bar completely engulfs the second bar and is a bearish bar }
Encontramos el patrón alcista de la misma manera:
//--- Finding bullish pattern BUOVB if(low1 < low2 &&// First bar's Low is below second bar's Low high1 > high2 &&// First bar's High is above second bar's High close1 > open2 && //First bar's Close price is higher than second bar's Open open1 < close1 && //First bar is a bullish bar open2 > close2) //Second bar is a bearish bar { //--- we have described all conditions indicating that the first bar completely engulfs the second bar and is a bullish bar }
- Creamos unas variables personalizables: órdenes Stop, deslizamiento (slippage), tiempo de expiración de órdenes, número mágico del Asesor Experto, lote del trading. Se puede omitir Stop Loss, puesto que se establece de acuerdo con las reglas del patrón.
- Introducimos variables locales para normalizar el formato de las variables.
- Además, hay que recordar que las órdenes Stop se colocan a cierta distancia de los precios de la barra. Para ello, añadimos la variable Interval que se encarga del intervalo entre los precios máximo/mínimo de las barras y de los niveles de las órdenes Stop, además de los niveles de las órdenes pendientes.
- Añadimos la variable timeBUOVB_BEOVB para evitar la reapertura de la orden en este patrón.
- Añadimos la variable bar1size para comprobar que la barra externa es los suficientemente grande. Por lo tanto, podemos suponer que el mercado actual no es plano.
Como resultado, obtenemos el siguiente código:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| BEOVB_BUOVB_bar.mq4 | //| Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry. | //| cjdmitri@gmail.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry." #property link "cjdmitri@gmail.com" #property version "1.00" #property strict extern int interval = 25; //Interval extern double lot = 0.1; //Lot Size extern int TP = 400; //Take Profit extern int magic = 962231; //Magic number extern int slippage = 2; //Slippage extern int ExpDate = 48; //Expiration Hour Order extern int bar1size = 900; //Bar 1 Size double buyPrice,//define BuyStop setting price buyTP, //Take Profit BuyStop buySL, //Stop Loss BuyStop sellPrice, //define SellStop setting price sellTP, //Take Profit SellStop sellSL; //Stop Loss SellStop double open1,//first candle Open price open2, //second candle Open price close1, //first candle Close price close2, //second candle Close price low1, //first candle Low price low2, //second candle Low price high1, //first candle High price high2; //second candle High price datetime _ExpDate =0; // local variable for defining pending orders expiration time double _bar1size;// local variable required to avoid a flat market datetime timeBUOVB_BEOVB;// time of a bar when pattern orders were opened, to avoid re-opening //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { double _bid = NormalizeDouble(MarketInfo (Symbol(), MODE_BID), Digits); // define Low price double _ask = NormalizeDouble(MarketInfo(Symbol(), MODE_ASK), Digits); //define High price double _point = MarketInfo(Symbol(), MODE_POINT); //--- define prices of necessary bars open1 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); open2 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); close1 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); close2 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); low1 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); low2 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); high1 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); high2 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); //--- _bar1size=NormalizeDouble(((high1-low1)/_point),0); //--- Finding bearish pattern BEOVB if(timeBUOVB_BEOVB!=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1) && //orders are not yet opened for this pattern _bar1size > bar1size && //first bar is big enough, so the market is not flat low1 < low2 &&//First bar's Low is below second bar's Low high1 > high2 &&//First bar's High is above second bar's High close1 < open2 && //First bar's Сlose price is lower than second bar's Open price open1 > close1 && //First bar is a bearish bar open2 < close2) //Second bar is a bullish bar { //--- we have described all conditions indicating that the first bar completely engulfs the second bar and is a bearish bar timeBUOVB_BEOVB=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1); // indicate that orders are already placed on this pattern } //--- Finding bullish pattern BUOVB if(timeBUOVB_BEOVB!=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1) && //orders are not yet opened for this pattern _bar1size > bar1size && //first bar is big enough not to consider a flat market low1 < low2 &&//First bar's Low is below second bar's Low high1 > high2 &&//First bar's High is above second bar's High close1 > open2 && //First bar's Close price is higher than second bar's Open price open1 < close1 && //First bar is a bullish bar open2 > close2) //Second bar is a bearish bar { //--- we have described all conditions indicating that the first bar completely engulfs the second bar and is a bullish bar timeBUOVB_BEOVB=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1); // indicate that orders are already placed on this pattern } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Determinar los niveles de las órdenes Stop
Hemos cumplido todas las condiciones y hemos encontrado unos patrones de gran calidad. Ahora necesitamos establecer los niveles de las órdenes Stop, los precios de las órdenes pendientes, así como el tiempo de expiración de las órdenes para cada patrón.
Vamos a añadir el siguiente código a la función OnTick():
//--- Define prices for placing orders and stop orders buyPrice =NormalizeDouble(high1 + interval * _point,Digits); //define a price of order placing with intervals buySL =NormalizeDouble(low1-interval * _point,Digits); //define stop-loss with an interval buyTP =NormalizeDouble(buyPrice + TP * _point,Digits); //define take profit _ExpDate =TimeCurrent() + ExpDate*60*60; //pending order expiration time calculation //--- We also calculate sell orders sellPrice=NormalizeDouble(low1-interval*_point,Digits); sellSL=NormalizeDouble(high1+interval*_point,Digits); sellTP=NormalizeDouble(sellPrice-TP*_point,Digits);
Corrección de los errores de ejecución
Si ya ha desarrollado algunos Asesores Expertos, seguro que sabe que los errores ocurren a menudo al cerrar y establecer las órdenes, incluyendo el tiempo de espera, los valores erróneos, etc. Para eliminar estos errores tenemos que escribir una función por separado que incluye un pequeño procesador de errores básicos.
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| The function opens or sets an order | //| symbol - symbol, at which a deal is performed. | //| cmd - a deal (may be equal to any of the deal values). | //| volume - amount of lots. | //| price - Open price. | //| slippage - maximum price deviation for market buy or sell orders. | //| stoploss - position close price when an unprofitability level is reached (0 if there is no unprofitability level).| //| takeprofit - position close price when a profitability level is reached (0 if there is no profitability level). | //| comment - order comment. The last part of comment can be changed by the trade server. | //| magic - order magic number. It can be used as a user-defined ID. | //| expiration - pending order expiration time. | //| arrow_color - open arrow color on a chart. If the parameter is absent or equal to CLR_NONE, | //| the open arrow is not displayed on a chart. | //+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OrderOpenF(string OO_symbol, int OO_cmd, double OO_volume, double OO_price, int OO_slippage, double OO_stoploss, double OO_takeprofit, string OO_comment, int OO_magic, datetime OO_expiration, color OO_arrow_color) { int result = -1;// result of opening an order int Error = 0; // error when opening an order int attempt = 0; // amount of performed attempts int attemptMax = 3; // maximum amount of attempts bool exit_loop = false; // exit the loop string lang =TerminalInfoString(TERMINAL_LANGUAGE);// trading terminal language for defining the language of the messages double stopllvl =NormalizeDouble(MarketInfo (OO_symbol, MODE_STOPLEVEL) * MarketInfo (OO_symbol, MODE_POINT),Digits);// minimum stop loss/take profit level, in points //the module provides safe order opening //--- checking stop orders for buying if(OO_cmd==OP_BUY || OO_cmd==OP_BUYLIMIT || OO_cmd==OP_BUYSTOP) { double tp = (OO_takeprofit - OO_price)/MarketInfo(OO_symbol, MODE_POINT); double sl = (OO_price - OO_stoploss)/MarketInfo(OO_symbol, MODE_POINT); if(tp>0 && tp<=stopllvl) { OO_takeprofit=OO_price+stopllvl+2*MarketInfo(OO_symbol,MODE_POINT); } if(sl>0 && sl<=stopllvl) { OO_stoploss=OO_price -(stopllvl+2*MarketInfo(OO_symbol,MODE_POINT)); } } //--- checking stop orders for selling if(OO_cmd==OP_SELL || OO_cmd==OP_SELLLIMIT || OO_cmd==OP_SELLSTOP) { double tp = (OO_price - OO_takeprofit)/MarketInfo(OO_symbol, MODE_POINT); double sl = (OO_stoploss - OO_price)/MarketInfo(OO_symbol, MODE_POINT); if(tp>0 && tp<=stopllvl) { OO_takeprofit=OO_price -(stopllvl+2*MarketInfo(OO_symbol,MODE_POINT)); } if(sl>0 && sl<=stopllvl) { OO_stoploss=OO_price+stopllvl+2*MarketInfo(OO_symbol,MODE_POINT); } } //--- while loop while(!exit_loop) { result=OrderSend(OO_symbol,OO_cmd,OO_volume,OO_price,OO_slippage,OO_stoploss,OO_takeprofit,OO_comment,OO_magic,OO_expiration,OO_arrow_color); //attempt to open an order using the specified parameters //--- if there is an error when opening an order if(result<0) { Error = GetLastError(); //assign a code to an error switch(Error) //error enumeration { //order closing error enumeration and an attempt to fix them case 2: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt Sleep(3000); //3 seconds of delay RefreshRates(); break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt=0; //reset the amount of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 3: RefreshRates(); exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 4: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt Sleep(3000); //3 seconds of delay RefreshRates(); break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt = 0; //reset the amount of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 5: exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 6: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt Sleep(5000); //3 seconds of delay break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt = 0; //reset the amount of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 8: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt Sleep(7000); //3 seconds of delay break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt = 0; //reset the amount of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 64: exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 65: exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 128: Sleep(3000); RefreshRates(); continue; //exit switch case 129: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt Sleep(3000); //3 seconds of delay RefreshRates(); break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt = 0; //reset the amount of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 130: exit_loop=true; //exit while break; case 131: exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 132: Sleep(10000); //sleep for 10 seconds RefreshRates(); //update data //exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 133: exit_loop=true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 134: exit_loop=true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 135: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt RefreshRates(); break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt = 0; //set the number of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 136: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt RefreshRates(); break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt = 0; //set the amount of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 137: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; Sleep(2000); RefreshRates(); break; } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt=0; exit_loop=true; break; } case 138: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; Sleep(1000); RefreshRates(); break; } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt=0; exit_loop=true; break; } case 139: exit_loop=true; break; case 141: Sleep(5000); exit_loop=true; break; case 145: exit_loop=true; break; case 146: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; Sleep(2000); RefreshRates(); break; } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt=0; exit_loop=true; break; } case 147: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; OO_expiration=0; break; } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt=0; exit_loop=true; break; } case 148: exit_loop=true; break; default: Print("Error: ",Error); exit_loop=true; //exit while break; //other options } } //--- if no errors detected else { if(lang == "Russian") {Print("Ордер успешно открыт. ", result);} if(lang == "English") {Print("The order is successfully opened.", result);} Error = 0; //reset the error code to zero break; //exit while //errorCount =0; //reset the amount of attempts to zero } } return(result); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Como resultado, obtenemos el siguiente código:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| BEOVB_BUOVB_bar.mq4 | //| Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry. | //| cjdmitri@gmail.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry." #property link "cjdmitri@gmail.com" #property version "1.00" #property strict extern int interval = 25; //Interval extern double lot = 0.1; //Lot Size extern int TP = 400; //Take Profit extern int magic = 962231; //Magic number extern int slippage = 2; //Slippage extern int ExpDate = 48; //Expiration Hour Order extern int bar1size = 900; //Bar 1 Size double buyPrice,//define BuyStop price buyTP, //Take Profit BuyStop buySL, //Stop Loss BuyStop sellPrice, //define SellStop price sellTP, //Take Profit SellStop sellSL; //Stop Loss SellStop double open1,//first candle Open price open2, //second candle Open price close1, //first candle Close price close2, //second candle Close price low1, //first candle Low price low2, //second candle Low price high1, //first candle High price high2; //second candle High price datetime _ExpDate =0; // local variable for defining pending orders expiration time double _bar1size;// local variable required to avoid a flat market datetime timeBUOVB_BEOVB;// time of a bar when pattern orders were opened, to avoid re-opening //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { double _bid = NormalizeDouble(MarketInfo (Symbol(), MODE_BID), Digits); // define Low price double _ask = NormalizeDouble(MarketInfo(Symbol(), MODE_ASK), Digits); //define High price double _point = MarketInfo(Symbol(), MODE_POINT); //--- define prices of necessary bars open1 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); open2 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); close1 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); close2 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); low1 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); low2 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); high1 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); high2 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); //--- Define prices for placing orders and stop orders buyPrice =NormalizeDouble(high1 + interval * _point,Digits); //define a price of order placing with intervals buySL =NormalizeDouble(low1-interval * _point,Digits); //define stop loss with an interval buyTP =NormalizeDouble(buyPrice + TP * _point,Digits); //define take profit _ExpDate =TimeCurrent() + ExpDate*60*60; //pending order expiration time calculation //--- We also calculate sell orders sellPrice=NormalizeDouble(low1-interval*_point,Digits); sellSL=NormalizeDouble(high1+interval*_point,Digits); sellTP=NormalizeDouble(sellPrice-TP*_point,Digits); //--- _bar1size=NormalizeDouble(((high1-low1)/_point),0); //--- Finding bearish pattern BEOVB if(timeBUOVB_BEOVB!=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1) && //orders are not yet opened for this pattern _bar1size > bar1size && //first bar is big enough, so the market is not flat low1 < low2 &&//First bar's Low is below second bar's Low high1 > high2 &&//First bar's High is above second bar's High close1 < open2 && //First bar's Close price is lower than second bar's Open price open1 > close1 && //First bar is a bearish bar open2 < close2) //Second bar is a bullish bar { //--- we have described all conditions indicating that the first bar completely engulfs the second bar and is a bearish bar OrderOpenF(Symbol(),OP_SELLSTOP,lot,sellPrice,slippage,sellSL,sellTP,NULL,magic,_ExpDate,Blue); timeBUOVB_BEOVB=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1); //indicate that orders are already placed on this pattern } //--- Finding bullish pattern BUOVB if(timeBUOVB_BEOVB!=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1) && //orders are not yet opened for this pattern _bar1size > bar1size && //first bar is big enough, so the market is not flat low1 < low2 &&//First bar's Low is below second bar's Low high1 > high2 &&//First bar's High is above second bar's High close1 > open2 && //First bar's Close price is higher than second bar's Open price open1 < close1 && //First bar is a bullish bar open2 > close2) //Second bar is a bearish bar { //--- we have described all conditions indicating that the first bar completely engulfs the second bar and is a bullish bar OrderOpenF(Symbol(),OP_BUYSTOP,lot,buyPrice,slippage,buySL,buyTP,NULL,magic,_ExpDate,Blue); timeBUOVB_BEOVB = iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1); //indicate that orders are already placed on this pattern } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Vamos compilar el código y comprobar si hay mensajes de error en el registro.
Prueba del asesor experto
Es el momento de probar nuestro Asesor Experto. Vamos a ejecutar la prueba de estrategias y establecer los parámetros de entrada.
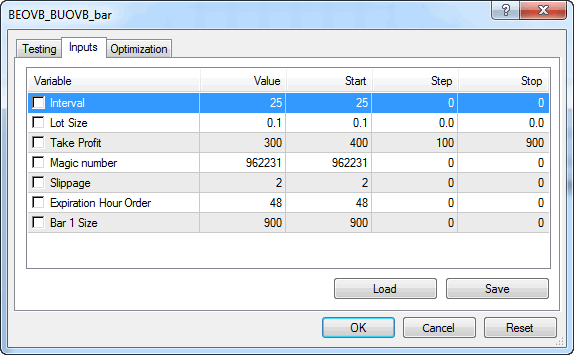
Fig. 5 Parámetros de entrada para la prueba
- Hay que seleccionar un par de divisas para la prueba. He optado por el EURAUD.
- Hay que asegurarse de elegir el modo "Cada tick" y seleccionar la casilla "Utilizar datos" para llevar a cabo la prueba. He seleccionado todo el año 2014.
- Establecemos el período de tiempo D1.
- Iniciamos la prueba.
- Una vez finalizada la prueba, comprobamos el diario. Como se puede observar, no se ha producido ningún error durante el proceso.
La siguiente figura muestra el diario de la prueba del Asesor Experto:
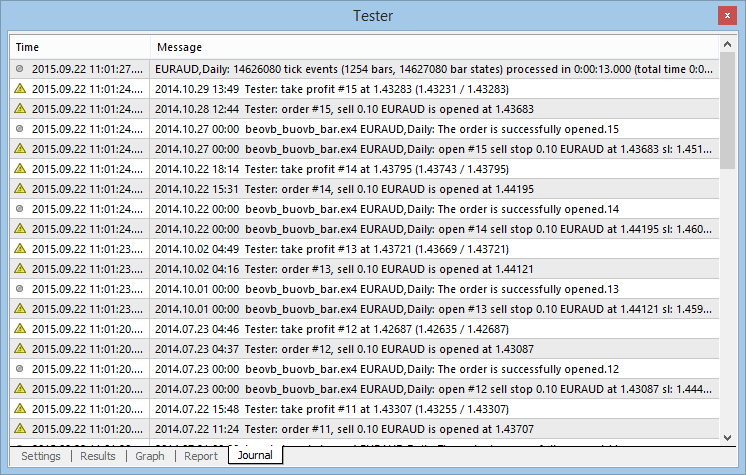
Fig. 7 Diario de la prueba del Asesor Experto
Nos aseguramos de que no hay ningún error y optimizamos el Asesor Experto
Optimización
He seleccionado los siguientes parámetros para la optimización:
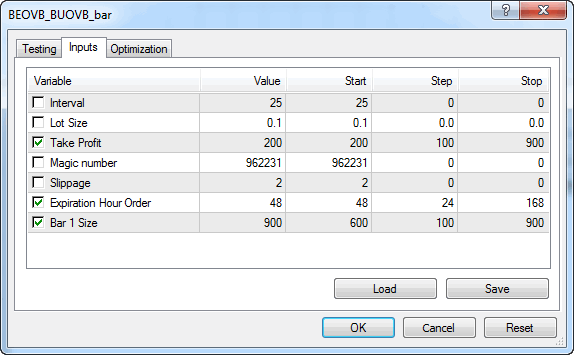
Fig. 8 Parámetros de la optimización
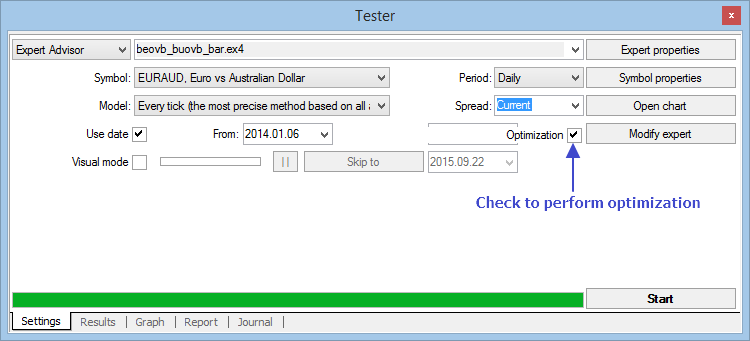
Fig. 9 Ajustes de la optimización
Como resultado de la optimización y la prueba, obtenemos el Asesor Experto listo para su uso.
Resultados de la optimización y la prueba
Después de realizar la optimización de los pares de divisas más conocidos, hemos obtenido el siguiente resultado:
| Par de divisas | Beneficio neto | Factor de beneficio | Disminución (%) | Beneficio bruto | Pérdida bruta |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EURAUD | 523,90 $ | 3,70 | 2,13 | 727,98 $ | 196,86 $ |
| USDCHF | 454,19 $ | - | 2,25 | 454,19 $ | 0,00 $ |
| GBPUSD | 638,71 $ | - | 1,50 | 638,71 $ | 0,00 $ |
| EURUSD | 638,86 $ | - | 1,85 | 638,86 $ | 0,00 $ |
| USDJPY | 423,85 $ | 5,15 | 2,36 | 525,51 $ | 102,08 $ |
| USDCAD | 198,82 $ | 2,41 | 2,74 | 379,08 $ | 180,26 $ |
| AUDUSD | 136,14 $ | 1,67 | 2,39 | 339,26 $ | 203,12 $ |
Tabla 1 Resultados de la optimización
Se han llevado a cabo unas pruebas más detalladas con el par de divisas EURAUD:
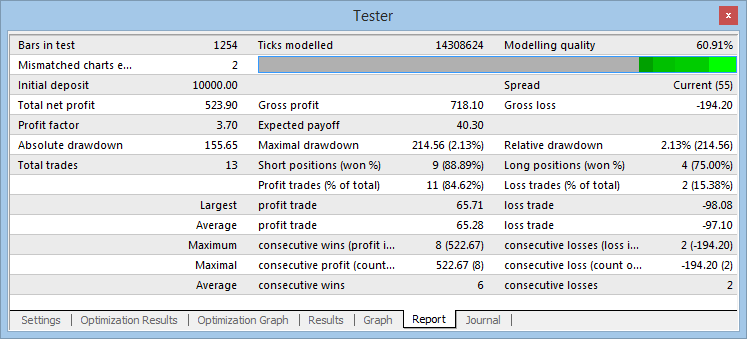
Fig. 10 Resultados de la prueba
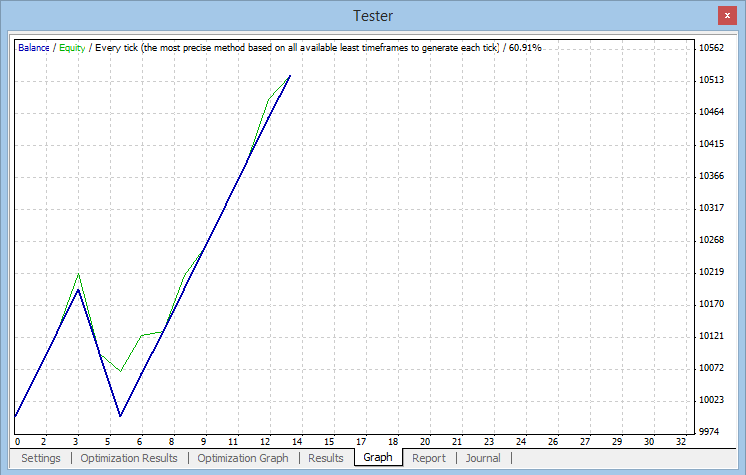
Fig. 11 Gráfico de los resultados de la prueba
Conclusión
- En este artículo, hemos creado un Asesor Experto para el trading con el patrón envolvente.
- Hemos visto que los patrones Price Action pueden funcionar incluso sin filtros adicionales para entrar al mercado.
- No hemos recurrido a ningún truco (tipo martingala o promediado).
- Al establecer correctamente las órdenes Stop, se ha reducido la disminución al mínimo.
- No se ha utilizado ningún indicador técnico. Se basa el Asesor Experto únicamente en la lectura del gráfico "básico".
¡Gracias por leer el artículo! y espero que le haya resultado útil.
Traducción del ruso hecha por MetaQuotes Ltd.
Artículo original: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/1946
 Un método de escritura de los niveles de soporte/resistencia
Un método de escritura de los niveles de soporte/resistencia
 Manejar el Terminal de MetaTrader mediante DLL
Manejar el Terminal de MetaTrader mediante DLL
 Mostrar los niveles de soporte/resistencia
Mostrar los niveles de soporte/resistencia
 Comprobación estadística del sistema de gestión de dinero de Labouchere
Comprobación estadística del sistema de gestión de dinero de Labouchere
- Aplicaciones de trading gratuitas
- 8 000+ señales para copiar
- Noticias económicas para analizar los mercados financieros
Usted acepta la política del sitio web y las condiciones de uso
Hola Buenos dias, muy buen articulo
estoy intentando probar el EA y me da este error en el probador de estrategias
2019.11.29 11:04:43.580 TestGenerator: unmatched data error (volume limit 22016 at 2019.01.03 00:00 exceeded)
Sale muchisimas veces