
Studying candlestick analysis techniques (part III): Library for pattern operations
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Library structure
- Library development
- CandleType. Selected candlestick type
- PatternType. Pattern type
- Found. The number of found patterns of the specified type
- Coincidence. How often the specified pattern type is found
- Probability. The probability of movement after the pattern occurrence
- Efficiency. The pattern efficiency coefficient
- Practical use
- CandleDetector. Candlestick searching indicator
- PatternDetector. Pattern searching indicator
- PatternExpert. Pattern trading Expert Advisor
- Conclusions
Introduction
We have already considered candlestick analysis techniques: the actuality of the patterns under current market conditions was checked in the first article, and an attempt to expand these research was made in the second article. Using the development evaluation criteria, we studied, tested and compared a wide range of possible pattern combinations. For this purpose, we developed a custom Pattern Analyzer application with a large set of settings for studying patterns. However, the theory and research can only provide information and conclusions. The logical continuation of the task is to use them in real conditions.
Therefore, the purpose of this article is to create a custom tool, which enables users to receive and use the entire array of information about patterns discussed earlier. We will create a library which you will be able to use in your own indicators, trading panels, Expert Advisors, etc.
Library structure
Before proceeding to the creation of the library structure, classes and connections, let us define the data which we will use. That is, we need to separate the methods responsible for the input data and the methods which will provide the results. The general library structure will be based on the visual solution developed in the previous articles — the Pattern Analyzer.
Let us start with the application input data which can influence the result when testing the patterns.
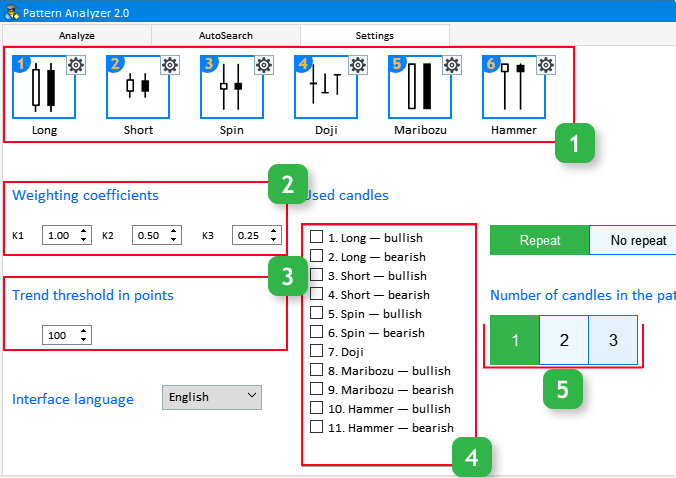
Fig.1 Input parameters in the Setting tab.
Block 1. This block features the list of candlestick types which the existing and generated patterns consist of. Each of the types has its settings, which you can view by clicking on the gear icon in the upper right corner of the candlestick visualization page. Candlestick types 1-5 have only one setting, while Hammer has two of them.
Block 2. Weight coefficients. There are three parameters К1, К2, К3 which affect the pattern efficiency evaluation result.
Block 3. Threshold trend value in points.
Block 4. Candlesticks used when testing generated patterns. Here we will need sequence numbers or candlestick indexes. Using this data we will be able to obtain information about any pattern of any size, up to three candlesticks.
Block 5. Number of candlesticks in the pattern. This setting is only applicable for custom patterns.
Then let us view the Analyze tab and input parameters contained therein.
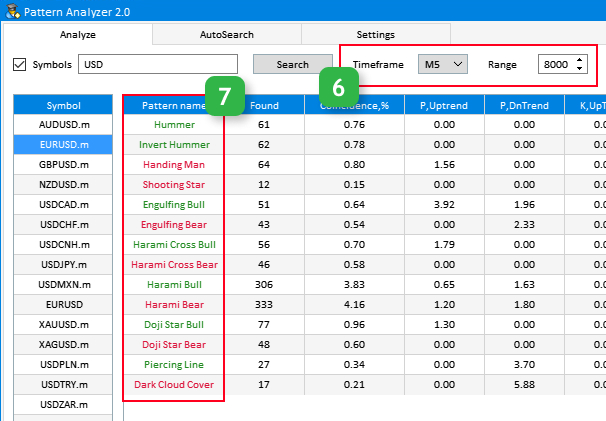
Fig.2 Input parameters in the Analyze tab.
Block 6. this block contains settings of the current timeframe and data sample range used for pattern analysis.
Block 7. Names of existing patterns. It also has an input which cannot be edited from the application, but is required for accessing a pattern and obtaining information about it.
Let us enumerate here the data which can be obtained from the pattern analysis. This is needed for the creation of a correct structure of methods in a class.
- Patterns found. The number of found patterns of the specified type.
- Occurrence. The percentage of the number of patterns found from the total sample range.
- Probability of upward or downward movement.
- Efficiency ratios during upward and downward movement for this candlestick pattern.
Library development
After determining the basic points, let us proceed to library creation. Let us start with the creation of a file with required enumerations Enums.mqh.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Enums.mqh | //| Copyright 2018, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.mql5.com/en/users/alex2356 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Candlestick type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum TYPE_CANDLESTICK { CAND_NONE, // Undefined CAND_MARIBOZU, // Marubozu CAND_DOJI, // Doji CAND_SPIN_TOP, // Spinning Top CAND_HAMMER, // Hammer CAND_INVERT_HAMMER, // Inverted Hammer CAND_LONG, // Long CAND_SHORT // Short }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Pattern type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum TYPE_PATTERN { NONE, HUMMER, INVERT_HUMMER, HANDING_MAN, SHOOTING_STAR, ENGULFING_BULL, ENGULFING_BEAR, HARAMI_BULL, HARAMI_BEAR, HARAMI_CROSS_BULL, HARAMI_CROSS_BEAR, DOJI_STAR_BULL, DOJI_STAR_BEAR, PIERCING_LINE, DARK_CLOUD_COVER }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Trend type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum TYPE_TREND { UPPER, //Uptrend DOWN, //Downtrend FLAT //Flat }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Here we will determine the list of simple candlestick types used, types of existing patterns as well as the type of trend - the data is required for identifying existing patterns on the chart.
After that we will create the Pattern.mqh file. The CPattern class will be created in it, and in its private section we will declare variables for the parameters mentioned in the previous section. Also we need to connect the file with the enumerations.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Pattern.mqh | //| Copyright 2018, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.mql5.com/en/users/alex2356 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #include "Enums.mqh" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CPattern { private: //--- Weights double m_k1; double m_k2; double m_k3; //--- Threshold trend value in points int m_threshold_value; //--- Long candlestick setup coefficient double m_long_coef; //--- Short candlestick setup coefficient double m_short_coef; //--- Doji candlestick setup coefficient double m_doji_coef; //--- Marubozu candlestick setup coefficient double m_maribozu_coef; //--- Spinning Top candlestick setup coefficient double m_spin_coef; //--- Hammer candlestick setup coefficient double m_hummer_coef1; double m_hummer_coef2; //--- Sampling range for the preset patterns int m_range_total; //--- Period to determine the trend int m_trend_period; //--- Found patterns int m_found; //--- Occurrence of patterns double m_coincidence; //--- Probability of upward or downward movement double m_probability1; double m_probability2; //--- Efficiency double m_efficiency1; double m_efficiency2; //--- Simple candlestick patterns struct CANDLE_STRUCTURE { double m_open; double m_high; double m_low; double m_close; // OHLC TYPE_TREND m_trend; // Trend bool m_bull; // Bullish candlestick double m_bodysize; // Body size TYPE_CANDLESTICK m_type; // Candlestick type }; //--- Pattern efficiency evaluation properties struct RATING_SET { int m_a_uptrend; int m_b_uptrend; int m_c_uptrend; int m_a_dntrend; int m_b_dntrend; int m_c_dntrend; };
As can be seen from the above code, two structures have been added to our program. The first structure, CANDLE_STRUCTURE is required for determining the candlestick type on the chart. Note that two types of trend enumerations are used in this structure: TYPE_TREND and TYPE_CANDLESTICK from the Enums.mqh file which was considered earlier and which was created for this structure. The second structure, RATING_SET, stores records of price movement estimates after the appearance of the pattern. Please read the first article for more details.
Now consider the part of the public section of the class, which describes the methods for customizing and retrieving the values of input parameters, which are described in the library structure section.
public: CPattern(void); ~CPattern(void); //--- Set and return weight coefficients void K1(const double k1) { m_k1=k1; } double K1(void) { return(m_k1); } void K2(const double k2) { m_k2=k2; } double K2(void) { return(m_k2); } void K3(const double k3) { m_k3=k3; } double K3(void) { return(m_k3); } //--- Set and return the threshold trend value void Threshold(const int threshold) { m_threshold_value=threshold; } int Threshold(void) { return(m_threshold_value); } //--- Set and return the long candlestick setup coefficient void Long_coef(const double long_coef) { m_long_coef=long_coef; } double Long_coef(void) { return(m_long_coef); } //--- Set and return the short candlestick setup coefficient void Short_coef(const double short_coef) { m_short_coef=short_coef; } double Short_coef(void) { return(m_short_coef); } //--- Set and return the doji candlestick setup coefficient void Doji_coef(const double doji_coef) { m_doji_coef=doji_coef; } double Doji_coef(void) { return(m_doji_coef); } //--- Set and return the marubozu candlestick setup coefficient void Maribozu_coef(const double maribozu_coef) { m_maribozu_coef=maribozu_coef; } double Maribozu_coef(void) { return(m_maribozu_coef); } //--- Set and return the Spinning Top candlestick setup coefficient void Spin_coef(const double spin_coef) { m_spin_coef=spin_coef; } double Spin_coef(void) { return(m_spin_coef); } //--- Set and return the Hammer candlestick setup coefficient void Hummer_coef1(const double hummer_coef1) { m_hummer_coef1=hummer_coef1; } void Hummer_coef2(const double hummer_coef2) { m_hummer_coef2=hummer_coef2; } double Hummer_coef1(void) { return(m_hummer_coef1); } double Hummer_coef2(void) { return(m_hummer_coef2); } //--- Set and return the sampling range for preset parameters void Range(const int range_total) { m_range_total=range_total; } int Range(void) { return(m_range_total); } //--- Set and return the number of candlesticks for trend calculation void TrendPeriod(const int period) { m_trend_period=period; } int TrendPeriod(void) { return(m_trend_period); }
In the class constructor, we will describe default parameters, as specified in the application, in the Setting tabs.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CPattern::CPattern(void) : m_k1(1), m_k2(0.5), m_k3(0.25), m_threshold_value(100), m_long_coef(1.3), m_short_coef(0.5), m_doji_coef(0.04), m_maribozu_coef(0.01), m_spin_coef(1), m_hummer_coef1(0.1), m_hummer_coef2(2), m_range_total(8000), m_trend_period(5) { }
The second part of the CPattern class public section provides a description of the methods for processing declared input parameters and for obtaining the properties and characteristics of the patterns.
Let us view each of them in detail. It is important to understand the operating algorithm in order to be able to efficiently use them when creating indicators, trading panels or Expert Advisors.
CandleType
TYPE_CANDLESTICK CandleType(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,const int shift);
Parameters
- symbol — Selected symbol for the search
- timeframe — selected timeframe
- shift — Index of the candlestick selected for the analysis starting with.
Return Value
The type of the selected candlestick from the TYPE_CANDLESTICK enumeration.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Candlestick type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum TYPE_CANDLESTICK { CAND_NONE, // Undefined CAND_MARIBOZU, // Marubozu CAND_DOJI, // Doji CAND_SPIN_TOP, // Spinning Top CAND_HAMMER, // Hammer CAND_INVERT_HAMMER, // Inverted Hammer CAND_LONG, // Long CAND_SHORT // Short };
Implementation
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the type of the selected candlestick | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ TYPE_CANDLESTICK CPattern::CandleType(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,const int shift) { CANDLE_STRUCTURE res; if(GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,res,shift)) return(res.m_type); return(CAND_NONE); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Candlestick type recognition | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CPattern::GetCandleType(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,CANDLE_STRUCTURE &res,const int shift) { MqlRates rt[]; int aver_period=m_trend_period; double aver=0; SymbolSelect(symbol,true); int copied=CopyRates(symbol,timeframe,shift,aver_period+1,rt); //--- Get details of the previous candlestick if(copied<aver_period) return(false); //--- res.m_open=rt[aver_period].open; res.m_high=rt[aver_period].high; res.m_low=rt[aver_period].low; res.m_close=rt[aver_period].close; //--- Determine the trend direction for(int i=0;i<aver_period;i++) aver+=rt[i].close; aver/=aver_period; if(aver<res.m_close) res.m_trend=UPPER; if(aver>res.m_close) res.m_trend=DOWN; if(aver==res.m_close) res.m_trend=FLAT; //--- Determine if it is a bullish or a bearish candlestick res.m_bull=res.m_open<res.m_close; //--- Get the absolute size of candlestick body res.m_bodysize=MathAbs(res.m_open-res.m_close); //--- Get sizes of shadows double shade_low=res.m_close-res.m_low; double shade_high=res.m_high-res.m_open; if(res.m_bull) { shade_low=res.m_open-res.m_low; shade_high=res.m_high-res.m_close; } double HL=res.m_high-res.m_low; //--- Calculate average body size of previous candlesticks double sum=0; for(int i=1; i<=aver_period; i++) sum=sum+MathAbs(rt[i].open-rt[i].close); sum=sum/aver_period; //--- Determine the candlestick type res.m_type=CAND_NONE; //--- long if(res.m_bodysize>sum*m_long_coef) res.m_type=CAND_LONG; //--- sort if(res.m_bodysize<sum*m_short_coef) res.m_type=CAND_SHORT; //--- doji if(res.m_bodysize<HL*m_doji_coef) res.m_type=CAND_DOJI; //--- marubozu if((shade_low<res.m_bodysize*m_maribozu_coef || shade_high<res.m_bodysize*m_maribozu_coef) && res.m_bodysize>0) res.m_type=CAND_MARIBOZU; //--- hammer if(shade_low>res.m_bodysize*m_hummer_coef2 && shade_high<res.m_bodysize*m_hummer_coef1) res.m_type=CAND_HAMMER; //--- invert hammer if(shade_low<res.m_bodysize*m_hummer_coef1 && shade_high>res.m_bodysize*m_hummer_coef2) res.m_type=CAND_INVERT_HAMMER; //--- spinning top if(res.m_type==CAND_SHORT && shade_low>res.m_bodysize*m_spin_coef && shade_high>res.m_bodysize*m_spin_coef) res.m_type=CAND_SPIN_TOP; //--- ArrayFree(rt); return(true); }
The candlestick recognition method GetCandleType() is used in the public GetCandleType() method. GetCandleType() is a private method. Its arguments include the current symbol, the timeframe and candlestick number, as well as a pointer to the structure. Pattern calculation and identification is performed based on these parameters.
PatternType
Recognizes the pattern type with the selected candle. It has 5 method overloads because arguments can be either existing patterns from the TYPE_PATTERN enumeration, or generated patterns consisting of one, two or three candlesticks. An argument can also be an array of patterns from the TYPE_PATTERN enumeration.
//--- Recognizing the pattern type bool PatternType(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,TYPE_PATTERN pattern,int shift); bool PatternType(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index,const int shift); bool PatternType(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,const int shift); bool PatternType(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,int index3,const int shift); //--- Recognizing the set of patterns bool PatternType(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,TYPE_PATTERN &pattern[],int shift);
Parameters
- symbol — Symbol selected for search.
- timeframe — Selected timeframe.
- pattern,pattern[] — Existing pattern type from TYPE_PATTERN.
A pointer to the array of existing patterns from the TYPE_PATTERN list.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Pattern type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum TYPE_PATTERN { NONE, HUMMER, INVERT_HUMMER, HANDING_MAN, SHOOTING_STAR, ENGULFING_BULL, ENGULFING_BEAR, HARAMI_BULL, HARAMI_BEAR, HARAMI_CROSS_BULL, HARAMI_CROSS_BEAR, DOJI_STAR_BULL, DOJI_STAR_BEAR, PIERCING_LINE, DARK_CLOUD_COVER };
- index,index1,index2,index3 — Index of the simple type candlestick (block 4 in Fig.1).
- shift — Index of the candlestick selected for the analysis beginning, starting with 0.
Return Value
A bool value.
Implementation
Since there are 5 types of PatternType method implementation, we will analyze it separately with various arguments. The first of them searches for an existing pattern from the TYPE_PATTERN enumeration. As can be seen below, this is done using the private method CheckPattern.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Recognizing a pre-defined pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CPattern::PatternType(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,TYPE_PATTERN pattern,const int shift) { if(CheckPattern(symbol,timeframe,shift)==pattern) return(true); return(false); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Checks and returns the pattern type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ TYPE_PATTERN CPattern::CheckPattern(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int shift) { CANDLE_STRUCTURE cand1,cand2; TYPE_PATTERN pattern=NONE; ZeroMemory(cand1); ZeroMemory(cand2); GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,cand2,shift); // Previous candlestick GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,cand1,shift-1); // Current candlestick //--- Inverted Hammer, bullish model if(cand2.m_trend==DOWN && // Checking the trend direction cand2.m_type==CAND_INVERT_HAMMER) // Checking the "Inverted Hammer" pattern=INVERT_HUMMER; //--- Hanging man, bearish else if(cand2.m_trend==UPPER && // Checking the trend direction cand2.m_type==CAND_HAMMER) // Checking "Hammer" pattern=HANDING_MAN; //--- Hammer, bullish model else if(cand2.m_trend==DOWN && // Checking the trend direction cand2.m_type==CAND_HAMMER) // Checking "Hammer" pattern=HUMMER; //--- Shooting Star, bearish model else if(cand1.m_trend==UPPER && cand2.m_trend==UPPER && // Checking the trend direction cand2.m_type==CAND_INVERT_HAMMER && cand1.m_close<=cand2.m_open) // Checking "Inverted Hammer" pattern=SHOOTING_STAR; //--- Engulfing, bullish model else if(cand1.m_trend==DOWN && cand1.m_bull && cand2.m_trend==DOWN && !cand2.m_bull && // Checking trend direction and candlestick direction cand1.m_bodysize>cand2.m_bodysize && cand1.m_close>=cand2.m_open && cand1.m_open<cand2.m_close) pattern=ENGULFING_BULL; //--- Engulfing, bearish model else if(cand1.m_trend==UPPER && cand1.m_bull && cand2.m_trend==UPPER && !cand2.m_bull && // Checking trend direction and candlestick direction cand1.m_bodysize<cand2.m_bodysize && cand1.m_close<=cand2.m_open && cand1.m_open>cand2.m_close) pattern=ENGULFING_BEAR; //--- Harami Cross, bullish else if(cand2.m_trend==DOWN && !cand2.m_bull && // Checking trend direction and candlestick direction (cand2.m_type==CAND_LONG || cand2.m_type==CAND_MARIBOZU) && cand1.m_type==CAND_DOJI && // Checking the "long" first candlestick and the doji candlestick cand1.m_close<cand2.m_open && cand1.m_open>=cand2.m_close) // Doji is inside the first candlestick body pattern=HARAMI_CROSS_BULL; //--- Harami Cross, bearish model else if(cand2.m_trend==UPPER && cand2.m_bull && // Checking trend direction and candlestick direction (cand2.m_type==CAND_LONG || cand2.m_type==CAND_MARIBOZU) && cand1.m_type==CAND_DOJI && // Checking the "long" candlestick and the doji candlestick cand1.m_close>cand2.m_open && cand1.m_open<=cand2.m_close) // Doji is inside the first candlestick body pattern=HARAMI_CROSS_BEAR; //--- Harami, bullish else if(cand1.m_trend==DOWN && cand1.m_bull && !cand2.m_bull && // Checking trend direction and candlestick direction (cand2.m_type==CAND_LONG || cand2.m_type==CAND_MARIBOZU) && // Checking the "long" first candlestick cand1.m_type!=CAND_DOJI && cand1.m_bodysize<cand2.m_bodysize && // The second candle is not Doji and first candlestick body is larger than that of the second one cand1.m_close<cand2.m_open && cand1.m_open>=cand2.m_close) // Second candlestick body is inside the first candlestick body pattern=HARAMI_BULL; //--- Harami, bearish else if(cand1.m_trend==UPPER && !cand1.m_bull && cand2.m_bull && // Checking trend direction and candlestick direction (cand2.m_type==CAND_LONG || cand2.m_type==CAND_MARIBOZU) && // Checking the "long" first candlestick cand1.m_type!=CAND_DOJI && cand1.m_bodysize<cand2.m_bodysize && // The second candle is not Doji and first candlestick body is larger than that of the second one cand1.m_close>cand2.m_open && cand1.m_open<=cand2.m_close) // Second candlestick body is inside the first candlestick body pattern=HARAMI_BEAR; //--- Doji Star, bullish else if(cand1.m_trend==DOWN && !cand2.m_bull && // Checking trend direction and candlestick direction (cand2.m_type==CAND_LONG || cand2.m_type==CAND_MARIBOZU) && cand1.m_type==CAND_DOJI && // Checking the 1st "long" candlestick and the 2nd doji cand1.m_close<=cand2.m_open) // Doji Open is lower or equal to 1st candle Close pattern=DOJI_STAR_BULL; //--- Doji Star, bearish else if(cand1.m_trend==UPPER && cand2.m_bull && // Checking trend direction and candlestick direction (cand2.m_type==CAND_LONG || cand2.m_type==CAND_MARIBOZU) && cand1.m_type==CAND_DOJI && // Checking the 1st "long" candlestick and the 2nd doji cand1.m_open>=cand2.m_close) //Doji Open price is higher or equal to 1st candle Close pattern=DOJI_STAR_BEAR; //--- Piercing, bullish model else if(cand1.m_trend==DOWN && cand1.m_bull && !cand2.m_bull && // Checking trend direction and candlestick direction (cand1.m_type==CAND_LONG || cand1.m_type==CAND_MARIBOZU) && (cand2.m_type==CAND_LONG || cand2.m_type==CAND_MARIBOZU) && // Checking the "long" candlestick cand1.m_close>(cand2.m_close+cand2.m_open)/2 && // 2nd candle Close is above the middle of the 1st candlestick cand2.m_open>cand1.m_close && cand2.m_close>=cand1.m_open) pattern=PIERCING_LINE; //--- Dark Cloud Cover, bearish else if(cand1.m_trend==UPPER && !cand1.m_bull && cand2.m_bull && // Checking trend direction and candlestick direction (cand1.m_type==CAND_LONG || cand1.m_type==CAND_MARIBOZU) && (cand2.m_type==CAND_LONG || cand2.m_type==CAND_MARIBOZU) && // Checking the "long" candlestick cand1.m_close<(cand2.m_close+cand2.m_open)/2 && // Close 2 is below the middle of the 1st candlestick body cand1.m_close<cand2.m_open && cand2.m_close<=cand1.m_open) pattern=DARK_CLOUD_COVER; return(pattern); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
The next type of the PatternType method differs from the previous one in that an array of searched patterns is passed instead of the pattern type argument:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Recognizing an array of patterns | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CPattern::PatternType(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,TYPE_PATTERN &pattern[],int shift) { for(int i=0;i<ArraySize(pattern);i++) { if(CheckPattern(symbol,timeframe,shift)==pattern[i]) return(true); } return(false); }
Next, let us consider the implementation of the PatternType method for working with patterns generated from simple candlestick types. There are three types of these patterns: consisting of one, two or three candlesticks. Let us consider them one by one:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Recognizing a pattern by candlestick index | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CPattern::PatternType(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index,int shift) { //--- Verify the candlestick index if(index<0 || index>11) return(false); //--- CANDLE_STRUCTURE cand,cur_cand; RATING_SET ratings; ZeroMemory(cand); IndexToPatternType(cand,index); //--- Get the current candlestick type GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,cur_cand,shift); // Current candlestick //--- if(cur_cand.m_type==cand.m_type && cur_cand.m_bull==cand.m_bull) return(true); return(false); }
This is implementation of a method searching for a one-candlestick pattern, which is very similar to the CandleType() method, though the type and range of passed arguments is different. Pay attention to the private method IndextoPatternType() which has not been used earlier:
//--- Converts the candlestick index to its type void IndexToPatternType(CANDLE_STRUCTURE &res,int index);
It converts the index of a simple type of candlestick into its type and passes it to the specified structure.
Here is the method for a two-candlestick pattern:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Recognizing a pattern by candlestick index | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CPattern::PatternType(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,int shift) { //--- Verify the candlestick index if(index1<0 || index1>11 || index2<0 || index2>11) return(false); //--- CANDLE_STRUCTURE cand1,cand2,cand3,cur_cand,prev_cand; RATING_SET ratings; ZeroMemory(cand1); ZeroMemory(cand2); IndexToPatternType(cand1,index1); IndexToPatternType(cand2,index2); //--- Get the current candlestick type GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,prev_cand,shift+1); // Previous candlestick GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,cur_cand,shift); // Current candlestick //--- if(cur_cand.m_type==cand1.m_type && cur_cand.m_bull==cand1.m_bull && prev_cand.m_type==cand2.m_type && prev_cand.m_bull==cand2.m_bull) return(true); return(false); }
The code implementation is very similar to the previous one. However, please note that the following feature should be taken into account when selecting candlestick index for analysis: since the pattern consists of two candlesticks, the type candlestick 'index1' will be shifted by 'shift', and for index2 - by 'shift+1'. The same peculiarity concerns the method implementation for three-candlestick patterns:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Recognizing a pattern by candlestick index | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CPattern::PatternType(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,int index3,int shift) { CANDLE_STRUCTURE cand1,cand2,cand3,cur_cand,prev_cand,prev_cand2; RATING_SET ratings; //--- ZeroMemory(cand1); ZeroMemory(cand2); ZeroMemory(cand3); //--- IndexToPatternType(cand1,index1); IndexToPatternType(cand2,index2); IndexToPatternType(cand3,index3); //--- Get the current candlestick type GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,prev_cand2,shift+2); // Previous candlestick GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,prev_cand,shift+1); // Previous candlestick GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,cur_cand,shift); // Current candlestick //--- if(cur_cand.m_type==cand1.m_type && cur_cand.m_bull==cand1.m_bull && prev_cand.m_type==cand2.m_type && prev_cand.m_bull==cand2.m_bull && prev_cand2.m_type==cand3.m_type && prev_cand2.m_bull==cand3.m_bull) return(true); return(false); }
Found
Returns the number of found patterns of the specified type. It has 3 method overloads for existing patterns TYPE_PATTERN, as well as for generated patterns consisting of 1-3 simple candlestick types.
//--- Returns the number of found patterns of the specified type int Found(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,TYPE_PATTERN pattern); int Found(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index); int Found(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2); int Found(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,int index3);
Parameters
- symbol — Symbol selected for search.
- timeframe — Selected timeframe.
- pattern — Existing pattern type from TYPE_PATTERN.
- index,index1,index2,index3 — Index of the simple type candlestick (block 4 in Fig.1).
Return Value
The number of found patterns of the specified type.
Implementation
The implementation of this method is quite simple. The main operations related to collecting statistics is performed by the private method PatternStat().
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the number of found patterns of the specified type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CPattern::Found(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,TYPE_PATTERN pattern) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,pattern); return(m_found); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the number of found patterns of the specified type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CPattern::Found(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,index1); return(m_found); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the number of found patterns of the specified type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CPattern::Found(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,index1,index2); return(m_found); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the number of found patterns of the specified type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CPattern::Found(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,int index3) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,index1,index2,index3); return(m_found); }
The PatternStat() method has two types: for existing and generated patterns. Let us examine them in detail. The first one is intended for patterns from the TYPE_PATTERN enumeration:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Get statistics on the given pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CPattern::PatternStat(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,TYPE_PATTERN pattern) { //--- int pattern_counter=0; //--- RATING_SET pattern_coef={0,0,0,0,0,0}; //--- for(int i=m_range_total;i>4;i--) { if(CheckPattern(symbol,timeframe,i)==pattern) { pattern_counter++; if(pattern==HUMMER || pattern==INVERT_HUMMER || pattern==HANDING_MAN) GetCategory(symbol,timeframe,pattern_coef,i-3); else GetCategory(symbol,timeframe,pattern_coef,i-4); } } //--- CoefCalculation(pattern_coef,pattern_counter); }
The second one is used for generated patterns consisting of indexes of simple candlestick types.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Get statistics on the given pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CPattern::PatternStat(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2=0,int index3=0) { CANDLE_STRUCTURE cand1,cand2,cand3,cur_cand,prev_cand,prev_cand2; RATING_SET rating={0,0,0,0,0,0}; int pattern_total=0,pattern_size=1; //--- ZeroMemory(cand1); ZeroMemory(cand2); ZeroMemory(cand3); ZeroMemory(cur_cand); ZeroMemory(prev_cand); ZeroMemory(prev_cand2); //--- if(index2>0) pattern_size=2; if(index3>0) pattern_size=3; //--- if(pattern_size==1) IndexToPatternType(cand1,index1); else if(pattern_size==2) { IndexToPatternType(cand1,index1); IndexToPatternType(cand2,index2); } else if(pattern_size==3) { IndexToPatternType(cand1,index1); IndexToPatternType(cand2,index2); IndexToPatternType(cand3,index3); } //--- for(int i=m_range_total;i>5;i--) { if(pattern_size==1) { //--- Get the current candlestick type GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,cur_cand,i); // Current candlestick //--- if(cur_cand.m_type==cand1.m_type && cur_cand.m_bull==cand1.m_bull) { pattern_total++; GetCategory(symbol,timeframe,rating,i-3); } } else if(pattern_size==2) { //--- Get the current candlestick type GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,prev_cand,i); // Previous candlestick GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,cur_cand,i-1); // Current candlestick //--- if(cur_cand.m_type==cand1.m_type && cur_cand.m_bull==cand1.m_bull && prev_cand.m_type==cand2.m_type && prev_cand.m_bull==cand2.m_bull) { pattern_total++; GetCategory(symbol,timeframe,rating,i-4); } } else if(pattern_size==3) { //--- Get the current candlestick type GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,prev_cand2,i); // Previous candlestick GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,prev_cand,i-1); // Previous candlestick GetCandleType(symbol,timeframe,cur_cand,i-2); // Current candlestick //--- if(cur_cand.m_type==cand1.m_type && cur_cand.m_bull==cand1.m_bull && prev_cand.m_type==cand2.m_type && prev_cand.m_bull==cand2.m_bull && prev_cand2.m_type==cand3.m_type && prev_cand2.m_bull==cand3.m_bull) { pattern_total++; GetCategory(symbol,timeframe,rating,i-5); } } } //--- CoefCalculation(rating,pattern_total); }
These two method implementations contain one new method. This is the private method CoefCalculation():
//--- Calculates coefficients bool CoefCalculation(RATING_SET &rate,int found);
It processes all the results obtained when searching and testing patterns. Its arguments contain a pointer to the RATING_SET structure which is responsible for the collection of data concerning pattern efficiency testing results and the number of found patterns. All other parameters and properties of analyzed patterns are calculated in the CoefCalculation() method.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Calculating efficiency assessment coefficients | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CPattern::CoefCalculation(RATING_SET &rate,int found) { int sum1=0,sum2=0; sum1=rate.m_a_uptrend+rate.m_b_uptrend+rate.m_c_uptrend; sum2=rate.m_a_dntrend+rate.m_b_dntrend+rate.m_c_dntrend; //--- m_probability1=(found>0)?NormalizeDouble((double)sum1/found*100,2):0; m_probability2=(found>0)?NormalizeDouble((double)sum2/found*100,2):0; m_efficiency1=(found>0)?NormalizeDouble((m_k1*rate.m_a_uptrend+m_k2*rate.m_b_uptrend+m_k3*rate.m_c_uptrend)/found,3):0; m_efficiency2=(found>0)?NormalizeDouble((m_k1*rate.m_a_dntrend+m_k2*rate.m_b_dntrend+m_k3*rate.m_c_dntrend)/found,3):0; m_found=found; m_coincidence=((double)found/m_range_total*100); return(true); }
Coincidence
Returns the frequency of pattern occurrence. It has 3 method overloads for existing patterns TYPE_PATTERN, as well as for generated patterns consisting of 1-3 simple candlestick types.
//--- Returns the frequency of the pattern occurrence double Coincidence(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,TYPE_PATTERN pattern); double Coincidence(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index); double Coincidence(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2); double Coincidence(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,int index3);
Parameters
- symbol — Symbol selected for search.
- timeframe — Selected timeframe.
- pattern — Existing pattern type from TYPE_PATTERN.
- index,index1,index2,index3 — Index of the simple type candlestick (block 4 in Fig.1).
Return Value
The frequency of pattern occurrence in percent.
Implementation
Similar to the Found() method. The only difference is that it returns the value of the m_coincidence variable.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the frequency of the pattern occurrence | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CPattern::Coincidence(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,TYPE_PATTERN pattern) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,pattern); return(m_coincidence); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the frequency of the pattern occurrence | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CPattern::Coincidence(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,index1); return(m_coincidence); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the frequency of the pattern occurrence | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CPattern::Coincidence(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,index1,index2); return(m_coincidence); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the frequency of the pattern occurrence | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CPattern::Coincidence(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,int index3) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,index1,index2,index3); return(m_coincidence); }
Probability
Returns the percentage probability of movement after the given pattern. It has 3 method overloads for existing patterns TYPE_PATTERN, as well as for generated patterns consisting of 1-3 simple candlestick types.
//--- Returns the probability of movement after the given pattern double Probability(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,TYPE_PATTERN pattern,TYPE_TREND trend); double Probability(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index,TYPE_TREND trend); double Probability(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,TYPE_TREND trend); double Probability(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,int index3,TYPE_TREND trend);
Parameters
- symbol — Symbol selected for search.
- timeframe — Selected timeframe.
- pattern — Existing pattern type from TYPE_PATTERN.
- index,index1,index2,index 3— Index of the simple type candlestick (block 4 in Fig.1).
-
- trend— TYPE_TREND
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Trend type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum TYPE_TREND { UPPER, //Uptrend DOWN, //Downtrend FLAT //Flat }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Return Value
The percentage probability of movement after the given pattern.
Implementation
Similar to the Found() method. The only difference is that it returns the value of the m_probability1 or m_probability2 variable depending on the selected trend type.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the probability of movement after the given pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CPattern::Probability(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,TYPE_PATTERN pattern,TYPE_TREND trend) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,pattern); if(trend==UPPER) return(m_probability1); if(trend==DOWN) return(m_probability2); return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the probability of movement after the given pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CPattern::Probability(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,TYPE_TREND trend) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,index1); if(trend==UPPER) return(m_probability1); if(trend==DOWN) return(m_probability2); return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the probability of movement after the given pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CPattern::Probability(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,TYPE_TREND trend) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,index1,index2); if(trend==UPPER) return(m_probability1); if(trend==DOWN) return(m_probability2); return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the probability of movement after the given pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CPattern::Probability(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,int index3,TYPE_TREND trend) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,index1,index2,index3); if(trend==UPPER) return(m_probability1); if(trend==DOWN) return(m_probability2); return(0); }
Efficiency
Returns the pattern efficiency coefficient. It has 3 method overloads for existing patterns TYPE_PATTERN, as well as for generated patterns consisting of 1-3 simple candlestick types.
//--- Returns the pattern efficiency coefficient double Efficiency(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,TYPE_PATTERN pattern,TYPE_TREND trend); double Efficiency(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index,TYPE_TREND trend); double Efficiency(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,TYPE_TREND trend); double Efficiency(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,int index3,TYPE_TREND trend);
Parameters
- symbol — Symbol selected for search.
- timeframe — Selected timeframe.
- pattern — Existing pattern type from TYPE_PATTERN.
- index,index1,index2,index3 — Index of the simple type candlestick (block 4 in Fig.1).
- trend — trend type, TYPE_TREND
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Trend type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum TYPE_TREND { UPPER, //Uptrend DOWN, //Downtrend FLAT //Flat }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Return Value
The pattern efficiency coefficient.
Implementation
Similar to the Found() method. The only difference is that it returns the value of the m_efficiency1 or m_efficiency2 variable depending on the selected trend type.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the probability of movement after the given pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CPattern::Efficiency(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,TYPE_PATTERN pattern,TYPE_TREND trend) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,pattern); if(trend==UPPER) return(m_efficiency1); if(trend==DOWN) return(m_efficiency2); return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the probability of movement after the given pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CPattern::Efficiency(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,TYPE_TREND trend) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,index1); if(trend==UPPER) return(m_efficiency1); if(trend==DOWN) return(m_efficiency2); return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the probability of movement after the given pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CPattern::Efficiency(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,TYPE_TREND trend) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,index1,index2); if(trend==UPPER) return(m_efficiency1); if(trend==DOWN) return(m_efficiency2); return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the probability of movement after the given pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CPattern::Efficiency(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe,int index1,int index2,int index3,TYPE_TREND trend) { PatternStat(symbol,timeframe,index1,index2,index3); if(trend==UPPER) return(m_efficiency1); if(trend==DOWN) return(m_efficiency2); return(0); }
Practical use
Having considered tools for working with patterns, let us implement two indicators and an Expert Advisor to demonstrate library use examples.
CandleDetector
Let us start with the indicator which shows on a chart a candlestick of the selected type from the TYPE_CANDLESTICK enumeration. Create the Pattern folder in the Indicators folder. In this folder, create the CandleDetector.mq5 file in which the indicator will be created. Let us connect the Pattern.mqh library for pattern operations and set initial properties of the future indicator:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CandleDetector.mq5 | //| Copyright 2019, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.mql5.com/en/users/alex2356 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2019, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.mql5.com/en/users/alex2356" #property version "1.00" #property indicator_chart_window #property indicator_buffers 1 #property indicator_plots 1 #include <Pattern/Pattern.mqh> //+----------------------------------------------+ //| Indicator drawing parameters | //+----------------------------------------------+ //---- Drawing the indicator as a label #property indicator_type1 DRAW_ARROW //---- Indicator line width #property indicator_width1 1
The next step is to determine key settings which will affect the display of this or that candlestick type.
//+----------------------------------------------+ //| Indicator input parameters | //+----------------------------------------------+ input TYPE_CANDLESTICK CandleType=1; // Candlestick type input color LabelColor=clrCrimson; input double LongCoef=1.3; input double ShortCoef=0.5; input double DojiCoef=0.04; input double MaribozuCoef=0.01; input double SpinCoef=1; input double HummerCoef1=0.1; input double HummerCoef2=2; input int TrendPeriod=5;
Next, in the initialization, configure the indicator appearance and determine all the values from input parameters for search.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //---- Initialize variables of data calculation start min_rates_total=TrendPeriod+1; //---- Define the accuracy of indicator values to be displayed IndicatorSetInteger(INDICATOR_DIGITS,_Digits); //---- Set the dynamic array Signal[] as an indicator buffer SetIndexBuffer(0,Signal,INDICATOR_DATA); //---- Shift indicator 1 drawing start PlotIndexSetInteger(0,PLOT_DRAW_BEGIN,min_rates_total); //---- Set indexing of elements in buffers as in timeseries ArraySetAsSeries(Signal,true); //---- Set indicator values which will not be visible on the chart PlotIndexSetDouble(0,PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE,EMPTY_VALUE); //---- Indicator symbol PlotIndexSetInteger(0,PLOT_ARROW,108); //--- PlotIndexSetInteger(0,PLOT_LINE_COLOR,LabelColor); //---- Pat.Long_coef(LongCoef); Pat.Short_coef(ShortCoef); Pat.Doji_coef(DojiCoef); Pat.Maribozu_coef(MaribozuCoef); Pat.Spin_coef(SpinCoef); Pat.Hummer_coef1(HummerCoef1); Pat.Hummer_coef2(HummerCoef2); Pat.TrendPeriod(TrendPeriod); return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
Pay attention to the CandleType() method — it is used to search for the selected candlestick type on the chart.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator iteration function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnCalculate(const int rates_total, const int prev_calculated, const datetime &time[], const double &open[], const double &high[], const double &low[], const double &close[], const long &tick_volume[], const long &volume[], const int &spread[]) { //---- Check if there are enough bars for calculation if(rates_total<min_rates_total) return(0); //---- Declare local variables int limit,bar; //---- Set indexing of elements in arrays as in timeseries ArraySetAsSeries(low,true); //---- Calculate the 'first' starting number for the bars recalculation cycle if(prev_calculated>rates_total || prev_calculated<=0) // Check the first start of indicator calculation limit=rates_total-min_rates_total; // Starting index for calculating all bars else limit=rates_total-prev_calculated; // Starting index for calculating new bars //---- Main indicator calculation loop for(bar=limit; bar>=0; bar--) { Signal[bar]=0.0; if(Pat.CandleType(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,bar)==CandleType) Signal[bar]=low[bar]-200*_Point; } return(rates_total); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
The indicator operation example is shown in Fig.3 (Search for a Long type candlestick).
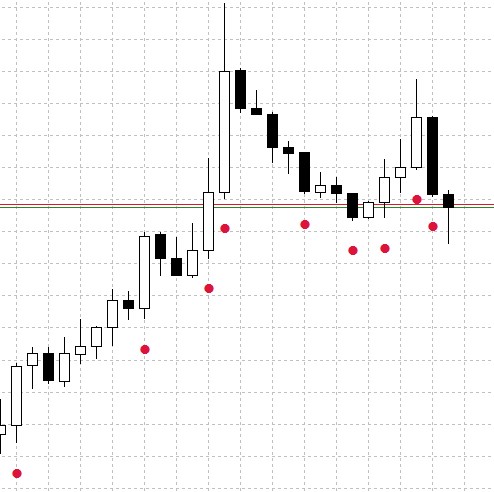
Fig.3 The CandleDetector indicator operation example.
PatternDetector
The second indicator will search for a specified pattern from the TYPE_PATTERN enumeration. The implementation is very similar to the previous one. This code differs in one input parameter and in the method used in the calculation part.
//+----------------------------------------------+ //| Indicator input parameters | //+----------------------------------------------+ input TYPE_PATTERN PatternType=1; // Pattern type input color LabelColor=clrCrimson; input double LongCoef=1.3; input double ShortCoef=0.5; input double DojiCoef=0.04; input double MaribozuCoef=0.01; input double SpinCoef=1; input double HummerCoef1=0.1; input double HummerCoef2=2; input int TrendPeriod=5; //--- CPattern Pat; double Signal[]; //---- Declare integer variables for the data calculation start int min_rates_total; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnInit() { //---- Initialize variables of data calculation start min_rates_total=TrendPeriod+2; //---- Define the accuracy of indicator values to be displayed IndicatorSetInteger(INDICATOR_DIGITS,_Digits); //---- Set SignUp[] dynamic array as an indicator buffer SetIndexBuffer(0,Signal,INDICATOR_DATA); //---- Shift indicator 1 drawing start PlotIndexSetInteger(0,PLOT_DRAW_BEGIN,min_rates_total); //---- Set indexing of elements in buffers as in timeseries ArraySetAsSeries(Signal,true); //---- Set indicator values which will not be visible on the chart PlotIndexSetDouble(0,PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE,EMPTY_VALUE); //---- Indicator symbol PlotIndexSetInteger(0,PLOT_ARROW,108); //--- PlotIndexSetInteger(0,PLOT_LINE_COLOR,LabelColor); //---- Pat.Long_coef(LongCoef); Pat.Short_coef(ShortCoef); Pat.Doji_coef(DojiCoef); Pat.Maribozu_coef(MaribozuCoef); Pat.Spin_coef(SpinCoef); Pat.Hummer_coef1(HummerCoef1); Pat.Hummer_coef2(HummerCoef2); Pat.TrendPeriod(TrendPeriod); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator iteration function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnCalculate(const int rates_total, const int prev_calculated, const datetime &time[], const double &open[], const double &high[], const double &low[], const double &close[], const long &tick_volume[], const long &volume[], const int &spread[]) { //---- Check if there are enough bars for calculation if(rates_total<min_rates_total) return(0); //---- Declare local variables int limit,bar; //---- Set indexing of elements in arrays as in timeseries ArraySetAsSeries(low,true); //---- Calculate the 'first' starting number for the bars recalculation cycle if(prev_calculated>rates_total || prev_calculated<=0) // Check the first start of indicator calculation limit=rates_total-min_rates_total; // Starting index for calculating all bars else limit=rates_total-prev_calculated; // Starting index for calculating new bars //---- Main indicator calculation loop for(bar=limit; bar>0; bar--) { Signal[bar]=0.0; if(Pat.PatternType(_Symbol,_Period,PatternType,bar)) Signal[bar]=low[bar]-200*_Point; } return(rates_total); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
PatternDetector operation results are shown in Fig.4 (search for the Engulfing - bullish pattern).
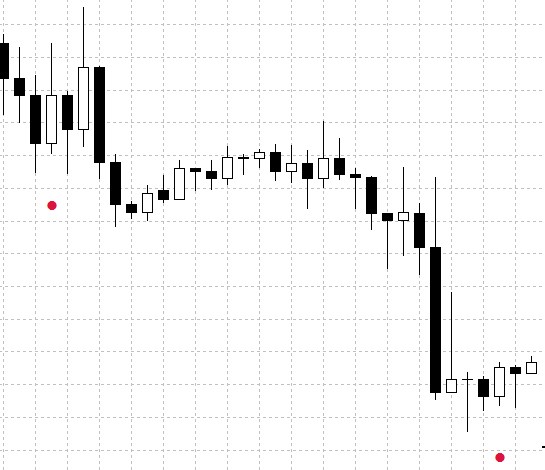
Fig.4 The PatternDetector indicator operation example.
Now let us create an Expert Advisor which can find patterns on the chart and open positions depending on the selected pattern. Individual pattern types can be used for each deal type. An additional mode will allow the choice between existing patterns and patterns generated using simple candlestick types.
Let us create the Pattern folder in the Experts folder and add the PatternExpert.mq5, in which the EA code will be written. At the first stage, connect the Pattern.mqh library for working with patterns and the Trade.mqh trade operations library. Declare class instances and introduce the PATTERN_MODE enumeration which enables switching between existing and generated patterns.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PatternExpert.mq5 | //| Copyright 2019, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.mql5.com/en/users/alex2356 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2018, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.mql5.com/en/users/alex2356" #property version "1.00" #include <Pattern/Pattern.mqh> #include "Trade.mqh" CTradeBase Trade; CPattern Pat; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Pattern search mode | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum PATTERN_MODE { EXISTING, GENERATED };
Now define the Expert Advisor input parameters. EA parameters are provided in the first block:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert Advisor input parameters | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ input string Inp_EaComment="Pattern Strategy"; // EA Comment input double Inp_Lot=0.01; // Lot input MarginMode Inp_MMode=LOT; // Money Management //--- EA parameters input string Inp_Str_label="===EA parameters==="; // Label input int Inp_MagicNum=1111; // Magic number input int Inp_StopLoss=40; // Stop Loss(points) input int Inp_TakeProfit=30; // Take Profit(points)
The second part contains settings and trading parameters.
//--- Trading parameters input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES Timeframe=PERIOD_CURRENT; // Current Timeframe input PATTERN_MODE PatternMode=0; // Pattern Mode input TYPE_PATTERN BuyPatternType=ENGULFING_BULL; // Buy Pattern Type input TYPE_PATTERN SellPatternType=ENGULFING_BEAR; // Sell Pattern Type input uint BuyIndex1=1; // BuyIndex of simple candle1 input uint BuyIndex2=0; // BuyIndex of simple candle2 input uint BuyIndex3=0; // BuyIndex of simple candle3 input uint SellIndex1=1; // SellIndex of simple candle1 input uint SellIndex2=0; // SellIndex of simple candle2 input uint SellIndex3=0; // SellIndex of simple candle3 input double LongCoef=1.3; // Long candle coef input double ShortCoef=0.5; // Short candle coef input double DojiCoef=0.04; // Doji candle coef input double MaribozuCoef=0.01; // Maribozu candle coef input double SpinCoef=1; // Spin candle coef input double HummerCoef1=0.1; // Hummer candle coef1 input double HummerCoef2=2; // Hummer candle coef2 input int TrendPeriod=5; // Trend Period
Let's consider some of these parameters in more detail:
- Current Timeframe — timeframe selected for operations. Enables timeframe selection during optimization. The current chart timeframe is selected by default.
- Pattern Mode — pattern selection mode. EXISTING — existing patterns; two settings Buy Pattern Type and Sell Pattern Type are applicable in this mode. GENERATED - generated patterns. In this mode, Buy/Sell Pattern Type settings are ignored and BuyIndex1-3 and SellIndex1-3 are used instead.
- Buy Pattern Type/ Sell Pattern Type — select patterns for opening appropriate trading operations.
- BuyIndex1-3/SellIndex1-3 — select a pattern generated of simple candlestick types (Fig.1 Block 4), upon the emergence of which a long/short position will be opened.
Other parameters are similar to the above considered indicators. In addition to checks, set in the initialization blocks the Trend Period value which affects on-chart detection of patterns.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- Checking connection to the trade server if(!TerminalInfoInteger(TERMINAL_CONNECTED)) { Print(Inp_EaComment,": No Connection!"); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- Checking automated trading permission if(!TerminalInfoInteger(TERMINAL_TRADE_ALLOWED)) { Print(Inp_EaComment,": Trade is not allowed!"); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- Pat.TrendPeriod(TrendPeriod); //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
The calculation part is easy to understand. Let us consider buy and sell signal search functions.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { if(!Trade.IsOpenedByMagic(Inp_MagicNum)) { //--- Opening an order if there is a buy signal if(BuySignal()) Trade.BuyPositionOpen(Symbol(),Inp_Lot,Inp_StopLoss,Inp_TakeProfit,Inp_MagicNum,Inp_EaComment); //--- Opening an order if there is a sell signal if(SellSignal()) Trade.SellPositionOpen(Symbol(),Inp_Lot,Inp_StopLoss,Inp_TakeProfit,Inp_MagicNum,Inp_EaComment); } }
These functions are similar and thus let us consider one of them BuySignal(), which searches for a buy signal.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Buy conditions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool BuySignal() { if(PatternMode==0) { if(BuyPatternType==NONE) return(false); if(Pat.PatternType(_Symbol,Timeframe,BuyPatternType,1)) return(true); } else if(PatternMode==1) { if(BuyIndex1>0 && BuyIndex2==0 && BuyIndex3==0) { if(Pat.PatternType(_Symbol,Timeframe,BuyIndex1,1)) return(true); } else if(BuyIndex1>0 && BuyIndex2>0 && BuyIndex3==0) { if(Pat.PatternType(_Symbol,Timeframe,BuyIndex1,BuyIndex2,1)) return(true); } else if(BuyIndex1>0 && BuyIndex2>0 && BuyIndex3>0) { if(Pat.PatternType(_Symbol,Timeframe,BuyIndex1,BuyIndex2,BuyIndex3,1)) return(true); } } return(false); }
The function contains a check of the currently selected mode, existing patterns or generated patterns. Input parameters are selected accordingly: TYPE_PATTERN or a set of indexes of the generated pattern.
Let us test and optimize the resulting Expert Advisor in two modes: with existing patterns from the TYPE_PATTERN enumeration and with generated patterns consisting of simple candlestick types shown in Fig.1 Block 4.
The Expert Advisor will be tested with the following parameters:
- Interval: for the Uptrend mode 01.01.2018 — 15.03.2018.
- Currency pair: EURUSD.
- Trading mode: No delay. These are not high-frequency trading strategies, so the effect of delays is very small.
- Testing: 1 Minute OHLC.
- Initial deposit: 1000 USD.
- Leverage: 1:500.
- Server: MetaQuotes-Demo.
- Quotes: 5-digit.
Generated Patterns mode.
Let us determine parameters to be tested and optimized.
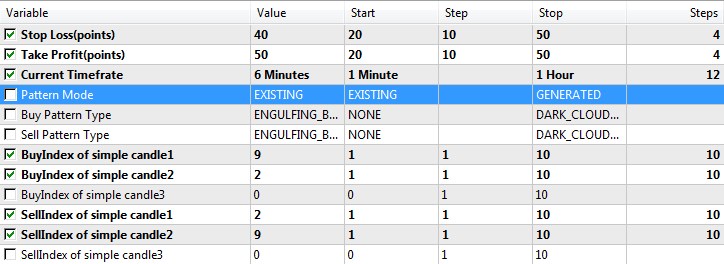
Fig.5 Set of parameters for optimization in the Generated Patterns mode.
Fig.5 shows testing and optimization conditions. The best parameters obtained as a result of testing are shown in the second Value column. The back testing results and chart are shown in Figure 6 below.
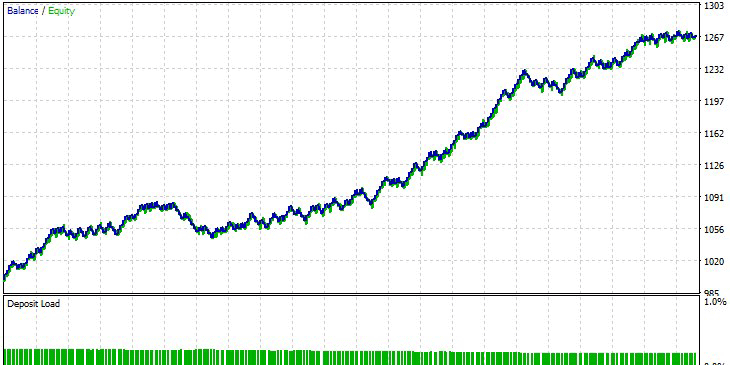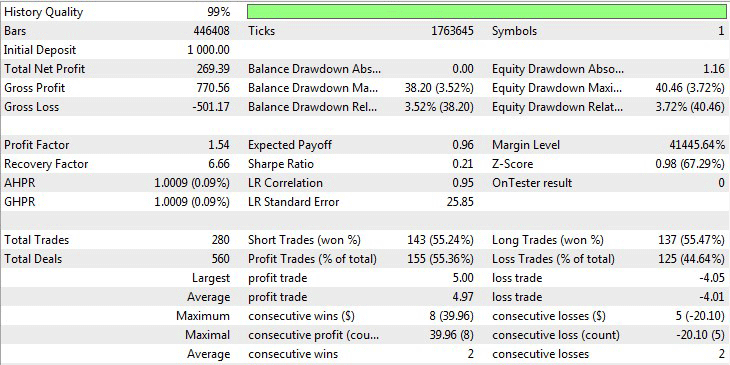
Fig.6 Best parameter testing results in the Generated Patterns mode.
Existing Patterns mode.
Set parameters for testing and optimization.
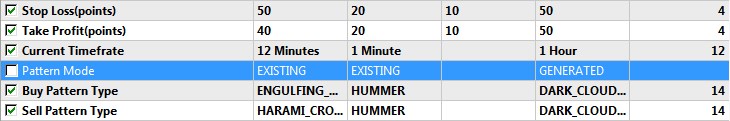
Fig.7 Set of parameters for optimization in the Existing Patterns mode.
Again, parameters of the best optimization result are shown in the second column. Now let us perform a single test. The results are shown below, in Figure 8.
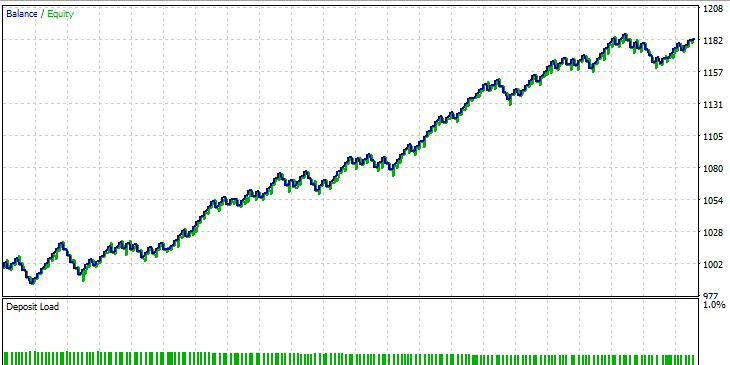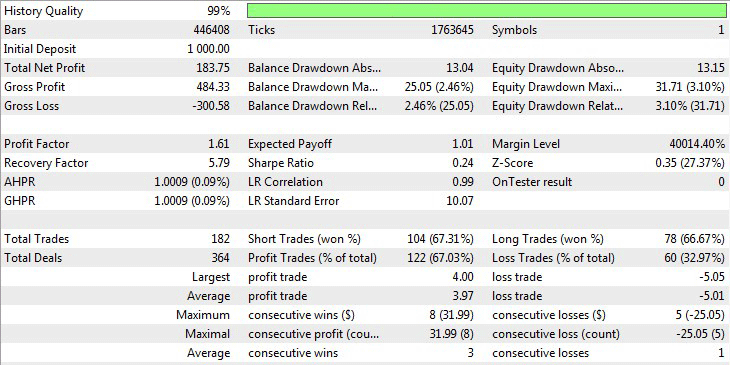
Fig.8 Best parameter testing results in the Existing Patterns mode.
Conclusions
The archive attached below contains all described files properly arranged into folders. For a correct operation, you should save the MQL5 folder to the terminal's root directory. To find this root folder in which the MQL5 folder is located, press Ctrl+Shift+D in MetaTrader 5 or use the context menu as shown in Figure 9.
Fig.9 How to find the MQL5 folder in the MetaTrader5 root directory.
Programs used in the article
| # |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Pattern.mqh | Library | Library for working with patterns |
| 2 | CandleDetector.mq5 | Indicator | Candlestick searching indicator |
| 3 | PatternDetector.mq5 | Indicator | Pattern searching indicator |
| 4 | PatternExpert.mq5 | Expert Advisor | A trading Expert Advisor working with patterns |
| 5 | Trade.mqh | Library | Class of trading functions |
Translated from Russian by MetaQuotes Ltd.
Original article: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/5751
Warning: All rights to these materials are reserved by MetaQuotes Ltd. Copying or reprinting of these materials in whole or in part is prohibited.
This article was written by a user of the site and reflects their personal views. MetaQuotes Ltd is not responsible for the accuracy of the information presented, nor for any consequences resulting from the use of the solutions, strategies or recommendations described.
 Extracting structured data from HTML pages using CSS selectors
Extracting structured data from HTML pages using CSS selectors
- Free trading apps
- Over 8,000 signals for copying
- Economic news for exploring financial markets
You agree to website policy and terms of use
Great work, Alexander..
I am a newbie in mql5 programming. I've tried to compile the PatternAnalyzer.mq5 but it ended up with 2 error found on 'method' which took place in Menultem.mqh.
First error on 'method' was "undeclared identifier", and the second was "some operator expected".
Could you help me please..
I do appreciate your work. Thank you..
Hi Alexander! I am grateful for your voluntary work. Please on install the MQL5 file I noticed there are other files in the
folder like include, image expert and indicator. My question is should we just copy MQL5 folder to the root directory
or should we copy out expert to expert and indicator to indicator etc..
Thanks
is this transferrable to mq4? Will the libraries work the same in mq4/mt4?
I love the article too. Thanks for your contribution!
Good evening.
Unfortunately I couldn't get it to work on my MT5.
I did the right procedure, but it doesn't appear in the MT% to test.
Hi Alexander, i am grateful if you give us a real data backtesting because i was tested your's ea and it doesn't working like you post..
Here the screenshot of it..