
Receitas MQL5: Calendário Econômico
Introdução
O terminal MetaTrader 5 e a linguagem de programação MQL5 estão em constante evolução, expandindo as possibilidades de análise de mercados, de criação de robôs de negociação mais complexos e muito mais. Uma das novas ferramentas do terminal é o calendário econômico que nos permite trabalhar quer seja manualmente ou com robôs.
É preciso dizer que o calendário embutido é bastante flexível. Ele pode ser configurado na guia Calendário do terminal, incorporado em seu site ou também baixado na versão móvel. Mas nós, como traders algorítmicos, estamos mais interessados nas funcionalidades programáticas dessa ferramenta.
E neste artigo vou tentar cobri-las desde nossa perspectiva.
1. Que encontramos sobre o calendário econômico na documentação?
Primeiro, demos uma vista de olhos ao material de ajuda. Sem entrar em pormenores, não vejo nenhuma dificuldade em particular. Normalmente, os recursos MQL5 incluem guias apresentados sistematicamente e ilustrados com pequenos exemplos.
1.1 Funções do calendário econômico
A documentação descreve 10 funções de calendário:
- CalendarCountryById();
- CalendarEventById();
- CalendarValueById();
- CalendarCountries();
- CalendarEventByCountry();
- CalendarEventByCurrency();
- CalendarValueHistoryByEvent();
- CalendarValueHistory();
- CalendarValueLastByEvent();
- CalendarValueLast().
De forma geral, estas funções devolvem propriedades de calendário (país, evento, valor) ou valores históricos de eventos.
1.2 Estruturas do calendário econômico
O desenvolvedor sugere o uso de 3 estruturas: MqlCalendarCountry, MqlCalendarEvent, MqlCalendarValue.
1.2.1 MqlCalendarCountry
Esta estrutura mostra informações detalhadas sobre o país em cujos eventos estamos interessados.
Revisei o calendário no site junto a várias corretoras: existem informações para 21 países, a UE e o mundo (eventos globais).
[id] [name] [code] [currency] [currency_symbol] [url_name] [reserved] [ 0] 999 "European Union" "EU" "EUR" "€" "european-union" ... [ 1] 124 "Canada" "CA" "CAD" "$" "canada" ... [ 2] 36 "Australia" "AU" "AUD" "$" "australia" ... [ 3] 554 "New Zealand" "NZ" "NZD" "$" "new-zealand" ... [ 4] 392 "Japan" "JP" "JPY" "¥" "japan" ... [ 5] 156 "China" "CN" "CNY" "¥" "china" ... [ 6] 276 "Germany" "DE" "EUR" "€" "germany" ... [ 7] 250 "France" "FR" "EUR" "€" "france" ... [ 8] 380 "Italy" "IT" "EUR" "€" "italy" ... [ 9] 76 "Brazil" "BR" "BRL" "R$" "brazil" ... [10] 344 "Hong Kong" "HK" "HKD" "HK$" "hong-kong" ... [11] 702 "Singapore" "SG" "SGD" "R$" "singapore" ... [12] 484 "Mexico" "MX" "MXN" "Mex$" "mexico" ... [13] 710 "South Africa" "ZA" "ZAR" "R" "south-africa" ... [14] 356 "India" "IN" "INR" "₹" "india" ... [15] 578 "Norway" "NO" "NOK" "Kr" "norway" ... [16] 0 "Worldwide" "WW" "ALL" "" "worldwide" ... [17] 840 "United States" "US" "USD" "$" "united-states" ... [18] 826 "United Kingdom" "GB" "GBP" "£" "united-kingdom" ... [19] 756 "Switzerland" "CH" "CHF" "₣" "switzerland" ... [20] 410 "South Korea" "KR" "KRW" "₩" "south-korea" ... [21] 724 "Spain" "ES" "EUR" "€" "spain" ... [22] 752 "Sweden" "SE" "SEK" "Kr" "sweden" ...
É um pouco estranho que a Rússia não esteja nesta lista. Esperemos que seja incluída em breve.
1.2.2 MqlCalendarEvent
Esta estrutura oferece informações detalhadas sobre o evento em si. É necessário dizer que esta estrutura tem bastantes propriedades. É possivelmente uma boa ferramenta para uma análise fundamental geral. Mais tarde veremos como podemos filtrar os eventos de acordo com um ou outro critério.
1.2.3 MqlCalendarValue
Esta estrutura oferece informações detalhadas sobre o valor do evento. É curioso que existam valores do período passado, do atual e do previsto.
Existem várias nuances ao trabalhar usando essa estrutura.
Nos campos actual_value, forecast_value, prev_value e revised_prev_value os valores são armazenados aumentados um milhão de vezes. Se o valor do campo não estiver definido, ele armazenará o valor LONG_MIN (-9223372036854775808). Mas se estiver definido, para obter seu valor, deveremos dividir o valor do campo por 1 000 000 (milhão).
Na verdade, a estrutura MqlCalendarValue tem seus próprios métodos, estes facilitam o manuseio dos valores dos campos especificados.
Os métodos podem ser divididos em 2 grupos.
O primeiro grupo verifica se um determinado valor está definido:
HasActualValue(void) — returns true if the actual value is set; otherwise returns false HasForecastValue(void) — returns true if the forecast value is set; otherwise returns false HasPreviousValue(void) — returns true if the previous value is set; otherwise returns false HasRevisedValue(void) — returns true if the revised value is set; otherwise returns false
O segundo grupo recebe diretamente um ou outro valor:
GetActualValue(void) — returns the actual value of an event (double) or nan if the relevant value is not set GetForecastValue(void) — returns the forecast value of an event (double) or nan if the relevant value is not set GetPreviousValue(void) — returns the previous value of an event (double) or nan if the relevant value is not set GetRevisedValue(void) — returns the revised value of an event (double) or nan if the relevant value is not set
Demonstraremos e exemplificaremos como a estrutura MqlCalendarValue recebe e verifica os valores dos campos. Peguemos na última Decisão da Taxa de Juros do Banco do Japão. Com o script Test_empty_value.mq5, que tem três maneiras de obter o valor, imprimimos no log a informações do nosso interesse.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| LongDouble | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ union LongDouble { long long_value; double double_value; }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- Bank of Japan (BoJ) Interest Rate Decision on 22 Sep 2021 02:47 GMT ulong event_id = 392060022; // "boj-interest-rate-decision" MqlCalendarValue values[]; datetime date_from, date_to; date_from = D'22.09.2021'; date_to = date_from + PeriodSeconds(PERIOD_D1); if(::CalendarValueHistoryByEvent(event_id, values, date_from, date_to)) { LongDouble forecast_val; //--- 1) "forecast_value" field forecast_val.long_value = values[0].forecast_value; ::PrintFormat("\"forecast_value\" field: %I64d", forecast_val.long_value); //--- 2) MqlCalendarValue::GetForecastValue() forecast_val.double_value = values[0].GetForecastValue(); ::PrintFormat("MqlCalendarValue::GetForecastValue(): %g", forecast_val.double_value); //--- 3) MqlCalendarValue::HasForecastValue() if(!values[0].HasForecastValue()) ::PrintFormat("MqlCalendarValue::HasForecastValue(): %s", (string)false); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
A primeira abordagem serve para obter o valor previsto. Como não houve previsão, recebemos LONG_MIN (-9223372036854775808). Já a segunda abordagem usa o método da estrutura MqlCalendarValue::GetForecastValue(). Ele retornará nan. A terceira abordagem é, talvez, a mais prudente, e verificará se existe algum valor de previsão.
Depois de executar o script, no log aparecerão as seguintes entradas:
GR 0 21:23:36.076 Test_empty_value (USDCAD,H1) "forecast_value" field: -9223372036854775808 LH 0 21:23:36.080 Test_empty_value (USDCAD,H1) MqlCalendarValue::GetForecastValue(): nan HM 0 21:23:36.080 Test_empty_value (USDCAD,H1) MqlCalendarValue::HasForecastValue(): false
1.2.4 Conexões estruturais
As estruturas estão interligadas pelas seguintes relações (Fig. 1).
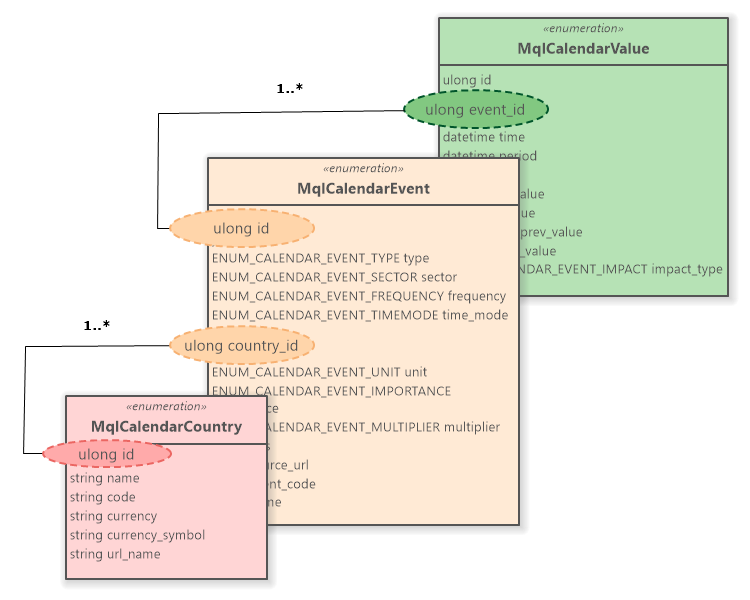
Fig. 1. Relações de estruturas de calendário
A estrutura MqlCalendarCountry está associada com MqlCalendarEvent por meio do identificador de país. Formulário de relacionamento um-para-muitos (1..*).
A estrutura MqlCalendarEvent está associada ao MqlCalendarValue por meio de um identificador de evento. Formulário de relacionamento um-para-muitos (1..*).
1.3 Erros
O desenvolvedor aloca um grupo de erros de tempo de execução ao trabalhar usando o calendário econômico, que inclui:
| Calendário econômico | ||
|---|---|---|
| ERR_CALENDAR_MORE_DATA | 5400 | Tamanho da matriz não é grande o suficiente para obter descrições de todos os valores |
| ERR_CALENDAR_TIMEOUT | 5401 | Limite de tempo de solicitação excedido |
| ERR_CALENDAR_NO_DATA | 5402 | País não encontrado |
2.Estruturas auxiliares e classe CiCalendarInfo
Meus sentimentos estão mais do lado da POO. Por isso, apresentarei um exemplo de uma classe que oferece acesso às propriedades do calendário.
Aqui eu gostaria de salientar que o calendário é uma coisa bastante heterogênea. Não sou um especialista em bancos de dados, mas pelo que entendi, o calendário está na forma de um banco de dados relacional com várias tabelas.
A implementação de classe CiCalendarInfo sugerida, além de obter propriedades, também visa criar uma série temporal do evento selecionado.
Primeiro, vamos ver as estruturas auxiliares.
2.1 Estrutura da série temporal
Como vamos encontrar informações para SR (série temporal), teremos que criar sua entidade programática. A estrutura SiTimeSeries é responsável por isso.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Time series structure | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ struct SiTimeSeries { private: bool init; // is initialized? uint size; datetime timevals[]; // time values double datavals[]; // data values string name; // ts name public: //--- constructor void SiTimeSeries(void); //--- destructor void ~SiTimeSeries(void); //--- copy consructor void SiTimeSeries(const SiTimeSeries &src_ts); //--- assignment operator void operator=(const SiTimeSeries &src_ts); //--- equality operator bool operator==(const SiTimeSeries &src_ts); //--- indexing operator SiTsObservation operator[](const uint idx) const; //--- initialization bool Init(datetime &ts_times[], const double &ts_values[], const string ts_name); //--- get series properties bool GetSeries(datetime &dst_times[], double &dst_values[], string &dst_name); bool GetSeries(SiTsObservation &dst_observations[], string &dst_name); //--- service bool IsInit(void) const { return init; }; uint Size(void) const { return size; }; void Print(const int digs = 2, const uint step = 0); }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Os elementos mais importantes desta estrutura são as matrizes timevals[] e datavals[]. O primeiro inclui uma série de tempos e o segundo, uma série de valores.
A estrutura é implementada para que seus elementos fiquem em uma seção privada. Ou seja, uma vez criada, a série temporal não pode ser modificada.
Vamos trabalhar usando a estrutura de série temporal no exemplo a seguir. O script Teste_TS.mq5 obtém dados não agrícolas dos EUA de 1º de janeiro de 2016 a 1º de novembro de 2021 e os exibe em um gráfico. Vamos fazer com que haja duas curvas no gráfico - valores reais e previstos. Vamos considerar o período de relatório do evento como uma escala de tempo.
Após executar o script, obteremos, primeiramente, a exibição dos valores da série temporal no log e, em segundo lugar, o desenho do diagrama no gráfico (Fig. 2).
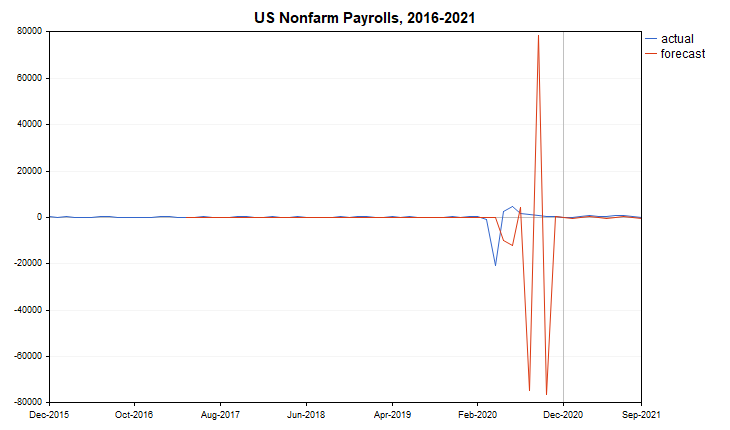
Fig. 2. Dados não agrícolas dos EUA (2016-2021)
O script tem algumas linhas onde os valores da série temporal estão sendo preenchidos:
//--- prepare time and data values for the timeseries for(int v_idx = 0; v_idx < nfp_values_size; v_idx++) { MqlCalendarValue curr_nfp_val = nfp_values[v_idx]; datetime curr_nfp_time = curr_nfp_val.period; timevals[v_idx] = curr_nfp_time; double curr_nfp_dataval = curr_nfp_val.GetActualValue(); datavals1[v_idx] = curr_nfp_dataval; curr_nfp_dataval = curr_nfp_val.GetForecastValue(); datavals2[v_idx] = curr_nfp_dataval; }
Com a função MqlCalendarValue::GetActualValue() e MqlCalendarValue::GetForecastValue() obtemos os valores de que precisamos de uma só vez.
2.2 Estrutura de observação da série temporal
Qualquer série temporal consiste em observações. Para a observação, foi criada a seguinte estrutura simples - SiTsObservation.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Time series observation structure | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ struct SiTsObservation { datetime time; // timestamp double val; // value //--- constructor void SiTsObservation(void): time(0), val(EMPTY_VALUE) {} }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
O operador de indexação é declarado na estrutura de série temporal SiTimeSeries. Retorna a observação desejada da série de acordo com o índice. No exemplo acima, onde foram renderizados os valores não agrícolas, a linha é composta por 70 valores. Então, a primeira e a última observação podem ser obtidas assim:
SiTsObservation first_observation, last_observation; first_observation = nfp_ts1[0]; last_observation = nfp_ts1[nfp_values_size - 1]; string time_str = ::TimeToString(first_observation.time, TIME_DATE); string data_str = ::DoubleToString(first_observation.val, 0); ::PrintFormat("\nFirst observation: %s, %s", time_str, data_str); time_str = ::TimeToString(last_observation.time, TIME_DATE); data_str = ::DoubleToString(last_observation.val, 0); ::PrintFormat("Last observation: %s, %s", time_str, data_str);
Após executar as linhas de código indicadas no log, receberemos as seguintes entradas:
KJ 0 21:27:16.386 Test_ts (USDCAD,H1) First observation: 2015.12.01, 292 HO 0 21:27:17.225 Test_ts (USDCAD,H1) Last observation: 2021.09.01, 194
2.3 Classe CiCalendarInfo
Vamos manter a continuidade e assumir que esta classe é criada para facilitar o acesso às propriedades do calendário e a recuperação dos valores dos eventos (parecido com as classes de negociação CAccountInfo, CSymbolInfo, etc.).
A declaração da classe é mostrada abaixo.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class CiCalendarInfo. | //| Appointment: Class for access to calendar info. | //| Derives from class CObject. | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CiCalendarInfo : public CObject { //--- === Data members === --- protected: string m_currency; ulong m_country_id; MqlCalendarCountry m_country_description; ulong m_event_id; MqlCalendarEvent m_event_description; static MqlCalendarCountry m_countries[]; bool m_is_init; //--- === Methods === --- public: //--- constructor/destructor void CiCalendarInfo(void); void ~CiCalendarInfo(void) {}; //--- initialization bool Init ( const string currency = NULL, // country currency code name const ulong country_id = WRONG_VALUE, // country ID const ulong event_id = WRONG_VALUE, // event ID const bool to_log = true // to log? ); void Deinit(void); //--- Сalendar structures descriptions bool CountryDescription(MqlCalendarCountry &country, const bool to_log = false); bool EventDescription(MqlCalendarEvent &event, const bool to_log = false); bool ValueDescription(ulong value_id, MqlCalendarValue &value, const bool to_log = false); bool EventsByCountryDescription(MqlCalendarEvent &events[], const bool to_log = false); bool EventsByCurrencyDescription(MqlCalendarEvent &events[], const bool to_log = false); bool EventsBySector(const ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_SECTOR event_sector, MqlCalendarEvent &events[], const bool to_log = false); //--- Сalendar enum descriptions string EventTypeDescription(const ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_TYPE event_type); string EventSectorDescription(const ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_SECTOR event_sector); string EventFrequencyDescription(const ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_FREQUENCY event_frequency); string EventTimeModeDescription(const ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_TIMEMODE event_time_mode); string EventUnitDescription(const ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_UNIT event_unit); string EventImportanceDescription(const ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPORTANCE event_importance); string EventMultiplierDescription(const ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_MULTIPLIER event_multiplier); string ValueImpactDescription(const ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPACT event_impact); //--- history bool ValueHistorySelectByEvent ( MqlCalendarValue &values[], // array for value descriptions datetime datetime_from, // left border of a time range datetime datetime_to = 0 // right border of a time range ) const; bool ValueHistorySelectByEvent ( SiTimeSeries &dst_ts, // timeseries for value descriptions datetime datetime_from, // left border of a time range datetime datetime_to = 0 // right border of a time range ) const; bool ValueHistorySelect ( MqlCalendarValue &values[], // array for value descriptions datetime datetime_from, // left border of a time range datetime datetime_to = 0 // right border of a time range ) const; bool ValueHistorySelect ( SiTimeSeries &dst_ts[], // array of timeseries for value descriptions datetime datetime_from, // left border of a time range datetime datetime_to = 0 // right border of a time range ); //--- the calendar database status int ValueLastSelectByEvent ( ulong& change_id, // Calendar change ID MqlCalendarValue& values[] // array for value descriptions ) const; int ValueLastSelect ( ulong& change_id, // Calendar change ID MqlCalendarValue& values[] // array for value descriptions ) const; //--- countries and continents bool GetCountries(CArrayString &countries_arr); bool GetCountries(MqlCalendarCountry &countries[]); bool GetUniqueContinents(string &continents[]); bool GetCountriesByContinent(const ENUM_CONTINENT src_continent, CArrayString &countries_arr); string GetCountryNameById(const ulong country_id); //--- events bool GetEventsByName(CArrayString &events_arr, const string name = NULL); bool GetEventsByName(MqlCalendarEvent &events[], const string name = NULL); bool FilterEvents(MqlCalendarEvent &filtered_events[], MqlCalendarEvent &src_events[], const ulong filter); //--- print void PrintCountryDescription(const MqlCalendarCountry &country); void PrintEventDescription(const MqlCalendarEvent &event); void PrintValueDescription(const MqlCalendarValue &value); //--- private: bool ValidateProperties(void); bool CountryById(const ulong country_id); bool EventId(void); }; MqlCalendarCountry CiCalendarInfo::m_countries[];
Esta classe consiste nos seguintes membros-dados:
- m_currency — código de moeda do país;
- m_country_id — identificador de país de acordo com o padrão ISO 3166-1;
- m_country_description — descrição do país;
- m_event_id — identificador de evento;
- m_event_description — descrição de evento;
- m_countries — matriz que contém as descrições dos países disponíveis no calendário;
- m_is_init — recurso de inicialização.
Os membros-dados m_currency, m_country_id e m_event_id — conjunto de critérios para a criação de solicitações para recuperar informações do banco de dados do calendário.
Os membros-dados m_country_description e m_event_description oferecem acesso rápido às descrições, se o país e o evento forem conhecidos.
Os membros-dados m_countries são estáticos. Como as informações do país são constantes, não precisam ser solicitadas sempre que um novo objeto CiCalendarInfo é inicializado.
Quanto aos métodos, mencionarei alguns.
2.3.1 Método de inicialização
Com este método começamos a trabalhar utilizando o objeto de classe. Ele é obrigatório para receber informações de calendário. O método toma como parâmetros um conjunto de critérios (código de moeda, identificador de país, identificador de evento) e um parâmetro para permitir exibir no log uma inicialização que tenha ocorrido. Os critérios permitem acessar de forma mais concreta o calendário.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Initialization | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CiCalendarInfo::Init(const string currency = NULL, // country currency code name const ulong country_id = WRONG_VALUE, // country ID const ulong event_id = WRONG_VALUE, // event ID const bool to_log = true // to log? ) { //--- check reinitialization if(m_is_init) { ::PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__ + ": CiCalendarInfo object already initialized!"); return false; } //--- check countries int countries_cnt = ::ArraySize(m_countries); if(countries_cnt < 1) { ::ResetLastError(); countries_cnt = ::CalendarCountries(m_countries); if(countries_cnt < 1) { ::PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__ + ": CalendarCountries() returned 0! Error %d", ::GetLastError()); return false; } } for(int c_idx = 0; c_idx < countries_cnt; c_idx++) { MqlCalendarCountry curr_country = m_countries[c_idx]; //--- check currency if(!::StringCompare(curr_country.currency, currency)) { m_currency = currency; } //--- check country if(country_id != WRONG_VALUE) if(curr_country.id == country_id) { m_country_id = country_id; } } //--- check event if(event_id != WRONG_VALUE) { m_event_id = event_id; } //--- validate properties if(!this.ValidateProperties()) return false; //--- if(to_log) { ::Print("\n---== New Calendar Info object ==---"); if(m_currency != NULL) ::PrintFormat(" Currency: %s", m_currency); if(m_country_id != WRONG_VALUE) ::PrintFormat(" Country id: %I64u", m_country_id); if(m_event_id != WRONG_VALUE) ::PrintFormat(" Event id: %I64u", m_event_id); } m_is_init = true; return true; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Vamos ilustrar como o método funciona usando um script simples - Test_initialization.mq5.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- TRUE //--- 1) all currencies, all countries, all events CiCalendarInfo calendar_info1; bool is_init = calendar_info1.Init(); //--- 2) EUR, all countries, all events CiCalendarInfo calendar_info2; is_init = calendar_info2.Init("EUR"); //--- 3) EUR, Germany, all events CiCalendarInfo calendar_info3; is_init = calendar_info3.Init("EUR", 276); //--- 4) EUR, Germany, HICP m/m CiCalendarInfo calendar_info4; is_init = calendar_info4.Init("EUR", 276, 276010022); //--- FALSE //--- 5) EUR, Germany, nonfarm-payrolls CiCalendarInfo calendar_info5; is_init = calendar_info5.Init("EUR", 276, 840030016); //--- 6) EUR, US, nonfarm-payrolls CiCalendarInfo calendar_info6; is_init = calendar_info6.Init("EUR", 840, 840030016); //--- 7) EUR, all countries, nonfarm-payrolls CiCalendarInfo calendar_info7; is_init = calendar_info7.Init("EUR", WRONG_VALUE, 840030016); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Depois de executar o script, obtemos a seguinte entrada no log:
DO 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) ---== New Calendar Info object ==--- GE 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) LL 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) ---== New Calendar Info object ==--- FI 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) Currency: EUR GO 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) LJ 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) ---== New Calendar Info object ==--- FS 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) Currency: EUR KO 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) Country id: 276 CH 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) PI 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) ---== New Calendar Info object ==--- JF 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) Currency: EUR OL 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) Country id: 276 HD 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) Event id: 276010022 HR 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) CiCalendarInfo::ValidateProperties: failed! Country ids must be the same! OP 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) CiCalendarInfo::ValidateProperties: failed! Currencies must be the same! GP 0 21:30:19.703 Test_initialization (USDCAD,H1) CiCalendarInfo::ValidateProperties: failed! Currencies must be the same!
O método de inicialização verifica se os parâmetros definidos pertencem a um país ou moeda. Por isso as seguintes combinações retornam "falso": EUR – Germany - nonfarm-payrolls, EUR – US - nonfarm-payrolls e EUR – all countries - nonfarm-payrolls.
Além disso, é necessário dizer que no método de inicialização no início há proteção contra reinicialização (reinicialização). O objeto de calendário ainda pode ser reinicializado, mas primeiro o método de desinicialização deve ser chamado. Por exemplo, primeiro definimos que o objeto calendário coleta informações sobre eventos com a moeda Euro. E então é preciso reorientar o objeto para a moeda USD. No script Test_reinitialization.mq5 é ilustrada a solução incorreta e correta deste problema.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- ERROR CiCalendarInfo calendar_info1; bool is_init = calendar_info1.Init("EUR"); is_init = calendar_info1.Init("USD"); //--- OK CiCalendarInfo calendar_info2; is_init = calendar_info2.Init("EUR"); calendar_info2.Deinit(); is_init = calendar_info2.Init("USD"); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
No primeiro caso errado, veremos no log esta entrada:
MP 0 21:34:19.397 Test_reinitialization (USDCAD,H1) FQ 0 21:34:19.397 Test_reinitialization (USDCAD,H1) ---== New Calendar Info object ==--- HO 0 21:34:19.397 Test_reinitialization (USDCAD,H1) Currency: EUR KI 0 21:34:19.397 Test_reinitialization (USDCAD,H1) CiCalendarInfo::Init: CiCalendarInfo object already initialized! EI 0 21:34:19.397 Test_reinitialization (USDCAD,H1) NO 0 21:34:19.397 Test_reinitialization (USDCAD,H1) ---== New Calendar Info object ==--- PF 0 21:34:19.397 Test_reinitialization (USDCAD,H1) Currency: EUR QL 0 21:34:19.397 Test_reinitialization (USDCAD,H1) RD 0 21:34:19.397 Test_reinitialization (USDCAD,H1) ---== New Calendar Info object ==--- DS 0 21:34:19.397 Test_reinitialization (USDCAD,H1) Currency: USD
2.3.2 Métodos para obter descrições de estruturas de calendário
Esses métodos são wrappers até certo ponto e permitem que você chame funções de calendário padrão. Os métodos CiCalendarInfo::CountryDescription() e CiCalendarInfo::EventDescription() retornam as descrições do país e do evento, caso tenham sido validadas quando o objeto calendário foi inicializado.
Além disso, os métodos permitem que você registre no log uma descrição da propriedade solicitada.
Vamos ilustrar como funcionam os métodos que recebem descrições, usando um script simples - Test_structures_descriptions.mq5.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- 1) events by country CiCalendarInfo calendar_info; ulong country_id = 276; // Germany if(calendar_info.Init(NULL, country_id)) { MqlCalendarEvent events[]; if(calendar_info.EventsByCountryDescription(events)) { Print("\n---== Events selected by country ==---"); PrintFormat(" Country id: %I64u", country_id); PrintFormat(" Events number: %d", ::ArraySize(events)); } } calendar_info.Deinit(); //--- 2) events by currency string country_currency = "EUR"; if(calendar_info.Init(country_currency)) { MqlCalendarEvent events[]; if(calendar_info.EventsByCurrencyDescription(events)) { Print("\n---== Events selected by currency ==---"); PrintFormat(" Currency: %s", country_currency); PrintFormat(" Events number: %d", ::ArraySize(events)); } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Nas linhas do log você encontrará as seguintes:
MK 0 21:36:35.659 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) DM 0 21:36:35.659 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) ---== New Calendar Info object ==--- MP 0 21:36:35.659 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) Country id: 276 FH 0 21:36:35.793 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) ON 0 21:36:35.793 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) ---== Events selected by country ==--- RR 0 21:36:35.793 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) Country id: 276 GD 0 21:36:35.793 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) Events number: 61 FP 0 21:36:35.793 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) OG 0 21:36:35.793 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) ---== New Calendar Info object ==--- KI 0 21:36:35.793 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) Currency: EUR MN 0 21:36:35.794 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) QE 0 21:36:35.794 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) ---== Events selected by currency ==--- FO 0 21:36:35.794 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) Currency: EUR FJ 0 21:36:35.794 Test_structures_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) Events number: 276
Ou seja, 61 eventos foram encontrados para a Alemanha e para países com moeda Euro- 276 eventos.
2.3.3 Métodos para obter descrições de enumerações de calendário
A composição das estruturas do calendário inclui 8 enumerações:
- ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_TYPE;
- ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_SECTOR;
- ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_FREQUENCY;
- ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_TIMEMODE;
- ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_UNIT;
- ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPORTANCE;
- ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_MULTIPLIER;
- ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPACT.
As sete primeiras referem-se à estrutura MqlCalendarEvent e as oito últimas, à estrutura MqlCalendarValue.
Na classe CiCalendarInfo, respectivamente, são definidos 8 métodos que descrevem o valor da enumeração selecionada a partir da lista proposta. Vamos testar os métodos usando o script Test_enums_descriptions.mq5. Este script selecionará aleatoriamente 10 eventos do Reino Unido e registrará no log informações para cada um deles.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { CiCalendarInfo calendar_info; ulong country_id = 826; // UK if(calendar_info.Init(NULL, country_id)) { MqlCalendarEvent events[]; if(calendar_info.EventsByCountryDescription(events)) { ::MathSrand(77); int events_num =::ArraySize(events); int n = 10; MqlCalendarEvent events_selected[]; ::ArrayResize(events_selected, n); for(int ev_idx = 0; ev_idx < n; ev_idx++) { int rand_val =::MathRand(); int rand_idx = rand_val % events_num; events_selected[ev_idx] = events[rand_idx]; } //--- 0) name ::Print("\n---== Name ==---"); for(int ev_idx = 0; ev_idx < n; ev_idx++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = events_selected[ev_idx]; ::PrintFormat(" [%d] - %s", ev_idx + 1, curr_event.name); } //--- 1) type ::Print("\n---== Type ==---"); for(int ev_idx = 0; ev_idx < n; ev_idx++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = events_selected[ev_idx]; ::PrintFormat(" [%d] - %s", ev_idx + 1, calendar_info.EventTypeDescription(curr_event.type)); } //--- 2) sector ::Print("\n---== Sector ==---"); for(int ev_idx = 0; ev_idx < n; ev_idx++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = events_selected[ev_idx]; ::PrintFormat(" [%d] - %s", ev_idx + 1, calendar_info.EventSectorDescription(curr_event.sector)); } //--- 3) frequency ::Print("\n---== Frequency ==---"); for(int ev_idx = 0; ev_idx < n; ev_idx++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = events_selected[ev_idx]; ::PrintFormat(" [%d] - %s", ev_idx + 1, calendar_info.EventFrequencyDescription(curr_event.frequency)); } //--- 3) time mode ::Print("\n---== Time mode ==---"); for(int ev_idx = 0; ev_idx < n; ev_idx++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = events_selected[ev_idx]; ::PrintFormat(" [%d] - %s", ev_idx + 1, calendar_info.EventTimeModeDescription(curr_event.time_mode)); } //--- 4) unit ::Print("\n---== Unit ==---"); for(int ev_idx = 0; ev_idx < n; ev_idx++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = events_selected[ev_idx]; ::PrintFormat(" [%d] - %s", ev_idx + 1, calendar_info.EventUnitDescription(curr_event.unit)); } //--- 5) importance ::Print("\n---== Importance ==---"); for(int ev_idx = 0; ev_idx < n; ev_idx++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = events_selected[ev_idx]; ::PrintFormat(" [%d] - %s", ev_idx + 1, calendar_info.EventImportanceDescription(curr_event.importance)); } //--- 6) multiplier ::Print("\n---== Multiplier ==---"); for(int ev_idx = 0; ev_idx < n; ev_idx++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = events_selected[ev_idx]; ::PrintFormat(" [%d] - %s", ev_idx + 1, calendar_info.EventMultiplierDescription(curr_event.multiplier)); } //--- 7) impact MqlCalendarValue values_by_event[]; datetime start_dt, stop_dt; start_dt = D'01.01.2021'; stop_dt = D'01.11.2021'; ::Print("\n---== Impact ==---"); for(int ev_idx = 0; ev_idx < n; ev_idx++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = events_selected[ev_idx]; CiCalendarInfo event_info; MqlCalendarValue ev_values[]; if(event_info.Init(NULL, WRONG_VALUE, curr_event.id)) if(event_info.ValueHistorySelectByEvent(ev_values, start_dt, stop_dt)) { int ev_values_size =::ArraySize(ev_values); ::PrintFormat(" [%d] - %s", ev_idx + 1, calendar_info.ValueImpactDescription(ev_values[--ev_values_size].impact_type)); } } } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Para reproduzir o resultado obtido, definimos o estado inicial do gerador de série de inteiros pseudo-aleatórios com algum número (::MathSrand(77)). Assim, o script selecionou os seguintes eventos:
- BoE Housing Equity Withdrawal q/q;
- BoE Deputy Governor Markets and Banking Ramsden Speech;
- Claimant Count Change;
- Core CPI y/y;
- Average Weekly Earnings, Total Pay y/y;
- Easter Monday;
- BoE Mortgage Lending m/m;
- BoE MPC Member Vlieghe Speech;
- Core RPI y/y;
- Claimant Count Change.
Em seguida, obtemos as seguintes descrições no log:
FP 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) ---== Type ==--- CG 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [1] - Indicator EN 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [2] - Event EI 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [3] - Indicator LP 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [4] - Indicator OK 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [5] - Indicator OD 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [6] - Holiday EL 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [7] - Indicator GG 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [8] - Event ON 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [9] - Indicator CJ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [10] - Indicator DO 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) PE 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) ---== Sector ==--- JR 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [1] - Money KJ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [2] - Money NQ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [3] - Labor market QS 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [4] - Prices HD 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [5] - Labor market JP 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [6] - Holidays OI 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [7] - Housing EQ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [8] - Money LD 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [9] - Prices JR 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [10] - Labor market RS 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) NF 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) ---== Frequency ==--- ML 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [1] - Quarterly QH 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [2] - None MN 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [3] - Monthly PI 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [4] - Monthly OP 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [5] - Monthly CE 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [6] - None CR 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [7] - Monthly CS 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [8] - None GE 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [9] - Monthly OO 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [10] - Monthly PI 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) NQ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) ---== Time mode ==--- FE 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [1] - Exact time MS 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [2] - Exact time PH 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [3] - Exact time CQ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [4] - Exact time RO 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [5] - Exact time PF 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [6] - Takes all day NR 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [7] - Exact time MK 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [8] - Exact time DQ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [9] - Exact time RM 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [10] - Exact time FK 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) HP 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) ---== Unit ==--- CI 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [1] - National currency OO 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [2] - None MG 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [3] - People CO 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [4] - Percentage NE 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [5] - Percentage OK 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [6] - None KQ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [7] - National currency CH 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [8] - None LQ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [9] - Percentage CE 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [10] - People LL 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) PD 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) ---== Importance ==--- FS 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [1] - Low PD 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [2] - Moderate DK 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [3] - High EM 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [4] - Low QJ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [5] - Moderate GQ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [6] - None PG 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [7] - Low RO 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [8] - Moderate LI 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [9] - Low FM 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [10] - High ND 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) CM 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) ---== Multiplier ==--- HE 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [1] - Billions MK 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [2] - None IM 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [3] - Thousands MI 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [4] - None HQ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [5] - None OH 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [6] - None DN 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [7] - Billions IF 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [8] - None LN 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [9] - None OH 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [10] - Thousands DM 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) FF 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) ---== Impact ==--- OK 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [1] - Positive OR 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [2] - None EJ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [3] - Positive RQ 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [4] - Negative CG 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [5] - Negative KN 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [6] - None JF 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [7] - None EM 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [8] - None GD 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [9] - Positive QH 0 21:14:19.340 Test_enums_descriptions (USDCAD,H1) [10] - Positive
Por exemplo, o primeiro evento "BoE Housing Equity Withdrawal q/q" é descrito assim:
- "Type" - Indicator;
- "Sector" - Money;
- "Frequency" - Quarterly;
- "Time mode" - Exact time;
- "Unit" - National currency;
- "Importance" - Low;
- "Multiplier" - Billions;
- "Impact" - Positive.
Já o último evento "Claimant Count Change" é descrito assim:
- "Type" - Indicator;
- "Sector" - Labor;
- "Frequency" - Quarterly;
- "Time mode" - Exact time;
- "Unit" - National currency;
- "Importance" - Low;
- "Multiplier" - Billions;
- "Impact" - Positive.
2.3.4 Métodos para acessar o histórico
Esses métodos também usam as funções de calendário internas e obtêm informações sobre valores de eventos. Por exemplo, as funções ::CalendarValueHistoryByEvent() são usadas por dois métodos sobrecarregados CiCalendarInfo::ValueHistorySelectByEvent(). Se o primeiro retorna uma matriz de valores de todos os eventos numa determinada faixa de tempo por identificador de evento como uma estrutura MqlCalendarValue, o segundo devolve uma matriz de valores convertida numa série temporal.
Vejamos como funciona o método CiCalendarInfo::ValueHistorySelectByEvent() usando o script Test_value_history_by_event.mq5.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- NFP CiCalendarInfo nfp_info; ulong nfp_id = 840030016; if(nfp_info.Init(NULL, WRONG_VALUE, nfp_id)) { SiTimeSeries nfp_ts; if(nfp_info.ValueHistorySelectByEvent(nfp_ts, 0, ::TimeTradeServer())) nfp_ts.Print(0); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Selecionamos todo o histórico pelo indicador United States Nonfarm Payrolls.
Obtemos as seguintes entradas no log:
PL 0 21:45:03.581 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) ---== New Calendar Info object ==--- NI 0 21:45:03.581 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) Event id: 840030016 OM 0 21:45:03.581 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) HG 0 21:45:03.581 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) ---== Times series - Nonfarm Payrolls==--- CJ 0 21:45:03.581 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) [1]: time - 2007.03.09 16:30, value - 97 RE 0 21:45:03.581 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) [2]: time - 2007.04.06 15:30, value - 177 MS 0 21:45:03.581 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) [3]: time - 2007.05.04 15:30, value - 80 FL 0 21:45:03.581 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) [4]: time - 2007.06.01 15:30, value - 190 LH 0 21:45:03.581 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) [5]: time - 2007.07.06 15:30, value - 69 ... JE 0 21:45:03.583 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) [172]: time - 2021.06.04 15:30, value - 559 JP 0 21:45:03.583 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) [173]: time - 2021.07.02 15:30, value - 850 IO 0 21:45:03.583 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) [174]: time - 2021.08.06 15:30, value - 943 NJ 0 21:45:03.583 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) [175]: time - 2021.09.03 15:30, value - 235 HI 0 21:45:03.583 Test_value_history_by_event (USDCAD,H1) [176]: time - 2021.10.08 15:30, value - 194
*Aqui, para exibição compacta, indiquei o primeiro e os últimos 5 valores do evento.
2.3.5 Métodos para verificar o status do banco de dados do calendário
Esses métodos também utilizam as funções de calendário embutidas correspondentes. Informam sobre um erro somente quando o número de valores de eventos recebidos for zero e o erro em si for maior que zero.
Exemplificaremos o funcionamento do método CiCalendarInfo::ValueLastSelectByEvent() na terceira seção "Posições Líquidas de Especuladores", onde será necessário capturar o surgimento de um novo valor.
2.3.6 Métodos para obter dados sobre países e continentes
Esses métodos retornam algumas informações sobre os países. Vamos dizer algo sobre cada um.
O método CiCalendarInfo::GetCountries(CArrayString &countries_arr) retorna a lista de países, obtida durante a inicialização, na forma de um matriz dinâmica de variáveis do tipo string.
O método CiCalendarInfo::GetCountries(MqlCalendarCountry &countries[]) retorna a lista de países, obtida durante a inicialização, na forma de um matriz dinâmica de variáveis do tipo MqlCalendarCountry.
O método CiCalendarInfo::GetUniqueContinents(string & continents[]) retorna a lista de continentes, em que há países. Estes últimos também foram recebidos durante a inicialização.
O método CiCalendarInfo:: GetCountriesByContinent(const ENUM_CONTINENT src_continent, CArrayString &countries_arr) retorna a lista de países por determinado continente.
O método CiCalendarInfo::GetCountryNameById(const ulong country_id) retorna o nome único de um país por seu identificador.
A enumeração ENUM_CONTINENT foi criada para trabalhar usando uma categoria geográfica, p.e. um continente. Descreve os seguintes continentes:
- World;
- Asia;
- Africa;
- Europe;
- North America;
- South America;
- Australia/Oceania;
- Antarctica.
Pode parecer engraçado que eu tenha incluído a Antártica na lista. Não importa que permaneça na lista, assim a lista de continentes será mais abrangente. E um continente separado é a constante "World".
Além disso, para trabalhar usando continentes foi criada a estrutura SCountryByContinent. No método de inicialização existem matrizes constantes de códigos de países, de nomes de países e de seus respectivos continentes. Na versão atual, são especificados 197 países, incluindo a União Europeia e o mundo inteiro.
Vamos criar um script Test_get_countries.mq5, no qual verificamos o funcionamento dos métodos de obtenção de dados do país e dos continentes.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { CiCalendarInfo country_calendar_info; if(country_calendar_info.Init()) { //--- 1) get countries (CArrayString) CArrayString countries_arr; if(country_calendar_info.GetCountries(countries_arr)) { int countries_num = countries_arr.Total(); if(countries_num > 0) { ::Print("\n---== CArrayString list ==---"); ::PrintFormat(" Countries list consists of %d countries.", countries_num); ::PrintFormat(" First country: %s", countries_arr.At(0)); ::PrintFormat(" Last country: %s", countries_arr.At(countries_num - 1)); } } //--- 2) get countries (MqlCalendarCountry) MqlCalendarCountry countries[]; if(country_calendar_info.GetCountries(countries)) { int countries_num = ::ArraySize(countries); if(countries_num > 0) { ::Print("\n---== MqlCalendarCountry array ==---"); ::PrintFormat(" Countries array consists of %d countries.", countries_num); ::PrintFormat(" First country: %s", countries[0].name); ::PrintFormat(" Last country: %s", countries[countries_num - 1].name); } } //--- 3) get unique continents string continent_names[]; int continents_num = 0; if(country_calendar_info.GetUniqueContinents(continent_names)) { continents_num = ::ArraySize(continent_names); if(continents_num > 0) { ::Print("\n---== Unique continent names ==---"); for(int c_idx = 0; c_idx < continents_num; c_idx++) { string curr_continent_name = continent_names[c_idx]; ::PrintFormat(" [%d] - %s", c_idx + 1, curr_continent_name); } } } //--- 4) get countries by continent if(continents_num) { ENUM_CONTINENT continents[]; ::ArrayResize(continents, continents_num); ::Print("\n---== Countries by continent ==---"); for(int c_idx = 0; c_idx < continents_num; c_idx++) { ENUM_CONTINENT curr_continent = SCountryByContinent::ContinentByDescription(continent_names[c_idx]); if(countries_arr.Shutdown()) if(country_calendar_info.GetCountriesByContinent(curr_continent, countries_arr)) { int countries_by_continent = countries_arr.Total(); ::PrintFormat(" Continent \"%s\" includes %d country(-ies):", continent_names[c_idx], countries_by_continent); for(int c_jdx = 0; c_jdx < countries_by_continent; c_jdx++) { ::PrintFormat(" [%d] - %s", c_jdx + 1, countries_arr.At(c_jdx)); } } } } //--- 5) get country description string country_code = "RU"; SCountryByContinent country_continent_data; if(country_continent_data.Init(country_code)) { ::Print("\n---== Country ==---"); ::PrintFormat(" Name: %s", country_continent_data.Country()); ::PrintFormat(" Code: %s", country_continent_data.Code()); ENUM_CONTINENT curr_continent = country_continent_data.Continent(); ::PrintFormat(" Continent enum: %s", ::EnumToString(curr_continent)); ::PrintFormat(" Continent description: %s", country_continent_data.ContinentDescription()); } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Como resultado, script exibirá as seguintes informações no log:
EH 0 23:05:16.492 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) ---== New Calendar Info object ==--- HR 0 23:05:16.492 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) QH 0 23:05:16.492 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) ---== CArrayString list ==--- NR 0 23:05:16.492 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Countries list consists of 23 countries. NP 0 23:05:16.492 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) First country: European Union LF 0 23:05:16.492 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Last country: Norway LQ 0 23:05:16.492 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) GG 0 23:05:16.492 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) ---== MqlCalendarCountry array ==--- IL 0 23:05:16.492 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Countries array consists of 23 countries. JP 0 23:05:16.492 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) First country: European Union HG 0 23:05:16.492 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Last country: Norway OR 0 23:05:16.493 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) FJ 0 23:05:16.493 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) ---== Unique continent names ==--- KS 0 23:05:16.493 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [1] - Africa NK 0 23:05:16.493 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [2] - Asia HR 0 23:05:16.493 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [3] - Australia/Oceania HM 0 23:05:16.493 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [4] - Europe RE 0 23:05:16.493 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [5] - North America CO 0 23:05:16.493 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [6] - South America GH 0 23:05:16.493 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [7] - World GP 0 23:05:18.606 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) LE 0 23:05:18.606 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) ---== Countries by continent ==--- HO 0 23:05:18.608 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Continent "Africa" includes 1 country(-ies): RR 0 23:05:18.608 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [1] - South Africa NH 0 23:05:18.610 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Continent "Asia" includes 6 country(-ies): CM 0 23:05:18.610 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [1] - China RK 0 23:05:18.610 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [2] - Hong Kong CL 0 23:05:18.610 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [3] - India LJ 0 23:05:18.610 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [4] - South Korea LJ 0 23:05:18.610 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [5] - Japan IR 0 23:05:18.610 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [6] - Singapore OK 0 23:05:18.614 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Continent "Australia/Oceania" includes 2 country(-ies): RM 0 23:05:18.614 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [1] - Australia NJ 0 23:05:18.614 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [2] - New Zealand MM 0 23:05:18.616 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Continent "Europe" includes 9 country(-ies): LO 0 23:05:18.616 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [1] - European Union DF 0 23:05:18.616 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [2] - Germany OQ 0 23:05:18.616 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [3] - France CE 0 23:05:18.616 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [4] - United Kingdom OM 0 23:05:18.616 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [5] - Switzerland RS 0 23:05:18.616 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [6] - Spain FE 0 23:05:18.616 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [7] - Sweden JS 0 23:05:18.616 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [8] - Italy DD 0 23:05:18.616 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [9] - Norway LR 0 23:05:18.618 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Continent "North America" includes 3 country(-ies): LK 0 23:05:18.618 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [1] - Canada HS 0 23:05:18.618 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [2] - United States CK 0 23:05:18.618 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [3] - Mexico GL 0 23:05:18.619 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Continent "South America" includes 1 country(-ies): EQ 0 23:05:18.619 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [1] - Brazil DH 0 23:05:18.622 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Continent "World" includes 1 country(-ies): JK 0 23:05:18.622 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) [1] - Worldwide QM 0 23:05:18.622 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) KH 0 23:05:18.622 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) ---== Country ==--- PQ 0 23:05:18.622 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Name: Russian Federation KG 0 23:05:18.622 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Code: RU MR 0 23:05:18.622 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Continent enum: CONTINENT_EUROPE MI 0 23:05:18.622 Test_get_countries (USDCAD,H1) Continent description: Europe
Assim, a versão atual do calendário descreve eventos relacionados às economias de 23 países localizados em 7 continentes (incluindo a constante "World").
2.3.7 Métodos de recepção de dados de eventos
Esses métodos permitem selecionar eventos de acordo com algum critério.
O método CiCalendarInfo::GetEventsByName(CArrayString &events_arr, const string name = NULL) gera uma amostra na forma de uma matriz dinâmica de variáveis do tipo string. O critério de amostra é o nome do evento.
O método CiCalendarInfo::GetEventsByName(MqlCalendarEvent & events[], const string name = NULL) é parecido com o anterior, a única diferença é que ela gera a amostra como uma matriz de variáveis do tipo MqlCalendarCountry.
O método CiCalendarInfo::FilterEvents(MqlCalendarEvent &filtered_events[], MqlCalendarEvent &src_events[], const ulong filter) também gera uma amostra na forma de matriz de variáveis de tipo MqlCalendarCountry. Mas aqui já existe um critério múltiplo que implementa um conjunto de sinalizadores. No total existem 49 critérios desse tipo. Eles abrangem todos os valores das enumerações: ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_TYPE, ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_SECTOR, ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_FREQUENCY, ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_TIMEMODE, ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_UNIT, ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPORTANCE, ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_MULTIPLIER.
Não foi possível criar uma nova mega enumeração abrangente, porque enum é um tipo de dado de 4 bytes (32 bits), porem, nesta situação são necessários 49 bits. Por outro lado, é bom que exista um tipo long de 64 bits.
O código a seguir é usado para resolver o problema:
//--- defines for events filtering //--- 1) type (3) #define FILTER_BY_TYPE_EVENT 0x1 // 1 by type "event" #define FILTER_BY_TYPE_INDICATOR 0x2 // 2 by type "indicator" #define FILTER_BY_TYPE_HOLIDAY 0x4 // 3 by type "holiday" //--- 2) sector (13) #define FILTER_BY_SECTOR_NONE 0x8 // 4 by sector "none" #define FILTER_BY_SECTOR_MARKET 0x10 // 5 by sector "market" #define FILTER_BY_SECTOR_GDP 0x20 // 6 by sector "GDP" #define FILTER_BY_SECTOR_JOBS 0x40 // 7 by sector "jobs" #define FILTER_BY_SECTOR_PRICES 0x80 // 8 by sector "prices" #define FILTER_BY_SECTOR_MONEY 0x100 // 9 by sector "money" #define FILTER_BY_SECTOR_TRADE 0x200 // 10 by sector "trade" #define FILTER_BY_SECTOR_GOVERNMENT 0x400 // 11 by sector "government" #define FILTER_BY_SECTOR_BUSINESS 0x800 // 12 by sector "business" #define FILTER_BY_SECTOR_CONSUMER 0x1000 // 13 by sector "consumer" #define FILTER_BY_SECTOR_HOUSING 0x2000 // 14 by sector "housing" #define FILTER_BY_SECTOR_TAXES 0x4000 // 15 by sector "taxes" #define FILTER_BY_SECTOR_HOLIDAYS 0x8000 // 16 by sector "holidays" //--- 3) frequency (6) #define FILTER_BY_FREQUENCY_NONE 0x10000 // 17 by frequency "none" #define FILTER_BY_FREQUENCY_WEEK 0x20000 // 18 by frequency "week" #define FILTER_BY_FREQUENCY_MONTH 0x40000 // 19 by frequency "month" #define FILTER_BY_FREQUENCY_QUARTER 0x80000 // 20 by frequency "quarter" #define FILTER_BY_FREQUENCY_YEAR 0x100000 // 21 by frequency "year" #define FILTER_BY_FREQUENCY_DAY 0x200000 // 22 by frequency "day" //--- 4) importance (4) #define FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_NONE 0x400000 // 23 by importance "none" #define FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_LOW 0x800000 // 24 by importance "low" #define FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_MODERATE 0x1000000 // 25 by importance "medium" #define FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_HIGH 0x2000000 // 26 by importance "high" //--- 5) unit (14) #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_NONE 0x4000000 // 27 by unit "none" #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_PERCENT 0x8000000 // 28 by unit "percentage" #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_CURRENCY 0x10000000 // 29 by unit "currency" #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_HOUR 0x20000000 // 30 by unit "hours" #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_JOB 0x40000000 // 31 by unit "jobs" #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_RIG 0x80000000 // 32 by unit "drilling rigs" #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_USD 0x100000000 // 33 by unit "USD" #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_PEOPLE 0x200000000 // 34 by unit "people" #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_MORTGAGE 0x400000000 // 35 by unit "mortgage loans" #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_VOTE 0x800000000 // 36 by unit "votes" #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_BARREL 0x1000000000 // 37 by unit "barrels" #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_CUBICFEET 0x2000000000 // 38 by unit "cubic feet" #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_POSITION 0x4000000000 // 39 by unit "net positions" #define FILTER_BY_UNIT_BUILDING 0x8000000000 // 40 by unit "buildings" //--- 6) multiplier (5) #define FILTER_BY_MULTIPLIER_NONE 0x10000000000 // 41 by multiplier "none" #define FILTER_BY_MULTIPLIER_THOUSANDS 0x20000000000 // 42 by multiplier "thousands" #define FILTER_BY_MULTIPLIER_MILLIONS 0x40000000000 // 43 by multiplier "millions" #define FILTER_BY_MULTIPLIER_BILLIONS 0x80000000000 // 44 by multiplier "billions" #define FILTER_BY_MULTIPLIER_TRILLIONS 0x100000000000 // 45 by multiplier "trillions" //--- 7) time mode (4) #define FILTER_BY_TIMEMODE_DATETIME 0x200000000000 // 46 by time mode "na" #define FILTER_BY_TIMEMODE_DATE 0x400000000000 // 47 by time mode "positive" #define FILTER_BY_TIMEMODE_NOTIME 0x800000000000 // 48 by time mode "negative" #define FILTER_BY_TIMEMODE_TENTATIVE 0x1000000000000 // 49 by time mode "na" //--- type #define IS_TYPE_EVENT(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_TYPE_EVENT)!=0) #define IS_TYPE_INDICATOR(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_TYPE_INDICATOR)!=0) #define IS_TYPE_HOLIDAY(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_TYPE_HOLIDAY)!=0) //--- sector #define IS_SECTOR_NONE(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_SECTOR_NONE)!=0) #define IS_SECTOR_MARKET(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_SECTOR_MARKET)!=0) #define IS_SECTOR_GDP(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_SECTOR_GDP)!=0) #define IS_SECTOR_JOBS(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_SECTOR_JOBS)!=0) #define IS_SECTOR_PRICES(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_SECTOR_PRICES)!=0) #define IS_SECTOR_MONEY(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_SECTOR_MONEY)!=0) #define IS_SECTOR_TRADE(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_SECTOR_TRADE)!=0) #define IS_SECTOR_CONSUMER(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_SECTOR_CONSUMER)!=0) #define IS_SECTOR_HOUSING(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_SECTOR_HOUSING)!=0) #define IS_SECTOR_TAXES(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_SECTOR_TAXES)!=0) #define IS_SECTOR_HOLIDAYS(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_SECTOR_HOLIDAYS)!=0) //--- frequency #define IS_FREQUENCY_NONE(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_FREQUENCY_NONE)!=0) #define IS_FREQUENCY_WEEK(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_FREQUENCY_WEEK)!=0) #define IS_FREQUENCY_MONTH(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_FREQUENCY_MONTH)!=0) #define IS_FREQUENCY_QUARTER(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_FREQUENCY_QUARTER)!=0) #define IS_FREQUENCY_YEAR(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_FREQUENCY_YEAR)!=0) #define IS_FREQUENCY_DAY(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_FREQUENCY_DAY)!=0) //--- importance #define IS_IMPORTANCE_NONE(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_NONE)!=0) #define IS_IMPORTANCE_LOW(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_LOW)!=0) #define IS_IMPORTANCE_MODERATE(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_MODERATE)!=0) #define IS_IMPORTANCE_HIGH(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_HIGH)!=0) //--- unit #define IS_UNIT_NONE(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_NONE)!=0) #define IS_UNIT_PERCENT(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_PERCENT)!=0) #define IS_UNIT_CURRENCY(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_CURRENCY)!=0) #define IS_UNIT_HOUR(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_HOUR)!=0) #define IS_UNIT_JOB(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_JOB)!=0) #define IS_UNIT_RIG(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_RIG)!=0) #define IS_UNIT_USD(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_USD)!=0) #define IS_UNIT_PEOPLE(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_PEOPLE)!=0) #define IS_UNIT_MORTGAGE(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_MORTGAGE)!=0) #define IS_UNIT_VOTE(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_VOTE)!=0) #define IS_UNIT_BARREL(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_BARREL)!=0) #define IS_UNIT_CUBICFEET(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_CUBICFEET)!=0) #define IS_UNIT_POSITION(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_POSITION)!=0) #define IS_UNIT_BUILDING(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_UNIT_BUILDING)!=0) //--- multiplier #define IS_MULTIPLIER_NONE(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_MULTIPLIER_NONE)!=0) #define IS_MULTIPLIER_THOUSANDS(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_MULTIPLIER_THOUSANDS)!=0) #define IS_MULTIPLIER_MILLIONS(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_MULTIPLIER_MILLIONS)!=0) #define IS_MULTIPLIER_BILLIONS(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_MULTIPLIER_BILLIONS)!=0) #define IS_MULTIPLIER_TRILLIONS(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_MULTIPLIER_TRILLIONS)!=0) //--- time mode #define IS_TIMEMODE_DATETIME(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_TIMEMODE_DATETIME)!=0) #define IS_TIMEMODE_DATE(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_TIMEMODE_DATE)!=0) #define IS_TIMEMODE_NOTIME(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_TIMEMODE_NOTIME)!=0) #define IS_TIMEMODE_TENTATIVE(filter) ((filter&FILTER_BY_TIMEMODE_TENTATIVE)!=0)
Vejamos o exemplo de teste, isto é, o script Test_filter_events.mq5. Primeiro, um objeto de calendário é criado para a moeda Euro especificada.
Depois, no bloco 1 selecionamos todos os eventos relacionados à moeda Euro que tenham "Unemployment" no nome. Haverá apenas 33 eventos desse tipo. Os nomes dos eventos entram numa matriz dinâmica de variáveis do tipo string.
No bloco 2 realizamos o mesmo procedimento, apenas preenchemos uma matriz do tipo MqlCalendarEvent.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { CiCalendarInfo event_calendar_info; if(event_calendar_info.Init("EUR")) { //--- 1) get events by name (CArrayString) CArrayString events_arr; string ev_name = "Unemployment"; if(event_calendar_info.GetEventsByName(events_arr, ev_name)) { int events_num = events_arr.Total(); if(events_num > 0) { ::Print("\n---== CArrayString list ==---"); ::PrintFormat(" Events list consists of %d events.", events_num); ::PrintFormat(" First event: %s", events_arr.At(0)); ::PrintFormat(" Last event: %s", events_arr.At(events_num - 1)); } } //--- 2) get events by name (MqlCalendarEvent) MqlCalendarEvent events[]; if(event_calendar_info.GetEventsByName(events, ev_name)) { int events_num = ::ArraySize(events); if(events_num > 0) { ::Print("\n---== MqlCalendarEvent array ==---"); ::PrintFormat(" Events array consists of %d events.", events_num); ::PrintFormat(" First event: %s", events[0].name); ::PrintFormat(" Last event: %s", events[events_num - 1].name); } } //--- 3) filter events MqlCalendarEvent filtered_events[]; int indices[2]; indices[0] = 0; string events_str[2]; events_str[0] = "First"; events_str[1] = "Last"; ulong filter = 0; filter |= FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_HIGH; if(event_calendar_info.FilterEvents(filtered_events, events, filter)) { int f_events_num = ::ArraySize(filtered_events); ::Print("\n---== Filtered events array ==---"); ::Print(" Filtered by: importance high"); ::PrintFormat(" Events array consists of %d events.", ::ArraySize(filtered_events)); if(f_events_num > 0) { indices[1] = f_events_num - 1; for(int ind = 0; ind <::ArraySize(indices); ind++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = filtered_events[indices[ind]]; ::PrintFormat(" \n%s event:", events_str[ind]); event_calendar_info.PrintEventDescription(curr_event); } } ::ArrayFree(filtered_events); filter ^= FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_HIGH; } filter |= FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_MODERATE; if(event_calendar_info.FilterEvents(filtered_events, events, filter)) { int f_events_num = ::ArraySize(filtered_events); ::Print("\n---== Filtered events array ==---"); ::Print(" Filtered by: importance medium"); ::PrintFormat(" Events array consists of %d events.", ::ArraySize(filtered_events)); if(f_events_num > 0) { indices[1] = f_events_num - 1; for(int ind = 0; ind <::ArraySize(indices); ind++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = filtered_events[indices[ind]]; ::PrintFormat(" \n%s event:", events_str[ind]); event_calendar_info.PrintEventDescription(curr_event); } } ::ArrayFree(filtered_events); filter ^= FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_MODERATE; } filter |= FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_LOW; if(event_calendar_info.FilterEvents(filtered_events, events, filter)) { int f_events_num = ::ArraySize(filtered_events); ::Print("\n---== Filtered events array ==---"); ::Print(" Filtered by: importance low"); ::PrintFormat(" Events array consists of %d events.", ::ArraySize(filtered_events)); if(f_events_num > 0) { indices[1] = f_events_num - 1; for(int ind = 0; ind <::ArraySize(indices); ind++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = filtered_events[indices[ind]]; ::PrintFormat(" \n%s event:", events_str[ind]); event_calendar_info.PrintEventDescription(curr_event); } } ::ArrayFree(filtered_events); filter ^= FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_LOW; } filter |= FILTER_BY_IMPORTANCE_NONE; if(event_calendar_info.FilterEvents(filtered_events, events, filter)) { int f_events_num = ::ArraySize(filtered_events); ::Print("\n---== Filtered events array ==---"); ::Print(" Filtered by: importance none"); ::PrintFormat(" Events array consists of %d events.", ::ArraySize(filtered_events)); if(f_events_num > 0) { indices[1] = f_events_num - 1; for(int ind = 0; ind <::ArraySize(indices); ind++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = filtered_events[indices[ind]]; ::PrintFormat(" \n%s event:", events_str[ind]); event_calendar_info.PrintEventDescription(curr_event); } } } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
No bloco 3 filtramos eventos por critério de importância. Primeiro, vamos ver quantos dos trinta e três eventos previamente selecionados pelo nome são importantes. Eles não estarão completamente. Há 27 eventos de média importância, 6 eventos de baixa importância e 0 eventos onde não é dada importância.
No log, veremos as seguintes entradas:
JL 0 13:18:48.419 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) FM 0 13:18:48.421 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) ---== New Calendar Info object ==--- JP 0 13:18:48.421 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Currency: EUR CE 0 13:18:48.630 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) EL 0 13:18:48.631 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) ---== CArrayString list ==--- IF 0 13:18:48.631 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Events list consists of 33 events. MQ 0 13:18:48.631 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) First event: Unemployment Rate RK 0 13:18:48.631 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Last event: NAV Unemployment Change HF 0 13:18:48.635 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) OR 0 13:18:48.635 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) ---== MqlCalendarEvent array ==--- JH 0 13:18:48.635 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Events array consists of 33 events. ER 0 13:18:48.635 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) First event: Unemployment Rate JM 0 13:18:48.635 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Last event: NAV Unemployment Change DH 0 13:18:48.635 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) CR 0 13:18:48.635 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) ---== Filtered events array ==--- HH 0 13:18:48.635 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Filtered by: importance high DO 0 13:18:48.635 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Events array consists of 0 events. CN 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) PI 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) ---== Filtered events array ==--- NO 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Filtered by: importance medium PE 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Events array consists of 27 events. KG 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) KI 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) First event: IS 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) EJ 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) ---== Event description ==--- JF 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Id: 999030020 DP 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Type: Indicator KJ 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Sector: Labor market JM 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Frequency: Monthly QJ 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Time mode: Exact time CN 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Country id: 999 KK 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Unit: Percentage JP 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Importance: Moderate JH 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Multiplier: None JF 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Digits: 1 PL 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Source URL: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat NH 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Event code: unemployment-rate MQ 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Name: Unemployment Rate GI 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) OO 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Last event: OJ 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) OP 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) ---== Event description ==--- QH 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Id: 578040001 NO 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Type: Indicator ID 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Sector: Labor market DF 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Frequency: Monthly KS 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Time mode: Exact time LI 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Country id: 578 QR 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Unit: Percentage LJ 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Importance: Moderate DQ 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Multiplier: None LH 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Digits: 1 IS 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Source URL: https://www.nav.no/en/Home EQ 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Event code: nav-unemployment-rate-nsa PJ 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Name: NAV Unemployment Rate n.s.a. ED 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) FF 0 13:18:48.636 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) ---== Filtered events array ==--- PK 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Filtered by: importance low JS 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Events array consists of 6 events. FH 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) FS 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) First event: LI 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) LO 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) ---== Event description ==--- EK 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Id: 276060003 IM 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Type: Indicator FE 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Sector: Labor market OP 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Frequency: Monthly HQ 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Time mode: Exact time HH 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Country id: 276 KM 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Unit: People DJ 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Importance: Low RM 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Multiplier: Millions KJ 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Digits: 3 LS 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Source URL: https://www.arbeitsagentur.de/en/welcome MN 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Event code: unemployment-nsa ND 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Name: Unemployment n.s.a. LP 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) LE 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Last event: DP 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) DG 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) ---== Event description ==--- CS 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Id: 578040002 QE 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Type: Indicator NM 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Sector: Labor market GH 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Frequency: Monthly PI 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Time mode: Exact time GS 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Country id: 578 CE 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Unit: People LS 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Importance: Low HJ 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Multiplier: Thousands QR 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Digits: 3 NI 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Source URL: https://www.nav.no/en/Home MQ 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Event code: nav-unemployment-change ES 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Name: NAV Unemployment Change PI 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) CS 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) ---== Filtered events array ==--- DK 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Filtered by: importance none DH 0 13:18:48.637 Test_filter_events (USDCAD,H1) Events array consists of 0 events.
Novamente menciono que existem 49 critérios para selecionar eventos. Eles podem ser usados separadamente ou combinados.
3. Posições líquidas de especuladores
Há muitos eventos no calendário econômico. Como exemplo, escolhi um dos mais interessantes, o relatório semanal da Commodity Futures Trading Commission, que reflete a diferença entre o volume total de posições longas e curtas.
Vamos criar um indicador que exibirá os dados do ativo selecionado no gráfico numa janela separada.
Existem 11 ativos assim. Vamos criar a seguinte enumeração:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CFTC Non-Commercial Net Positions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_NON_COM_NET_POSITIONS { NON_COM_NET_POSITIONS_COPPER = 0, // Copper NON_COM_NET_POSITIONS_SILVER = 1, // Silver NON_COM_NET_POSITIONS_GOLD = 2, // Gold NON_COM_NET_POSITIONS_CRUDE_OIL = 3, // Crude oil NON_COM_NET_POSITIONS_SP_500 = 4, // S&P 500 NON_COM_NET_POSITIONS_AlUMINIUM = 5, // Aluminium NON_COM_NET_POSITIONS_CORN = 6, // Corn NON_COM_NET_POSITIONS_NGAS = 7, // Natural gas NON_COM_NET_POSITIONS_SOYBEANS = 8, // Soybeans NON_COM_NET_POSITIONS_WHEAT = 9, // Wheat NON_COM_NET_POSITIONS_NASDAQ_100 = 10, // Nasdaq 100 };
O indicador exibirá dados de valores anteriores e monitorará o surgimento de novos. E a primeira coisa a fazer é implementar o seguinte bloco de código no manipulador OnCalculate():
//--- first call if(prev_calculated == 0) { //--- initialize buffer ::ArrayInitialize(gBuffer, EMPTY_VALUE); //--- 1) collect all events by country ulong country_id = 840; // US if(gPtrEventsInfo.Init(NULL, country_id)) { MqlCalendarEvent events[]; if(gPtrEventsInfo.EventsByCountryDescription(events, false)) { string event_code_substr = GetEventCodeSubstring(); if(event_code_substr != NULL) for(int ev_idx = 0; ev_idx <::ArraySize(events); ev_idx++) { MqlCalendarEvent curr_event = events[ev_idx]; if(::StringFind(curr_event.event_code, event_code_substr) > -1) { //--- 2) collect all values by event id if(gPtrValuesInfo.Init(NULL, WRONG_VALUE, curr_event.id)) { SiTimeSeries net_positions_ts; if(gPtrValuesInfo.ValueHistorySelectByEvent(net_positions_ts, 0)) { string net_positions_name; SiTsObservation ts_observations[]; if(net_positions_ts.GetSeries(ts_observations, net_positions_name)) { //--- consider only past observations int new_size = 0; for(int obs_idx =::ArraySize(ts_observations) - 1; obs_idx >= 0; obs_idx--) { if(ts_observations[obs_idx].val != EMPTY_VALUE) break; new_size = obs_idx; } if(new_size > 0) ::ArrayResize(ts_observations, new_size); //--- find the starting date datetime start_dtime, ts_start_dtime; start_dtime = time[0]; ts_start_dtime = ts_observations[0].time; if(ts_start_dtime > start_dtime) start_dtime = ts_start_dtime; ::IndicatorSetString(INDICATOR_SHORTNAME, net_positions_name); ::IndicatorSetInteger(INDICATOR_DIGITS, 1); //--- int start_bar_idx =::iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, ts_start_dtime); if(start_bar_idx > -1) { start_bar_idx = rates_total - start_bar_idx; uint observations_cnt = 0; SiTsObservation curr_observation = ts_observations[observations_cnt]; uint ts_size = ::ArraySize(ts_observations); for(int bar = start_bar_idx; bar < rates_total; bar++) { if((observations_cnt + 1) < ts_size) { SiTsObservation next_observation = ts_observations[observations_cnt + 1]; if(time[bar] >= next_observation.time) { curr_observation = next_observation; gLastValueDate = curr_observation.time; gLastValue = curr_observation.val; observations_cnt++; } } gBuffer[bar] = curr_observation.val; } //--- just to get a change id MqlCalendarValue values[]; gPtrValuesInfo.ValueLastSelectByEvent(gChangeId, values); } } } } break; } } } } }
Nele inicializamos o primeiro objeto de calendário. Além disso, especificamos apenas o identificador do país - USA. Em seguida, selecionamos todos os eventos por país e encontramos nosso ativo pelo código do evento. Ele é definido na variável input. Depois disso, inicializamos o segundo objeto de calendário e solicitamos o histórico. Logo, preenchemos o buffer do indicador.
O segundo bloco capturará o surgimento de novo valor no manipulador OnCalculate():
MqlCalendarValue values[]; if(gPtrValuesInfo.ValueLastSelectByEvent(gChangeId, values) > 0) if(values[0].time > gLastValueDate) { gLastValueDate = values[0].time; gLastValue = values[0].GetActualValue(); //--- to log if(InpTpLog) { ::Print("\n---== New event value ==---"); ::PrintFormat(" Time: %s", ::TimeToString(gLastValueDate)); datetime server_time =::TimeTradeServer(); ::PrintFormat(" Release time: %s", ::TimeToString(server_time)); ::PrintFormat(" Actual value: %0.1f", gLastValue); } } //--- if a new bar if(rates_total > prev_calculated) for(int bar = prev_calculated; bar < rates_total; bar++) gBuffer[bar] = gLastValue;
Como resultado, teremos mais o menos isto (Fig. 3).
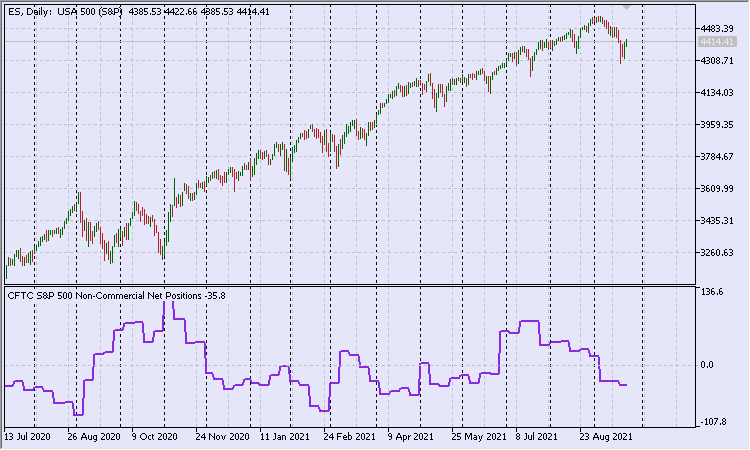
Fig. 3. Posições líquidas de especuladores do índice S&P 500 relatadas pela CFTC
No código do indicador, podemos ver que os objetos de calendário são criados dinamicamente. Isso se deve à reinicialização das variáveis globais nos indicadores.
Conclusão
Como parte deste artigo, criamos uma classe para um objeto de calendário. Esta facilita o acesso às propriedades do calendário e obter valores de eventos. O banco de dados do calendário é suficientemente abrangente para permitir a análise de eventos econômicos importantes sem ter que consultar recursos de terceiros.
O arquivo contém os códigos-fonte que foram usados no artigo. Todos os meus arquivos e pastas estão localizados na pasta %MQL5\Shared Projects\Testing\Calendar. Se os arquivos-fonte estiverem localizados de forma diferente, preste atenção à inclusão correta do arquivo de cabeçalho CalendarInfo.mqh por meio da diretiva #include.
Traduzido do russo pela MetaQuotes Ltd.
Artigo original: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/9874
Aviso: Todos os direitos sobre esses materiais pertencem à MetaQuotes Ltd. É proibida a reimpressão total ou parcial.
Esse artigo foi escrito por um usuário do site e reflete seu ponto de vista pessoal. A MetaQuotes Ltd. não se responsabiliza pela precisão das informações apresentadas nem pelas possíveis consequências decorrentes do uso das soluções, estratégias ou recomendações descritas.
 Conjunto de ferramentas para marcação manual de gráficos e negociação (Parte III). Otimização e novas ferramentas
Conjunto de ferramentas para marcação manual de gráficos e negociação (Parte III). Otimização e novas ferramentas
 Quase-construtor para criar um Expert Advisor
Quase-construtor para criar um Expert Advisor
 Como se tornar um bom programador (Parte 6): 9 hábitos para desenvolver de maneira produtiva
Como se tornar um bom programador (Parte 6): 9 hábitos para desenvolver de maneira produtiva
 Trabalhando com o tempo (Parte 1): princípios básicos
Trabalhando com o tempo (Parte 1): princípios básicos
- Aplicativos de negociação gratuitos
- 8 000+ sinais para cópia
- Notícias econômicas para análise dos mercados financeiros
Você concorda com a política do site e com os termos de uso
Acho que deve haver uma maneira )) A tarefa é criar um banco de dados antes de fazer o backtesting das notícias...
Oi Denis,
Esse é um artigo realmente interessante. Estou prestes a adicionar um código ao meu EA para bloqueio de negociações com base em notícias. Na página do calendário econômico do site mql5.com, há um intervalo máximo de 90 dias para a visualização de dados anteriores. Esse limite é o mesmo para os comandos da API do calendário econômico da MQL5? Eu também estou procurando fazer backtesting.
Muito obrigado
@KjLNi, removi acidentalmente a postagem a seguir. Minhas desculpas.