MQL5における拡張ディッキー–フラー検定の実装
はじめに
拡張ディッキー–フラー検定(ADF)は、時系列が定常かどうかを評価するために使用される一般的な手法です。 しかし、金融時系列は本質的に非定常であることはよく知られています。定常性の恩恵を受ける多くの統計手法は、通常、分析前に非定常データセットを何らかの方法で変換する必要があります。ADF検定は、これらの変換が定常性を誘導する効果を評価するために用いることができます。あるいは、系列間の共和分を評価する際にも、定常性の検定が用いられます。これは、関連する金融商品の価格設定の不一致を利用した取引戦略の開発に役立ちます。この記事では、純粋なMQL5でのADF検定の実装を紹介し、MetaTrader 5で共和分された銘柄を識別するために使用することで、その適用を実証します。
ADF検定について
簡単に言えば、ADF検定は仮説検定であり、観測されたデータの特定の特性が統計的に有意かどうかを判断することができます。この場合、求められる特性は系列の定常性です。 統計的仮説とは、標本で表されるデータセットについて立てた仮定です。データ全体を扱うことによってのみ、本当の真実を知ることができます。しかし、それは通常、何らかの理由で不可能です。つまり、データセットの標本は、データセット全体の仮定をするためにテストされます。ここで忘れてはならない重要な点は、統計的仮説の真偽は、標本を扱う場合には決して確実にはわからないということです。得られるのは、仮定が真か偽かということです。
ADF検定では、2つのシナリオを考えます。
- 時系列に単位根が存在するという帰無仮説
- 時系列が単位根を示さないという対立仮説
時系列分析において、単位根とは、順次データセットの特別な特性です。犬を散歩している男性を想像してみてください。その人は目的地に向かってほぼまっすぐ歩くでしょう。その一方で、犬は何かを嗅いだり、気になった生き物を追いかけたりするために、しばしばふらふらと歩き出きまが、最終的には飼い主に従います。犬の軌道をプロットしてみると、ある種の振動が観察できるかもしれません。犬はふらふらと歩き出しますが、やがて男性が従ってい予想通りの方向に戻ります。
犬の経路上の任意の点は、特定の時間における変数の値を表します。これらの値を評価すれば、中心傾向を中心とした一定の範囲にとどまる可能性が高くなります。統計的特性は、時間の経過とともに大きく変化することはありません。このような系列は単位根を持ちません。もし、その男性が同じ通りでしつけの悪い犬を散歩させていたらと想像してみましょう。そのような犬は逃げ出し、飼い主のもとに戻ってこない可能性が高いです。この犬が通る道に関連する数値は予測不可能に変化します。このような系列は単位根を持ちます。
単位根という概念は、確率過程の特性方程式に由来します。確率過程とは、ランダムに進化するシステムを記述する、時間によってインデックス付けされた変数の列です。確率過程の特性方程式は、システムの特性をとらえる方程式です。単位根とは、特性方程式の解が1に等しくなることです。プロセスが単位根を持つ場合、それはショックまたはランダム効果がプロセスに持続的な影響を与えることを意味します。このようなシステムは、ランダム効果とラグ値によってモデル化されます。つまり、自己回帰的であるということです。
したがって、ADF検定では回帰モデルを用いて単位根を検定します。モデルの最も一般的な形は、以下の式で与えられます。
ここで、
- Y:時系列の最初の差分
- a:定数項
- b:時系列の遅行レベルの係数
- x:時間トレンド(t)の係数
- V:遅延一次差分の係数
- E:誤差項
このテストでは係数bに注目します。b = 0であれば単位根が存在し、b < 0であれば時系列は定常です。ADF統計量は、bの推定値とその標準誤差に基づいて計算されます。これは、ディッキー–フラー分布の臨界値と比較されます。ADF統計量が特定の有意水準で臨界値より負が大きい場合、単位根の帰無仮説は棄却されます。系列は定常です。
実装
実装が正確であることを保証するために、PythonでのADF検定の既存の実装を参照として使用します。statsmodels Pythonパッケージでは、adfuller関数がADF検定を実行するために使用されます。
adfuller(x, maxlag: 'int | None' = None, regression='c', autolag='AIC', store=False, regresults=False)
この関数は、まず入力系列の自己回帰モデルのパラメータを、通常の最小二乗法を用いて推定します。推定されたパラメータに基づいて検定統計量が計算されます。これはp値の計算に使用されます。信頼度を表す分布表から3つの臨界値が引き出されます。最後に、系列が定常かどうかを決定するために、検定統計量をこれらの値のいずれかと比較することができます。
この概要に基づき、実装しなければならない3つの重要な要素があります。1つ目は、通常の最小二乗回帰モデルです。ここでの誤差はテストの他の段階に伝播するため、おそらく最も重要な要素です。これは、分析対象の系列の最も適切な自己回帰モデルを決定するために使用されます。モデルパラメータ以外にも、モデルの様々な特性、例えば赤池情報量規準やベイズ情報量規準を計算する必要があります。
2つ目の要素は、p値の計算に関するものです。p値は、最適自己回帰モデルのt統計量から導かれる検定統計量によって決定されます。t統計量は、2つのグループの平均値の間に有意差があるかどうかを決定するために使用される尺度です。これは標本平均の差をとり、それを差の標準誤差で割ることによって計算されます。この文脈では、t統計量はモデルのパラメータをモデルの標準誤差で割ることによって計算されます。p値の算出に採用された方法は、J.G.MacKinnon(英語)によって提案されたため、MacKinnonの近似p値法と呼ばれており、統計的検定の臨界値に関連するp値の近似値を提供します。
ADF検定を完了するために必要な最後の要素は、臨界値の計算です。これらの値は、MacKinnonによって書かれた論文で示された近似値から導き出されたものです。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Ordinary least squares class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class OLS { private: matrix m_exog, //design matrix m_pinv, //pseudo-inverse of matrix m_cov_params, //covariance of matrix m_m_error, //error matrix m_norm_cov_params; //normalized covariance matrix vector m_endog, //dependent variables m_weights, //weights m_singularvalues, //singular values of solution m_params, //coefficients of regression model(solution) m_tvalues, //test statistics of model m_bse, //standard errors of model m_resid; //residuals of model ulong m_obs, //number of observations m_model_dof, //degrees of freedom of model m_resid_dof, //degrees of freedom of residuals m_kconstant, //number of constants m_rank; //rank of design matrix double m_aic, //Akiake information criteria m_bic, //Bayesian information criteria m_scale, //scale of model m_llf, //loglikelihood of model m_sse, //sum of squared errors m_rsqe, //r-squared of model m_centeredtss, //centered sum of squares m_uncenteredtss; //uncentered sum of squares uint m_error; //error flag // private methods ulong countconstants(void); void scale(void); void sse(void); void rsqe(void); void centeredtss(void); void uncenteredtss(void); void aic(void); void bic(void); void bse(void); void llf(void); void tvalues(void); void covariance_matrix(void); public: //constructor OLS(void); //destructor ~OLS(void); //public methods bool Fit(vector &y_vars,matrix &x_vars); double Predict(vector &inputs); double Predict(double _input); //get properties of OLS model ulong ModelDOF(void) { if(m_error) return 0; else return m_model_dof;} ulong ResidDOF(void) { if(m_error) return 0; else return m_resid_dof;} double Scale(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; else return m_scale; } double Aic(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; else return m_aic; } double Bic(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; else return m_bic; } double Sse(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; else return m_sse; } double Rsqe(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; else return m_rsqe; } double C_tss(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; else return m_centeredtss;} double Loglikelihood(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; return m_llf; } vector Tvalues(void) { if(m_error) return m_m_error.Col(0); return m_tvalues; } vector Residuals(void) { if(m_error) return m_m_error.Col(0); return m_resid; } vector ModelParameters(void) { if(m_error) return m_m_error.Col(0); return m_params; } vector Bse(void) { if(m_error) return m_m_error.Col(0); return m_bse; } matrix CovarianceMatrix(void) { if(m_error) return m_m_error; return m_cov_params; } };
OLS.mqhはOLSクラスの定義で、通常の最小二乗法回帰モデルを表します。このクラスにはいくつかのpublicメソッドがあります。その最初のメソッドがFit()です。これは、このクラスのインスタンスを作成した後、ユーザーが最初に呼び出すメソッドです。入力としてベクトルと行列が必要です。ベクトルy_varsは従属値で埋められ、x_varsは設計行列です。Fit()は、実行に成功するとtrueを返し、その時点で他のpublicメソッドを呼び出すことができます。これらのメソッドはすべて、計算されたモデルの特定のプロパティを返します。これらの特性は以下の表にまとめられています。
| 戻りデータ型 | エラー時に返される値 | メソッド | 詳細 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ulong | 0 | ModelDOF() | モデルの自由度 |
| ulong | 0 | ResidDOF() | モデルの残差の自由度 |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | Scale() | 誤差項の分散であり、独立変数によって説明されない従属変数の変動を示す |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | Aic() | 赤池情報量基準 |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | Bic() | ベイズ情報量基準 |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | Sse() | モデルの二乗誤差の和 |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | Rsqe() | モデルのR2(決定係数) |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | C_tss() | 平均を中心とする二乗誤差の総和 |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | Loglikelihood() | OLSモデルの尤度関数 |
| vector | 空の値のベクトル | Tvalues() | モデルの各パラメータ推定値のt統計量 |
| vector | 空の値のベクトル | Residuals() | モデルの残差(予測値と実際値の差) |
| vector | 空の値のベクトル | Bse() | パラメータ推定値の標準誤差 |
| matrix | 空の値の行列 | CovarianceMatrix() | 変数の分散と変数間の共分散を表す行列 |
Predict()には、入力データ型によって異なる2つのオーバーロードがあります。double型ベクトルとスカラー値です。どちらも、新しい独立変数(複数可)が与えられると、単一の予測を返します。
実装の次の部分は、ADF.mqhファイルに移ります。このファイルには、ADF検定に関連する関数定義のコレクションが含まれます。その1つがadfuller()です。OLSクラスのOLS.mqh、標準ライブラリのMath.mqh、Alglibライブラリのspecialfunctions.mqhを含みます。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ADF.mqh | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #include<Math\Stat\Math.mqh> #include<Math\Alglib\specialfunctions.mqh> #include<OLS.mqh>
実装の次の部分は、ADF.mqhファイルに移ります。このファイルには、CAdfクラスの定義と同様に、関数定義のコレクションが含まれます。OLSクラスのOLS.mqh、標準ライブラリのMath.mqh、Alglibライブラリのspecialfunctions.mqhを含みます。ADF.mqhは、いくつかの列挙型の定義から始まります。ENUM_INFO_CRITは、特定の系列に最適な回帰モデルを決定する際に利用可能なオプションを表します。適切なモデルを選択するための指標を定義しています。ENUM_TRIM、ENUM_ORIGINAL、ENUM_HAS_CONST、ENUM_TRENDは、デザイン行列の構築に使用されます。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Information criterion | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_INFO_CRIT { INFO_NONE=0, INFO_AIC, INFO_BIC }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Options for trimming invalid observations | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_TRIM { TRIM_NONE=0, TRIM_FORWARD, TRIM_BACKWARD, TRIM_BOTH }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| options for how to handle original data set | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_ORIGINAL { ORIGINAL_EX=0, ORIGINAL_IN, ORIGINAL_SEP }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constant and trend used in regression model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_TREND { TREND_NONE=0, TREND_CONST_ONLY, TREND_LINEAR_ONLY, TREND_LINEAR_CONST, TREND_QUAD_LINEAR_CONST }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Options for how to handle existing constants | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_HAS_CONST { HAS_CONST_RAISE=0, HAS_CONST_SKIP, HAS_CONST_ADD };
CAdfのAdfuller()メソッドは、テストが正常に実行されたことを示すブール値を返します。系列の定常性ではありません。falseが返された場合は、エラーが発生したことになります。エラーが発生すると、端末の操作ログに冗長なメッセージが出力されます。このメソッドには分析対象の系列を配列で入力します。 関数へのその他の引数は任意です。ほとんどの場合、ユーザーはこれらのパラメータを気にする必要はありません。前述のパラメータで関数を呼び出せば十分でしょう。
//+---------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|Class CAdf | //| encapsulates the the Augmented Dickey Fuller Test for Stationarity| //+---------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CAdf { private: double m_adf_stat, //adf statistic m_bestic, //optimal bic or aic m_pvalue; //p-value ulong m_usedlag; //lag used for optimal reg model vector m_critvals; //estimated critical values OLS *m_ols; //internal ordinary least squares reg model // private methods bool gridsearch(vector &LHS, matrix &RHS, ulong f_lag, ulong l_lag,ENUM_INFO_CRIT crit, double &b_ic, ulong &best_lag); bool lagmat(matrix &in,matrix &out[],ulong mlag,ENUM_TRIM trim=TRIM_BOTH,ENUM_ORIGINAL original=ORIGINAL_IN); bool prepare_lhs_rhs(vector &lhs, matrix &rhs, double &in[], double &in_diff[],ulong lag); public: CAdf(void); ~CAdf(void); bool Adfuller(double &array[],ulong max_lag = 0,ENUM_TREND trend = TREND_CONST_ONLY, ENUM_INFO_CRIT autolag=INFO_AIC); vector CriticalValues(void) { return m_critvals; } double AdfStatistic(void) { return m_adf_stat; } double Pvalue(void) { return m_pvalue; } };
max_lagは、回帰モデルのラグの最大数を定義します。trendは、回帰モデルのトレンドと定数の構成を指定できる列挙です。autolagは、入力系列を最もよく記述する最適なモデルを選択するために、どのような尺度が使用されるかを決定します。Adfuller()では、回帰モデルの従属変数と独立変数を構築する前に、まず関数のパラメータが確認されます。
この初期設計行列のいくつかのバリエーションが、入力系列に最も適合するものを決定するために標本化されます。最適なモデルを導き出すための基準は、autolagパラメータの値に依存します。検索はgridsearch()関数によっておこなわれます。
最適なモデルが見つかったら、このモデルのラグ特性(初期設計行列に含まれる列の数)を用いて最適モデルを定義します。これらのパラメータは系列の定常性を推定するために使用されます。最適OLSモデルの最初のt統計量は、ADF検定のADF統計量を定義します。p値はmackinnop()関数で計算されます。CAdfのPvalue()メソッドを呼び出すと、対応するp値が返されます。
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| calculates MacKinnon's approximate p-value for a given test statistic| //+----------------------------------------------------------------------+ double mackinnonp(double teststat, ENUM_TREND trend = TREND_CONST_ONLY,ulong nseries = 1, uint lags =0) { vector small_scaling = {1, 1, 1e-2}; vector large_scaling = {1, 1e-1, 1e-1, 1e-2}; double tau_star_nc []= {-1.04, -1.53, -2.68, -3.09, -3.07, -3.77}; double tau_min_nc []= {-19.04, -19.62, -21.21, -23.25, -21.63, -25.74}; double tau_max_nc []= {double("inf"), 1.51, 0.86, 0.88, 1.05, 1.24}; double tau_star_c []= {-1.61, -2.62, -3.13, -3.47, -3.78, -3.93}; double tau_min_c []= {-18.83, -18.86, -23.48, -28.07, -25.96, -23.27}; double tau_max_c []= {2.74, 0.92, 0.55, 0.61, 0.79, 1}; double tau_star_ct []= {-2.89, -3.19, -3.50, -3.65, -3.80, -4.36}; double tau_min_ct []= {-16.18, -21.15, -25.37, -26.63, -26.53, -26.18}; double tau_max_ct []= {0.7, 0.63, 0.71, 0.93, 1.19, 1.42}; double tau_star_ctt []= {-3.21, -3.51, -3.81, -3.83, -4.12, -4.63}; double tau_min_ctt []= {-17.17, -21.1, -24.33, -24.03, -24.33, -28.22}; double tau_max_ctt []= {0.54, 0.79, 1.08, 1.43, 3.49, 1.92}; double tau_nc_smallp [][3]= { {0.6344, 1.2378, 3.2496}, {1.9129, 1.3857, 3.5322}, {2.7648, 1.4502, 3.4186}, {3.4336, 1.4835, 3.19}, {4.0999, 1.5533, 3.59}, {4.5388, 1.5344, 2.9807} }; double tau_c_smallp [][3]= { {2.1659, 1.4412, 3.8269}, {2.92, 1.5012, 3.9796}, {3.4699, 1.4856, 3.164}, {3.9673, 1.4777, 2.6315}, {4.5509, 1.5338, 2.9545}, {5.1399, 1.6036, 3.4445} }; double tau_ct_smallp [][3]= { {3.2512, 1.6047, 4.9588}, {3.6646, 1.5419, 3.6448}, {4.0983, 1.5173, 2.9898}, {4.5844, 1.5338, 2.8796}, {5.0722, 1.5634, 2.9472}, {5.53, 1.5914, 3.0392} }; double tau_ctt_smallp [][3]= { {4.0003, 1.658, 4.8288}, {4.3534, 1.6016, 3.7947}, {4.7343, 1.5768, 3.2396}, {5.214, 1.6077, 3.3449}, {5.6481, 1.6274, 3.3455}, {5.9296, 1.5929, 2.8223} }; double tau_nc_largep [][4]= { {0.4797, 9.3557, -0.6999, 3.3066}, {1.5578, 8.558, -2.083, -3.3549}, {2.2268, 6.8093, -3.2362, -5.4448}, {2.7654, 6.4502, -3.0811, -4.4946}, {3.2684, 6.8051, -2.6778, -3.4972}, {3.7268, 7.167, -2.3648, -2.8288} }; double tau_c_largep [][4]= { {1.7339, 9.3202, -1.2745, -1.0368}, {2.1945, 6.4695, -2.9198, -4.2377}, {2.5893, 4.5168, -3.6529, -5.0074}, {3.0387, 4.5452, -3.3666, -4.1921}, {3.5049, 5.2098, -2.9158, -3.3468}, {3.9489, 5.8933, -2.5359, -2.721} }; double tau_ct_largep [][4]= { {2.5261, 6.1654, -3.7956, -6.0285}, {2.85, 5.272, -3.6622, -5.1695}, {3.221, 5.255, -3.2685, -4.1501}, {3.652, 5.9758, -2.7483, -3.2081}, {4.0712, 6.6428, -2.3464, -2.546}, {4.4735, 7.1757, -2.0681, -2.1196} }; double tau_ctt_largep [][4]= { {3.0778, 4.9529, -4.1477, -5.9359}, {3.4713, 5.967, -3.2507, -4.2286}, {3.8637, 6.7852, -2.6286, -3.1381}, {4.2736, 7.6199, -2.1534, -2.4026}, {4.6679, 8.2618, -1.822, -1.9147}, {5.0009, 8.3735, -1.6994, -1.6928} }; vector maxstat,minstat,starstat; matrix tau_smallps, tau_largeps; switch(trend) { case TREND_NONE: if(!maxstat.Assign(tau_max_nc) || !minstat.Assign(tau_min_nc) || !starstat.Assign(tau_star_nc)|| !tau_smallps.Assign(tau_nc_smallp)|| !tau_largeps.Assign(tau_nc_largep)) { Print("assignment error :", GetLastError()); return double("inf"); } else break; case TREND_CONST_ONLY: if(!maxstat.Assign(tau_max_c) || !minstat.Assign(tau_min_c) || !starstat.Assign(tau_star_c)|| !tau_smallps.Assign(tau_c_smallp)|| !tau_largeps.Assign(tau_c_largep)) { Print("assignment error :", GetLastError()); return double("inf"); } else break; case TREND_LINEAR_CONST: if(!maxstat.Assign(tau_max_ct) || !minstat.Assign(tau_min_ct) || !starstat.Assign(tau_star_ct)|| !tau_smallps.Assign(tau_ct_smallp)|| !tau_largeps.Assign(tau_ct_largep)) { Print("assignment error :", GetLastError()); return double("inf"); } else break; case TREND_QUAD_LINEAR_CONST: if(!maxstat.Assign(tau_max_ctt) || !minstat.Assign(tau_min_ctt) || !starstat.Assign(tau_star_ctt)|| !tau_smallps.Assign(tau_ctt_smallp)|| !tau_largeps.Assign(tau_ctt_largep)) { Print("assignment error :", GetLastError()); return double("inf"); } else break; default: Print(__FUNCTION__," Error invalid input for trend argument"); return double("nan"); } if(teststat>maxstat[nseries-1]) return 1.0; else if(teststat<minstat[nseries-1]) return 0.0; vector tau_coef; if(teststat<=starstat[nseries-1]) tau_coef = small_scaling*(tau_smallps.Row(nseries-1)); else tau_coef = large_scaling*(tau_largeps.Row(nseries-1)); double rv,tau[]; ArrayResize(tau,int(tau_coef.Size())); for(ulong i=0; i<tau_coef.Size(); i++) tau[i]=tau_coef[tau_coef.Size()-1-i]; rv=polyval(tau,teststat); return CNormalDistr::NormalCDF(rv); }臨界値はmackinnoncrit()によって計算されます。その結果は、CAdfのCriticalValues()メソッドからアクセスできます。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|Computes critical values | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ vector mackinnoncrit(ulong nseries = 1,ENUM_TREND trend = TREND_CONST_ONLY, ulong num_obs=ULONG_MAX) { matrix tau_nc_2010 [] = {{ {-2.56574, -2.2358, -3.627, 0}, // N [] = 1 {-1.94100, -0.2686, -3.365, 31.223}, {-1.61682, 0.2656, -2.714, 25.364} } }; matrix tau_c_2010 [] = { { {-3.43035, -6.5393, -16.786, -79.433}, // N [] = 1, 1% {-2.86154, -2.8903, -4.234, -40.040}, // 5 % {-2.56677, -1.5384, -2.809, 0} }, // 10 % { {-3.89644, -10.9519, -33.527, 0}, // N [] = 2 {-3.33613, -6.1101, -6.823, 0}, {-3.04445, -4.2412, -2.720, 0} }, { {-4.29374, -14.4354, -33.195, 47.433}, // N [] = 3 {-3.74066, -8.5632, -10.852, 27.982}, {-3.45218, -6.2143, -3.718, 0} }, { {-4.64332, -18.1031, -37.972, 0}, // N [] = 4 {-4.09600, -11.2349, -11.175, 0}, {-3.81020, -8.3931, -4.137, 0} }, { {-4.95756, -21.8883, -45.142, 0}, // N [] = 5 {-4.41519, -14.0405, -12.575, 0}, {-4.13157, -10.7417, -3.784, 0} }, { {-5.24568, -25.6688, -57.737, 88.639}, // N [] = 6 {-4.70693, -16.9178, -17.492, 60.007}, {-4.42501, -13.1875, -5.104, 27.877} }, { {-5.51233, -29.5760, -69.398, 164.295}, // N [] = 7 {-4.97684, -19.9021, -22.045, 110.761}, {-4.69648, -15.7315, -5.104, 27.877} }, { {-5.76202, -33.5258, -82.189, 256.289}, // N [] = 8 {-5.22924, -23.0023, -24.646, 144.479}, {-4.95007, -18.3959, -7.344, 94.872} }, { {-5.99742, -37.6572, -87.365, 248.316}, // N [] = 9 {-5.46697, -26.2057, -26.627, 176.382}, {-5.18897, -21.1377, -9.484, 172.704} }, { {-6.22103, -41.7154, -102.680, 389.33}, // N [] = 10 {-5.69244, -29.4521, -30.994, 251.016}, {-5.41533, -24.0006, -7.514, 163.049} }, { {-6.43377, -46.0084, -106.809, 352.752}, // N [] = 11 {-5.90714, -32.8336, -30.275, 249.994}, {-5.63086, -26.9693, -4.083, 151.427} }, { {-6.63790, -50.2095, -124.156, 579.622}, // N [] = 12 {-6.11279, -36.2681, -32.505, 314.802}, {-5.83724, -29.9864, -2.686, 184.116} } }; matrix tau_ct_2010 [] = { { {-3.95877, -9.0531, -28.428, -134.155}, // N [] = 1 {-3.41049, -4.3904, -9.036, -45.374}, {-3.12705, -2.5856, -3.925, -22.380} }, { {-4.32762, -15.4387, -35.679, 0}, // N [] = 2 {-3.78057, -9.5106, -12.074, 0}, {-3.49631, -7.0815, -7.538, 21.892} }, { {-4.66305, -18.7688, -49.793, 104.244}, // N [] = 3 {-4.11890, -11.8922, -19.031, 77.332}, {-3.83511, -9.0723, -8.504, 35.403} }, { {-4.96940, -22.4694, -52.599, 51.314}, // N [] = 4 {-4.42871, -14.5876, -18.228, 39.647}, {-4.14633, -11.2500, -9.873, 54.109} }, { {-5.25276, -26.2183, -59.631, 50.646}, // N [] = 5 {-4.71537, -17.3569, -22.660, 91.359}, {-4.43422, -13.6078, -10.238, 76.781} }, { {-5.51727, -29.9760, -75.222, 202.253}, // N [] = 6 {-4.98228, -20.3050, -25.224, 132.03}, {-4.70233, -16.1253, -9.836, 94.272} }, { {-5.76537, -33.9165, -84.312, 245.394}, // N [] = 7 {-5.23299, -23.3328, -28.955, 182.342}, {-4.95405, -18.7352, -10.168, 120.575} }, { {-6.00003, -37.8892, -96.428, 335.92}, // N [] = 8 {-5.46971, -26.4771, -31.034, 220.165}, {-5.19183, -21.4328, -10.726, 157.955} }, { {-6.22288, -41.9496, -109.881, 466.068}, // N [] = 9 {-5.69447, -29.7152, -33.784, 273.002}, {-5.41738, -24.2882, -8.584, 169.891} }, { {-6.43551, -46.1151, -120.814, 566.823}, // N [] = 10 {-5.90887, -33.0251, -37.208, 346.189}, {-5.63255, -27.2042, -6.792, 177.666} }, { {-6.63894, -50.4287, -128.997, 642.781}, // N [] = 11 {-6.11404, -36.4610, -36.246, 348.554}, {-5.83850, -30.1995, -5.163, 210.338} }, { {-6.83488, -54.7119, -139.800, 736.376}, // N [] = 12 {-6.31127, -39.9676, -37.021, 406.051}, {-6.03650, -33.2381, -6.606, 317.776} } }; matrix tau_ctt_2010 [] = { { {-4.37113, -11.5882, -35.819, -334.047}, // N [] = 1 {-3.83239, -5.9057, -12.490, -118.284}, {-3.55326, -3.6596, -5.293, -63.559} }, { {-4.69276, -20.2284, -64.919, 88.884}, // N [] =2 {-4.15387, -13.3114, -28.402, 72.741}, {-3.87346, -10.4637, -17.408, 66.313} }, { {-4.99071, -23.5873, -76.924, 184.782}, // N [] = 3 {-4.45311, -15.7732, -32.316, 122.705}, {-4.17280, -12.4909, -17.912, 83.285} }, { {-5.26780, -27.2836, -78.971, 137.871}, // N [] = 4 {-4.73244, -18.4833, -31.875, 111.817}, {-4.45268, -14.7199, -17.969, 101.92} }, { {-5.52826, -30.9051, -92.490, 248.096}, // N [] = 5 {-4.99491, -21.2360, -37.685, 194.208}, {-4.71587, -17.0820, -18.631, 136.672} }, { {-5.77379, -34.7010, -105.937, 393.991}, // N [] = 6 {-5.24217, -24.2177, -39.153, 232.528}, {-4.96397, -19.6064, -18.858, 174.919} }, { {-6.00609, -38.7383, -108.605, 365.208}, // N [] = 7 {-5.47664, -27.3005, -39.498, 246.918}, {-5.19921, -22.2617, -17.910, 208.494} }, { {-6.22758, -42.7154, -119.622, 421.395}, // N [] = 8 {-5.69983, -30.4365, -44.300, 345.48}, {-5.42320, -24.9686, -19.688, 274.462} }, { {-6.43933, -46.7581, -136.691, 651.38}, // N [] = 9 {-5.91298, -33.7584, -42.686, 346.629}, {-5.63704, -27.8965, -13.880, 236.975} }, { {-6.64235, -50.9783, -145.462, 752.228}, // N [] = 10 {-6.11753, -37.056, -48.719, 473.905}, {-5.84215, -30.8119, -14.938, 316.006} }, { {-6.83743, -55.2861, -152.651, 792.577}, // N [] = 11 {-6.31396, -40.5507, -46.771, 487.185}, {-6.03921, -33.8950, -9.122, 285.164} }, { {-7.02582, -59.6037, -166.368, 989.879}, // N [] = 12 {-6.50353, -44.0797, -47.242, 543.889}, {-6.22941, -36.9673, -10.868, 418.414} } }; vector ret_vector = {0,0,0}; switch(trend) { case TREND_CONST_ONLY: process(tau_c_2010,ret_vector,num_obs,nseries); break; case TREND_NONE: process(tau_nc_2010,ret_vector,num_obs,nseries); break; case TREND_LINEAR_CONST: process(tau_ct_2010,ret_vector,num_obs,nseries); break; case TREND_QUAD_LINEAR_CONST: process(tau_ctt_2010,ret_vector,num_obs,nseries); break; default: Print("Invalid input for trend argument"); return ret_vector; } return ret_vector; }
テストと検証
実装が正しく実行されていることを検証するために、まずPythonでランダム系列に対してADFテストを実施します。次に、Metatrader 5で同じ系列のADFテストを実行し、出力を比較します。
PythonによるADF検定のコードを以下に示します。
import numpy as np from statsmodels.tsa.stattools import adfuller #initialize array with 100 elements x = np.array([0.97841555,0.31931195,0.68205832,0.56256707,0.05741117,0.30310286, 0.13354023,0.61382247,0.20699517,0.61969826,0.55718307,0.90422809, 0.24220947,0.08719106,0.26714434,0.39439596,0.93919107,0.07756139, 0.53188798,0.5074042,0.40468052,0.41235659,0.79233157,0.58948591, 0.22049794,0.68278894,0.09500558,0.40421058,0.9971231,0.29665678, 0.08254796,0.8089725,0.61434576,0.97610604,0.84084868,0.8034953, 0.765576,0.25014613,0.16268394,0.34259495,0.40085009,0.8416158, 0.6321962,0.45165205,0.12209775,0.40556958,0.96253644,0.30619429, 0.70573114,0.51574979,0.90168104,0.80757639,0.94321618,0.58849563, 0.38905617,0.04574506,0.63134219,0.89198262,0.24102367,0.45749333, 0.76804682,0.50868223,0.91132151,0.7372344,0.32551467,0.27799709, 0.04059095,0.86024797,0.74600612,0.01264258,0.89364963,0.99373472, 0.36177673,0.47173929,0.15124127,0.77354455,0.45131917,0.27258213, 0.69618127,0.35105122,0.1261404,0.21705172,0.88979093,0.97598448, 0.03787156,0.54034132,0.58336702,0.61701685,0.11673483,0.99940389, 0.99371688,0.04428256,0.00239077,0.34609507,0.57588045,0.20222325, 0.20684364,0.29630613,0.65178447,0.86559185]) #perform ADF test on array result = adfuller(x) #print ADF statistic and p-value print(f"ADF statistic: {result[0]}, p-value:{result[1]}") #print critical values print(f"Critical values:{result[4]}")
次に、同じ配列に対してMQL5バージョンのADFテストを実行します。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ADF_test.mq5 | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #include<ADF.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //---series double rand_array[] = { 0.97841555,0.31931195,0.68205832,0.56256707,0.05741117,0.30310286, 0.13354023,0.61382247,0.20699517,0.61969826,0.55718307,0.90422809, 0.24220947,0.08719106,0.26714434,0.39439596,0.93919107,0.07756139, 0.53188798,0.5074042,0.40468052,0.41235659,0.79233157,0.58948591, 0.22049794,0.68278894,0.09500558,0.40421058,0.9971231,0.29665678, 0.08254796,0.8089725,0.61434576,0.97610604,0.84084868,0.8034953, 0.765576,0.25014613,0.16268394,0.34259495,0.40085009,0.8416158, 0.6321962,0.45165205,0.12209775,0.40556958,0.96253644,0.30619429, 0.70573114,0.51574979,0.90168104,0.80757639,0.94321618,0.58849563, 0.38905617,0.04574506,0.63134219,0.89198262,0.24102367,0.45749333, 0.76804682,0.50868223,0.91132151,0.7372344,0.32551467,0.27799709, 0.04059095,0.86024797,0.74600612,0.01264258,0.89364963,0.99373472, 0.36177673,0.47173929,0.15124127,0.77354455,0.45131917,0.27258213, 0.69618127,0.35105122,0.1261404,0.21705172,0.88979093,0.97598448, 0.03787156,0.54034132,0.58336702,0.61701685,0.11673483,0.99940389, 0.99371688,0.04428256,0.00239077,0.34609507,0.57588045,0.20222325, 0.20684364,0.29630613,0.65178447,0.86559185 }; //---variables that will be used to store test results CAdf adf; //--- Do ADF test if(adf.Adfuller(rand_array)) Print("ADF test statistic: ", adf.AdfStatistic(), " P-value:", adf.Pvalue(),"\nCritical values \n",adf.CriticalValues()); else Print("ADF test failed"); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
まずpythonスクリプトを実行します。
LD 0 18:30:22.912 Test_adfuller (NFLX_us,Daily) ADF statistic: -8.495443215534635, p-value:1.2796318143567197e-13
GJ 0 18:30:22.913 Test_adfuller (NFLX_us,Daily) Critical values:{'1%': -3.4989097606014496, '5%': -2.891516256916761, '10%': -2.5827604414827157} 次にMetaTrader 5のスクリプトを使用しても、結果は同じです。
DO 0 18:30:48.460 ADF_test (NFLX_us,D1) ADF test statistic: -8.495443215534634 P-value:1.2796318143567197e-13 ND 0 18:30:48.460 ADF_test (NFLX_us,D1) Critical values OL 0 18:30:48.460 ADF_test (NFLX_us,D1) [-3.49890976060145,-2.891516256916761,-2.582760441482716]
共和分
相関と共和分は、特に時系列データの文脈で変数間の関係を測定するために使用される統計的概念です。どちらも関係を測定するものですが、その目的は異なり、適用されるシナリオも異なります。相関関係とは、2つの変数間の線形関係の強さと方向を示す統計的尺度のことです。
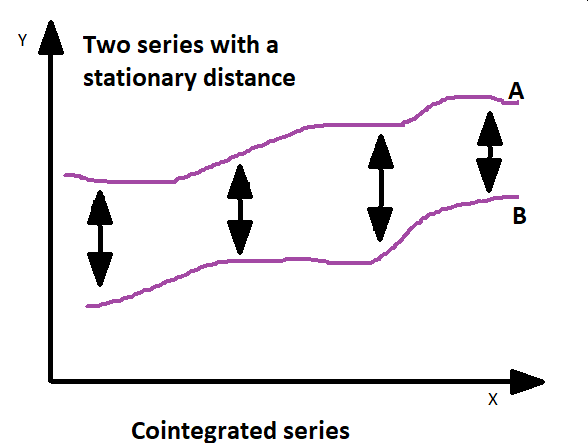
一方、共和分は、長期的な均衡関係や定常関係を持つ非定常時系列変数間の関係を扱います。より簡単に言えば、2つ以上の非定常変数の組み合わせが存在し、それらを一緒に考えたときに安定した長期的な関係があるかどうかを識別します。共和分は、短期的な変動にもかかわらず、時間とともに一緒に動く変数のペアを特定するのに有用です。これは、変数が長期的にリンクしていることを意味し、取引戦略やモデリングにこの関係を利用することが可能になります。
通常、共和分はEngle-Granger検定やジョハンセン検定のような統計的検定を用いて評価されます。これらの検定は、非定常変数の線形結合が定常系列を作るかどうかを確認し、長期的な関係を示します。Engle-Granger検定は、時系列設定における2つの変数間の共和分をテストする2段階の手続きです。回帰モデルを推定し、残差についてテストして、共和分が存在するかどうかを判断します。回帰モデルの残差が定常であることが分かれば、それは2つの変数の間の共和分を示唆します。この場合、変数が個々に定常でないにもかかわらず、それらの線形結合が定常であることを示しています。
Engle-Grangerテストには、複数の系列を同時に扱えないという限界があります。この限界はジョハンセン検定によって解決されます。これは本質的に、ベクトル自己回帰モデルにおける複数の系列間の共和分を検定するためのEngle-Granger法の拡張です。本稿ではジョハンセン検定は取り上げず、一度に2つの系列のみを扱うことにします。
CointegrationTest.mqhには関数CCointクラスが含まれています。CAdfクラスの助けを借りて、拡張されたEngle-Granger検定を実装しています。テストはCCointのAeg()メソッドを呼び出しておこなわれます。テストする系列を含む2つの入力配列が必要です。オプションの入力パラメータtrend、max_lag、autolagは、CAdfのAdfuller()メソッドのパラメータに似ています。ほとんどのテストでは、デフォルト値で十分です。次のセクションで説明します。 CCointの3つのメソッドを呼び出すことによって、共和分検定の結果が得られます。最初のCointStatisticは、内部ADF検定からのADF統計量を返します。CriticalValues()は、テストの臨界値のベクトルを返します。p値はPvalue()を呼び出すことで得られます。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CointegrationTest.mqh | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #include<ADF.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|Class CCoint | //| implements cointegration test of two series | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CCoint { private: double m_coint_stat; //ADF test statistic double m_coint_pvalue; //cointegration p-value vector m_coint_critvalues; //Cointegration critical values CAdf *m_adf; //CAdf object pointer public: CCoint(void); ~CCoint(void); bool Aeg(double &in_one[],double &in_two[],ENUM_TREND trend = TREND_CONST_ONLY,ulong max_lag=0,ENUM_INFO_CRIT autolag=INFO_AIC); double CointStatistic(void){ return m_coint_stat; } double Pvalue(void) { return m_coint_pvalue;} vector CriticalValues(void){ return m_coint_critvalues;} }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CCoint::CCoint(void) { m_adf = new CAdf(); m_coint_critvalues = vector::Zeros(3); m_coint_stat=m_coint_pvalue=EMPTY_VALUE; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Destructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CCoint::~CCoint(void) { if(CheckPointer(m_adf)==POINTER_DYNAMIC) delete m_adf; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Test for cointegration | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CCoint::Aeg(double &in_one[],double &in_two[],ENUM_TREND trend = TREND_CONST_ONLY,ulong max_lag=0,ENUM_INFO_CRIT autolag=INFO_AIC) { //--- if(CheckPointer(m_adf)==POINTER_INVALID) { Print("Critical Internal error: Invalid CAdf pointer"); return false; } //--- if(in_one.Size()<1 || in_two.Size()<1 || in_one.Size()!=in_two.Size()) { Print(__FUNCTION__," Invalid input for one or both arrays"); return false; } vector y1,temp; matrix y2; if(!y1.Assign(in_one) || !temp.Assign(in_two) || !y2.Resize(temp.Size(),1) || !y2.Col(temp,0)) { Print(__FUNCTION__," Assignment error: ", GetLastError()); return false; } ulong obs,kvars=1; obs = y2.Rows(); kvars++; matrix xx; if(trend==TREND_NONE) { if(!xx.Copy(y2)) { Print(__FUNCTION__," Assignment error: ", GetLastError()); return false; } } else if(!addtrend(y2,xx,trend,false)) { Print(__FUNCTION__," Assignment error: ", GetLastError()); return false; } OLS ols; if(!ols.Fit(y1,xx)) return false; if(ols.Rsqe()< 1 - 100*SQRTEPS) { double resid[]; vector resd = ols.Residuals(); ArrayResize(resid,int(resd.Size())); for(uint i = 0; i<resid.Size(); i++) resid[i]=resd[i]; if(!m_adf.Adfuller(resid,max_lag,TREND_NONE,autolag)) return false; m_coint_stat = m_adf.AdfStatistic(); } else { Print("They are (almost) perfectly collinear.\nCointegration test is not reliable in this case"); m_coint_stat=double("nan"); } if(trend==TREND_NONE) m_coint_critvalues.Fill(double("nan")); else m_coint_critvalues = mackinnoncrit(kvars,trend,obs-1); m_coint_pvalue = mackinnonp(m_coint_stat,trend,kvars); return true; }
銘柄の共和分関係のテスト
最後のデモでは、CCointを使用して、銘柄のリストに共和分関係があるかどうかをテストするMQL5スクリプトを作成します。ユーザーは、カンマで区切られた銘柄のリストを入力します。調査する終値の開始日と履歴の長さを設定します。ConfidenceLevelで、ユーザーは希望の有意水準を選択できます。これは、最終的な結果のためにADF統計量と比較される臨界値を決定します。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| SymbolCointegrationTester.mq5 | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #property script_show_inputs #include <CointegrationTest.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| enumeration maps to confidence levels of 99%,95%, and 90% | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_CONFIDENCE_LEVEL { CONF_99=0,//99% CONF_95,//95% CONF_90 //90% }; //--- input parameters input string Symbols = "FB_us,GOOG_us,MSFT_us,NFLX_us,NVDA_us,AAPL_us,TSLA_us";//Comma separated list of symbols to test input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES TimeFrame = PERIOD_D1; input datetime StartDate=D'2022.01.01 00:00:01'; input int Size = 250;//History length input ENUM_CONFIDENCE_LEVEL ConfidenceLevel=CONF_90; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //---Check Size input value if(Size<100) { Print("Invalid input for Size"); return; } //---array for symbols string symbols[]; //---process list of symbols from user input int num_symbols = StringSplit(Symbols,StringGetCharacter(",",0),symbols); //---incase list contains ending comma if(symbols[num_symbols-1]=="") num_symbols--; //---in case there are less than two symbols specified if(num_symbols<2) { Print("Invalid input. Please list at least two symbols"); return; } //---output matrix of indices matrix sym_combos; //---fill sym_combos with index values of symbols array PairedCombinations(symbols,sym_combos,num_symbols); //---price arrays for pair of symbols double symA_prices [], symB_prices[]; //---output vectors holding results of cointegration test vector stats, critvals; //---symbol pairs and result output string symA,symB,result; //---CCoint object CCoint coint; //---loop through all paired combinations from list for(ulong i=0; i<sym_combos.Rows(); i++) { //--- get symbol pair for current combination symA = symbols[int(sym_combos[i][0])]; symB = symbols[int(sym_combos[i][1])]; //--- get prices for the pair of symbols if(CopyClose(symA,TimeFrame,StartDate,Size,symA_prices)<Size|| CopyClose(symB,TimeFrame,StartDate,Size,symB_prices)<Size) { Print("Failed to copy close prices ", ::GetLastError()); return; } //--- test the pair for cointegreation if(!coint.Aeg(symA_prices,symB_prices)) { Print("Cointegration test failed ", ::GetLastError()); return; } //--- vector critvals = coint.CriticalValues(); //--- prepare results output for a test if(coint.CointStatistic()<critvals[ConfidenceLevel]) result="likely cointegrated."; else result="likely not cointegrated."; //--- output the result from cointegration test Print(symA," and ",symB, " are ", result); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Combinations: generates paired combinations | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool PairedCombinations(string &in[], matrix &out,int count = 0) { //---check input array if(in.Size()<1) { Print(__FUNCTION__," input array is empty"); return false; } //---set value for upto equal to the number of elements that should be //---considered in the input array int upto = (count>1 && count<ArraySize(in))?count:ArraySize(in); //--- calculate the number of rows equivalent to number of combinations ulong rows = ulong(MathFactorial(upto)/(MathFactorial(2)*MathFactorial(upto-2))); //---resize output matrix accordingly out.Resize(rows,2); //---fill output matrix with indexes of input array for(uint i=0,z=0; i<in.Size(); i++) { for(uint k = i+1; k<in.Size(); k++,z++) { out[z][0]=i; out[z][1]=k; } } //---return return true; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
この例では、グーグル、フェイスブック、マイクロソフト、ネットフリックス、エヌビディア、アップル、テスラの銘柄をテストします。スクリプトを実行した結果を以下に示します。
HN 0 18:37:31.239 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) FB_us and GOOG_us are likely not cointegrated. PQ 0 18:37:31.280 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) FB_us and MSFT_us are likely not cointegrated. IE 0 18:37:31.322 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) FB_us and NFLX_us are likely not cointegrated. MG 0 18:37:31.365 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) FB_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated. PH 0 18:37:31.411 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) FB_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated. NL 0 18:37:31.453 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) FB_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated. EO 0 18:37:31.496 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) GOOG_us and MSFT_us are likely not cointegrated. ES 0 18:37:31.540 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) GOOG_us and NFLX_us are likely not cointegrated. FE 0 18:37:31.582 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) GOOG_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated. CF 0 18:37:31.623 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) GOOG_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated. EJ 0 18:37:31.665 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) GOOG_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated. HM 0 18:37:31.705 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) MSFT_us and NFLX_us are likely not cointegrated. RN 0 18:37:31.744 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) MSFT_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated. LP 0 18:37:31.785 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) MSFT_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated. OD 0 18:37:31.825 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) MSFT_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated. IG 0 18:37:31.866 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) NFLX_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated. QI 0 18:37:31.906 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) NFLX_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated. FP 0 18:37:31.946 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) NFLX_us and TSLA_us are likely cointegrated. EO 0 18:37:31.987 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) NVDA_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated. RS 0 18:37:32.026 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) NVDA_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated. DE 0 18:37:32.072 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) AAPL_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated.
ネットフリックスとテスラに90%の信頼度で共和分関係がある可能性が高いことを示しています。
同じテストをPythonでおこなうコードを、結果とともに以下に示します。
""" Script demonstrates use of coint() from statsmodels to test symbols for cointegration """ # imports from statsmodels.tsa.stattools import coint from itertools import combinations from datetime import datetime import MetaTrader5 as mt5 import pandas as pd import numpy as np import pytz #initialize connection to mt5 if not mt5.initialize(): print("initialize() failed ") mt5.shutdown() #set up timezone infomation tz=pytz.timezone("Etc/UTC") #use time zone to set correct date for history data extraction startdate = datetime(2022,1,1,hour=0,minute=0,second=1,tzinfo=tz) #list the symbols Symbols = ["FB_us","GOOG_us","MSFT_us","NFLX_us","NVDA_us","AAPL_us","TSLA_us"] #set length of data history num_bars = 250 #set up the shape of the data structure to store prices data = np.zeros((num_bars,len(Symbols))) prices = pd.DataFrame(data,columns=Symbols) #fill prices dataframe with close prices for symbol in Symbols: prices[symbol]=[rate[4] for rate in mt5.copy_rates_from(symbol,mt5.TIMEFRAME_D1,startdate,num_bars)] #we donot need mt5 from here mt5.shutdown() #generate pairs from Symbols list pairs = list(combinations(prices.columns,2)) #set our desired significance level, 0.01->99%, 0.05->95%, 0.1->90% confidence_level = 0.1 #do the test for cointegration on each pair and print results for pair in pairs: df=prices[list(pair)] adf_stat,pvalue,critvalues=coint(df.values[:,0],df.values[:,1]) if pvalue < confidence_level: print(pair[0]," and ",pair[1], " are likely cointegrated") else: print(pair[0]," and ",pair[1], " are likely not cointegrated")
Pythonの結果
MR 0 18:35:17.835 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) FB_us and GOOG_us are likely not cointegrated GE 0 18:35:17.851 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) FB_us and MSFT_us are likely not cointegrated DI 0 18:35:17.867 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) FB_us and NFLX_us are likely not cointegrated CJ 0 18:35:17.867 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) FB_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated MO 0 18:35:17.882 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) FB_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated JQ 0 18:35:17.898 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) FB_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated CD 0 18:35:17.914 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) GOOG_us and MSFT_us are likely not cointegrated MF 0 18:35:17.930 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) GOOG_us and NFLX_us are likely not cointegrated QK 0 18:35:17.946 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) GOOG_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated HM 0 18:35:17.962 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) GOOG_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated OO 0 18:35:17.978 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) GOOG_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated MS 0 18:35:17.978 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) MSFT_us and NFLX_us are likely not cointegrated PD 0 18:35:17.994 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) MSFT_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated MF 0 18:35:18.010 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) MSFT_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated RJ 0 18:35:18.042 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) MSFT_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated RM 0 18:35:18.058 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) NFLX_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated GP 0 18:35:18.074 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) NFLX_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated LN 0 18:35:18.089 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) NFLX_us and TSLA_us are likely cointegrated EF 0 18:35:18.105 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) NVDA_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated QI 0 18:35:18.121 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) NVDA_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated OJ 0 18:35:18.137 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) AAPL_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated
結論
MQL5における拡張ディッキー–フラー検定の実装を見て、それを使用してEngle-Grangerの共和分検定を実装してきました。ADF検定は、ペア取引戦略や統計的裁定取引に関心のある人にとって重要なツールです。 記事で説明されているコードはすべてzipファイルに収められています。以下の表は、このファイルの全内容を示したものです。
| ファイル | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| Mql5\include\OLS.mqh | 通常の最小二乗回帰を実装するOLSクラスの定義 |
| Mql5\include\ADF.mqh | 様々な関数の定義と、ADF検定を実装したCAdfクラス |
| Mql5\include\CointegrationTest.mqh | AugmentedEngle-Grangerテクニックを用いた共和分検定を実装するCCointクラスを定義 |
| Mql5scriptsADF_test.mq5 | ADFテストのMQL5実装をテストするために使用されたMQL5スクリプト |
| Mql5\scripts\SymbolCointegrationTester.mq5 | MetaTrader 5で銘柄の共和分をテストするスクリプト |
| Mql5\scripts\Test_adfuller.py | MQL5の実装を検証するために使用したADFテストのstatsmodels実装を使用したpythonスクリプト |
| Mql5\scripts\SymbolCointegration.py | SymbolCointegrationTesterのPythonバージョン |
MetaQuotes Ltdにより英語から翻訳されました。
元の記事: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/13991
警告: これらの資料についてのすべての権利はMetaQuotes Ltd.が保有しています。これらの資料の全部または一部の複製や再プリントは禁じられています。
この記事はサイトのユーザーによって執筆されたものであり、著者の個人的な見解を反映しています。MetaQuotes Ltdは、提示された情報の正確性や、記載されているソリューション、戦略、または推奨事項の使用によって生じたいかなる結果についても責任を負いません。
 過去のポジションをチャート上に損益図として表示する
過去のポジションをチャート上に損益図として表示する
 知っておくべきMQL5ウィザードのテクニック(第10回):型破りなRBM
知っておくべきMQL5ウィザードのテクニック(第10回):型破りなRBM
 初心者のためのMetaTrader 5とRによるアルゴリズム取引
初心者のためのMetaTrader 5とRによるアルゴリズム取引
- 無料取引アプリ
- 8千を超えるシグナルをコピー
- 金融ニュースで金融マーケットを探索
新しい記事をご覧ください:MQL5におけるAugmented Dickey Fullerテストの実装。
著者フランシス・デュベ