
Package-based approach with KnitPkg for MQL5 development
For maximum reliability and productivity in MetaTrader products built with MQL, this article advocates a development approach based on reusable “packages” managed by KnitPkg, a project manager for MQL5/MQL4. A package can be used as a building block for other packages or as the foundation for final artifacts that run directly on the MetaTrader platform, such as EAs, indicators, and more.

MQL5 Trading Tools (Part 22): Graphing the Histogram and Probability Mass Function (PMF) of the Binomial Distribution
This article develops an interactive MQL5 plot for the binomial distribution, combining a histogram of simulated outcomes with the theoretical probability mass function. It implements mean, standard deviation, skewness, kurtosis, percentiles, and confidence intervals, along with configurable themes and labels, and supports dragging, resizing, and live parameter changes. Use it to assess expected wins, likely drawdowns, and confidence ranges when validating trading strategies.

Engineering Trading Discipline into Code (Part 2): Building a Daily Trade Limit Enforcer for All Trades in MQL5
We have developed a system that enforces a daily trade limit to keep you aligned with your trading rules. It monitors all executed trades across the account and automatically intervenes once the defined limit is reached, preventing any further activity. By embedding control directly into the platform, the system ensures discipline is maintained even when market pressure rises.

Larry Williams Market Secrets (Part 13): Automating Hidden Smash Day Reversal Patterns
The article builds a transparent MQL5 Expert Advisor for Larry Williams’ hidden smash day reversals. Signals are generated only on new bars: a setup bar is validated, then confirmed when the next session trades beyond its extreme. Risk is managed via ATR or structural stops with a defined risk-to-reward, position sizing can be fixed or balance-based, and direction filters plus a one-position policy ensure reproducible tests.

Neural Networks in Trading: Integrating Chaos Theory into Time Series Forecasting (Final Part)
We continue to integrate methods proposed by the authors of the Attraos framework into trading models. Let me remind you that this framework uses concepts of chaos theory to solve time series forecasting problems, interpreting them as projections of multidimensional chaotic dynamic systems.

The MQL5 Standard Library Explorer (Part 9): Using ALGLIB to Filter Excessive MA Crossover Signals
During sideways price movements, traders face excessive signals from multiple moving average crossovers. Today, we discuss how ALGLIB preprocesses raw price data to produce filtered crossover layers, which can also generate alerts when they occur. Join this discussion to learn how a mathematical library can be leveraged in MQL5 programs.

Formulating Dynamic Multi-Pair EA (Part 7): Cross-Pair Correlation Mapping for Real-Time Trade Filtering
In this part, we will integrate a real-time correlation matrix into a multi-symbol Expert Advisor to prevent redundant or risk-stacked trades. By dynamically measuring cross-pair relationships, the EA will filter entries that conflict with existing exposure, improving portfolio balance, reducing systemic risk, and enhancing overall trade quality.
Neural Networks in Trading: Integrating Chaos Theory into Time Series Forecasting (Attraos)
The Attraos framework integrates chaos theory into long-term time series forecasting, treating them as projections of multidimensional chaotic dynamic systems. Exploiting attractor invariance, the model uses phase space reconstruction and dynamic multi-resolution memory to preserve historical structures.

Price Action Analysis Toolkit Development (Part 63): Automating Rising and Falling Wedge Detection in MQL5
In this part of the Price Action Analysis Toolkit Development series, we develop an MQL5 indicator that automatically detects rising and falling wedge patterns in real time. The system confirms pivot structures, validates boundary convergence mathematically, prevents overlapping formations, and monitors breakout and failure conditions with precise visual feedback. Built using a clean object-oriented architecture, this implementation converts subjective wedge recognition into a structured, state-aware analytical component designed to strengthen disciplined price action analysis.

Overcoming Accessibility Challenges in MQL5 Trading Tools (Part II): Enabling EA Voice Using a Python Text-to-Speech Engine
Let's discuss how we can make our Expert Advisors speech‑capable using text‑to‑speech technology, partnering Python and MQL5. After reading this article, you will walk away with a working example of an EA that speaks dynamic market information. You will master the application of TTS, the WebRequest function, and learn how Python libraries integrate with the MQL5 language to create a truly voice‑aware trading tool.

MQL5 Trading Tools (Part 21): Adding Cyberpunk Theme to Regression Graphs
In this article, we enhance the regression graphing tool in MQL5 by adding a cyberpunk theme mode with neon glows, animations, and holographic effects for immersive visualization. We integrate theme toggling, dynamic backgrounds with stars, glowing borders, and neon points/lines, while maintaining standard mode compatibility. This dual-theme system elevates pair analysis with futuristic aesthetics, supporting real-time updates and interactions for engaging trading insights.

Price Action Analysis Toolkit Development (Part 62): Building an Adaptive Parallel Channel Detection and Breakout System in MQL5
This article presents an adaptive parallel channel detection and breakout system in MQL5. It explains how swing points are identified, channels are constructed and dynamically recalculated, and breakouts are confirmed and visualized with persistent signals. The framework integrates trendline geometry, ATR-based filtering, and retest validation to provide reliable, real-time price action analysis for professional charting and trading decisions.

Statistical Arbitrage Through Cointegrated Stocks (Final): Data Analysis with Specialized Database
The article shows how to pair SQLite (OLTP) with DuckDB (OLAP) for statistical arbitrage data processing. DuckDB’s columnar engine, ASOF JOIN, and array functions accelerate core tasks such as quote–trade alignment and RWEC, with measured speedups from 2x to 23x versus SQLite on larger inputs. You get simpler queries and faster analytics while keeping trade execution in SQLite.

Introduction to MQL5 (Part 42): Beginner Guide to File Handling in MQL5 (IV)
This article shows how to build an MQL5 indicator that reads a CSV trading history, extracts Profit($) values and total trades, and computes a cumulative balance progression. We plot the curve in a separate indicator window, auto-scale the Y-axis, and draw horizontal and vertical axes for alignment. The indicator updates on a timer and redraws only when new trades appear. Optional labels display per-trade profit and loss to help assess performance and drawdowns directly on the chart.

Swing Extremes and Pullbacks in MQL5 (Part 2): Automating the Strategy with an Expert Advisor
Built on lower-timeframe market structure, and then orchestrated on the higher-timeframe, this indicator detects swing extremes where price becomes statistically vulnerable to reversal. It visualizes overextension and pullback zones, offering early insight into mean-reversion behavior.
Implementation of a Breakeven Mechanism in MQL5 (Part 1): Base Class and Fixed-Points Breakeven Mode
This article discusses the application of a breakeven mechanism in automated strategies using the MQL5 language. We will start with a simple explanation of what the breakeven mode is, how it is implemented, and its possible variations. Next, this functionality will be integrated into the Order Blocks expert advisor, which we created in our last article on risk management. To evaluate its effectiveness, we will run two backtests under specific conditions: one using the breakeven mechanism and the other without it.

Larry Williams Market Secrets (Part 12): Context Based Trading of Smash Day Reversals
This article shows how to automate Larry Williams Smash Day reversal patterns in MQL5 within a structured context. We implement an Expert Advisor that validates setups over a limited window, aligns entries with Supertrend-based trend direction and day-of-week filters, and supports entry on level cross or bar close. The code enforces one position at a time and risk-based or fixed sizing. Step-by-step development, backtesting procedure, and reproducible settings are provided.

From Novice to Expert: Extending a Liquidity Strategy with Trend Filters
The article extends a liquidity-based strategy with a simple trend constraint: trade liquidity zones only in the direction of the EMA(50). It explains filtering rules, presents a reusable TrendFilter.mqh class and EA integration in MQL5, and compares baseline versus filtered tests. Readers gain a clear directional bias, reduced overtrading in countertrend phases, and ready-to-use source files.

Swing Extremes and Pullbacks in MQL5 (Part 1): Developing a Multi-Timeframe Indicator
In this discussion we will Automate Swing Extremes and the Pullback Indicator, which transforms raw lower-timeframe (LTF) price action into a structured map of market intent, precisely identifying swing highs, swing lows, and corrective phases in real time. By programmatically tracking microstructure shifts, it anticipates potential reversals before they fully unfold—turning noise into actionable insight.

Creating Custom Indicators in MQL5 (Part 8): Adding Volume Integration for Deeper Market Profile Analysis
In this article, we enhance the hybrid Time Price Opportunity (TPO) market profile indicator in MQL5 by integrating volume data to calculate volume-based point of control, value areas, and volume-weighted average price with customizable highlighting options. The system introduces advanced features like initial balance detection, key level extension lines, split profiles, and alternative TPO characters such as squares or circles for improved visual analysis across multiple timeframes.

MQL5 Trading Tools (Part 20): Canvas Graphing with Statistical Correlation and Regression Analysis
In this article, we create a canvas-based graphing tool in MQL5 for statistical correlation and linear regression analysis between two symbols, with draggable and resizable features. We incorporate ALGLIB for regression calculations, dynamic tick labels, data points, and a stats panel displaying slope, intercept, correlation, and R-squared. This interactive visualization aids in pair trading insights, supporting customizable themes, borders, and real-time updates on new bars

MetaTrader 5 Machine Learning Blueprint (Part 7): From Scattered Experiments to Reproducible Results
In the latest installment of this series, we move beyond individual machine learning techniques to address the "Research Chaos" that plagues many quantitative traders. This article focuses on the transition from ad-hoc notebook experiments to a principled, production-grade pipeline that ensures reproducibility, traceability, and efficiency.

Engineering Trading Discipline into Code (Part 1): Creating Structural Discipline in Live Trading with MQL5
Discipline becomes reliable when it is produced by system design, not willpower. Using MQL5, the article implements real-time constraints—trade-frequency caps and daily equity-based stops—that monitor behavior and trigger actions on breach. Readers gain a practical template for governance layers that stabilize execution under market pressure.

From Novice to Expert: Automating Intraday Strategies
We translate the EMA‑50 retest idea into a behavior‑driven Expert Advisor for intraday trading. The study formalizes trend bias, EMA interaction (pierce and close), reaction confirmation, and optional filters, then implements them in MQL5 with modular functions and resource‑safe handles. Visual testing in the Strategy Tester verifies signal correctness. The result is a clear template for coding discretionary bounces.
Market Simulation (Part 16): Sockets (X)
We are close to completing this challenge. However, before we begin, I want you to try to understand these two articles—this one and the previous one. That way, you will truly understand the next article, in which I will cover exclusively the part related to MQL5 programming. But I will also try to make it understandable. If you do not understand these last two articles, it will be difficult for you to understand the next one, because the material accumulates. The more things there are to do, the more you need to create and understand in order to achieve the goal.

Creating Custom Indicators in MQL5 (Part 7): Hybrid Time Price Opportunity (TPO) Market Profiles for Session Analysis
In this article, we develop a custom indicator in MQL5 for hybrid Time Price Opportunity (TPO) market profiles, supporting multiple session timeframes such as intraday, daily, weekly, monthly, and fixed periods with timezone adjustments. The indicator quantizes prices into a grid, tracks session data including highs, lows, opens, and closes, and calculates key elements like the point of control and value area based on TPO counts. It renders profiles visually on the chart with customizable colors for TPO letters, single prints, value areas, POC, and close markers, enabling detailed session analysis

MQL5 Trading Tools (Part 19): Building an Interactive Tools Palette for Chart Drawing
In this article, we build an interactive tools palette in MQL5 for chart drawing, with draggable, resizable panels and theme switching. We add buttons for tools like crosshair, trendlines, lines, rectangles, Fibonacci, text, and arrows, handling mouse events for activation and instructions. This system improves trading analysis through a customizable UI, supporting real-time interactions on charts

Market Simulation (Part 15): Sockets (IX)
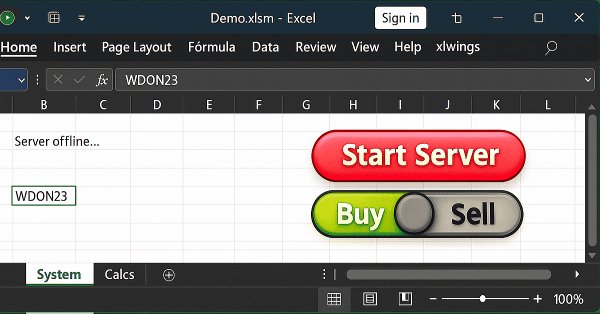
In this article, we will discuss one of the possible solutions to what we have been trying to demonstrate—namely, how to allow an Excel user to perform an action in MetaTrader 5 without sending orders or opening or closing positions. The idea is that the user employs Excel to conduct fundamental analysis of a particular symbol. And by using only Excel, they can instruct an expert advisor running in MetaTrader 5 to open or close a specific position.

Introduction to MQL5 (Part 41): Beginner Guide to File Handling in MQL5 (III)
Learn how to read a CSV file in MQL5 and organize its trading data into dynamic arrays. This article shows step by step how to count file elements, store all data in a single array, and separate each column into dedicated arrays, laying the foundation for advanced analysis and trading performance visualization.

Market Simulation (Part 13): Sockets (VII)
When we develop something in xlwings or any other package that allows reading and writing directly to Excel, we must note that all programs, functions, or procedures execute and then complete their task. They do not remain in a loop, no matter how hard we try to do things differently.

Using the MQL5 Economic Calendar for News Filtering (Part 1): Implementing Pre- and Post-News Windows in MQL5
We build a calendar‑driven news filter entirely in MQL5, avoiding web requests and external DLLs. Part 1 covers loading and caching events, mapping them to symbols by currency, filtering by impact level, defining pre/post windows, and blocking new trades during active news, with optional pre‑news position closure. The result is a configurable, prop‑firm‑friendly control that reduces false pauses and protects entries during volatility.

Market Simulation (Part 12): Sockets (VI)
In this article, we will look at how to solve certain problems and issues that arise when using Python code within other programs. More specifically, we will demonstrate a common issue encountered when using Excel in conjunction with MetaTrader 5, although we will be using Python to facilitate this interaction. However, this implementation has a minor drawback. It does not occur in all cases, but only in certain specific situations. When it does happen, it is necessary to understand the cause. In today’s article, we will begin explaining how to resolve this issue.

Risk Management (Part 5): Integrating the Risk Management System into an Expert Advisor
In this article, we will implement the risk management system developed in previous publications and add the Order Blocks indicator described in other articles. In addition, we will run a backtest so we can compare results with the risk management system enabled and evaluate the impact of dynamic risk.

Automating Market Memory Zones Indicator: Where Price is Likely to Return
This article turns Market Memory Zones from a chart-only concept into a complete MQL5 Expert Advisor. It automates Displacement, Structure Transition (CHoCH), and Liquidity Sweep zones using ATR- and candle-structure filters, applies lower-timeframe confirmation, and enforces risk-based position sizing with dynamic SL and structure-based TP. You will get the code architecture for detection, entries, trade management, and visualization, plus a brief backtest review.

Introduction to MQL5 (Part 40): Beginner Guide to File Handling in MQL5 (II)
Create a CSV trading journal in MQL5 by reading account history over a defined period and writing structured records to file. The article explains deal counting, ticket retrieval, symbol and order type decoding, and capturing entry (lot, time, price, SL/TP) and exit (time, price, profit, result) data with dynamic arrays. The result is an organized, persistent log suitable for analysis and reporting.

MQL5 Trading Tools (Part 18): Rounded Speech Bubbles/Balloons with Orientation Control
This article shows how to build rounded speech bubbles in MQL5 by combining a rounded rectangle with a pointer triangle and controlling orientation (up, down, left, right). It details geometry precomputation, supersampled filling, rounded apex arcs, and segmented borders with an extension ratio for seamless joins. Readers get configurable code for size, radii, colors, opacity, and thickness, ready for alerts or tooltips in trading interfaces.

Price Action Analysis Toolkit Development (Part 61): Structural Slanted Trendline Breakouts with 3-Swing Validation
We present a slanted trendline breakout tool that relies on three‑swing validation to generate objective, price‑action signals. The system automates swing detection, trendline construction, and breakout confirmation using crossing logic to reduce noise and standardize execution. The article explains the strategy rules, shows the MQL5 implementation, and reviews testing results; the tool is intended for analysis and signal confirmation, not automated trading.

Risk Management (Part 4): Completing the Key Class Methods
This is Part 4 of our series on risk management in MQL5, where we continue exploring advanced methods for protecting and optimizing trading strategies. Having laid important foundations in earlier articles, we will now focus on completing all remaining methods postponed in Part 3, including functions for checking whether specific profit or loss levels have been reached. In addition, we will introduce new key events that enable more accurate and flexible risk management.

From Basic to Intermediate: Struct (IV)
In this article, we will explore how to create so-called structural code, where the entire context and methods for manipulating variables and information are placed within a structure to create a suitable context for implementing any code. Therefore, we will examine the necessity of using a private section of the code to separate what is public from what is not, thereby adhering to the rule of encapsulation and preserving the context for which the data structure was created.

ARIMA Forecasting Indicator in MQL5
In this article we are implementing ARIMA forecasting indicator in MQL5. It examines how the ARIMA model generates forecasts, its applicability to the Forex market and the stock market in general. It also explains what AR autoregression is, how autoregressive models are used for forecasting, and how the autoregression mechanism works.