TAMA Trend Adaptive Moving Averages
- Indicators
- Patrick Helmut Werner Winter
- Version: 1.16
- Activations: 5
Honored with the VTAD Award 2022 (VTAD = Association of Technical Analysts Germany, German branch of IFTA).
Core Features:
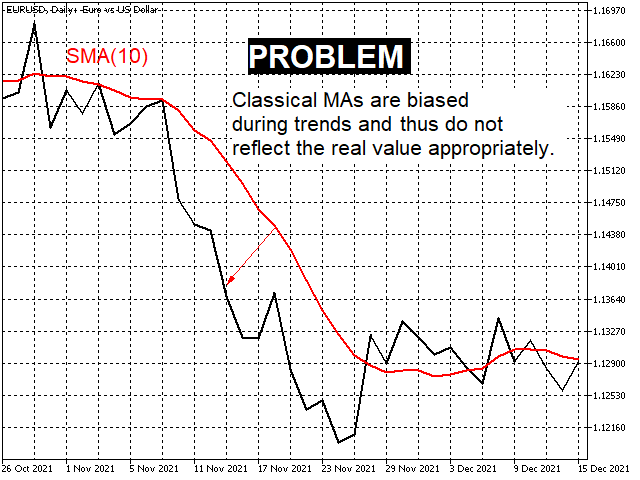
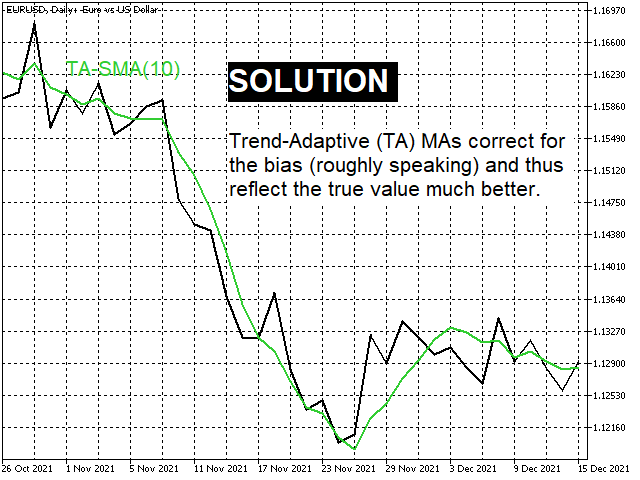
- Classic MAs are corrected in such a way that they then reflect the value without distortion during trends. (screenshots 1 and 2)
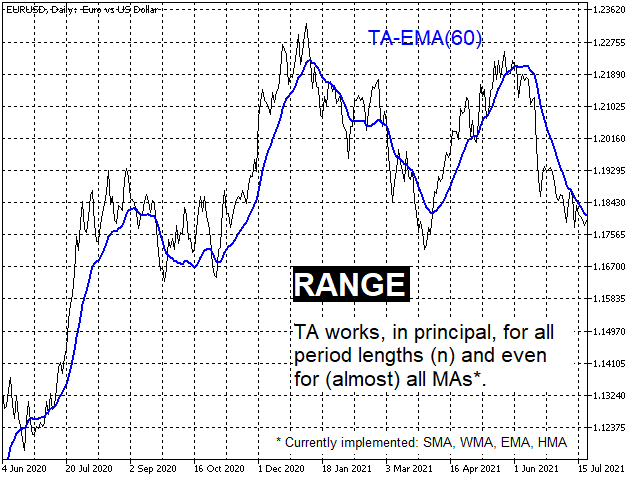
In principle, this works for (almost) any MA; implemented in the indicator are the four main ones: SMA, WMA, EMA and HMA. - The trend correction leads to better smoothing properties and usually significantly lower delays (lags). (screenshots 2 and 3)
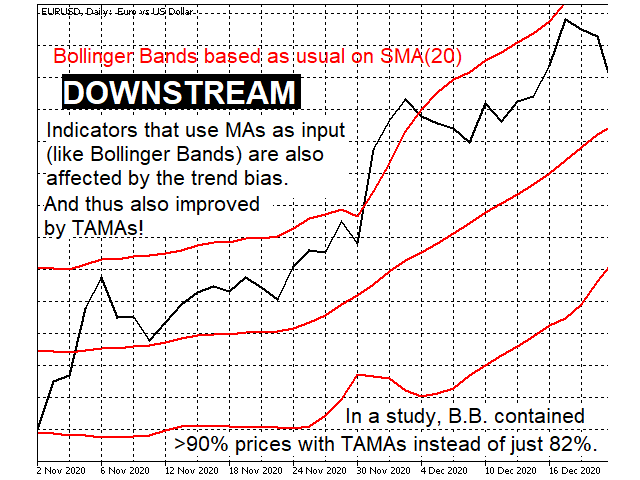
- Downstream indicators that are based on classic MAs receive trend-distortion-free input, which usually improves them. (screen shot 4)
For example, in the fundamental work*, Bollinger bands, which were wrapped around a classic SMA as usual, contained approx. 82% of all next-day prices (instead of the often postulated 95%),
while the corresponding value after the correction by TAMA was over 90% - with the same channel size!
Advanced features:
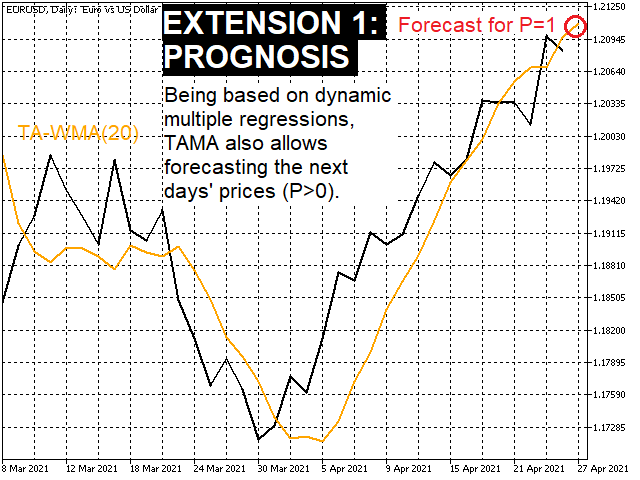
- Since TAMAs are based on regressions, they can be used to forecast future price values. (screen shot 5)
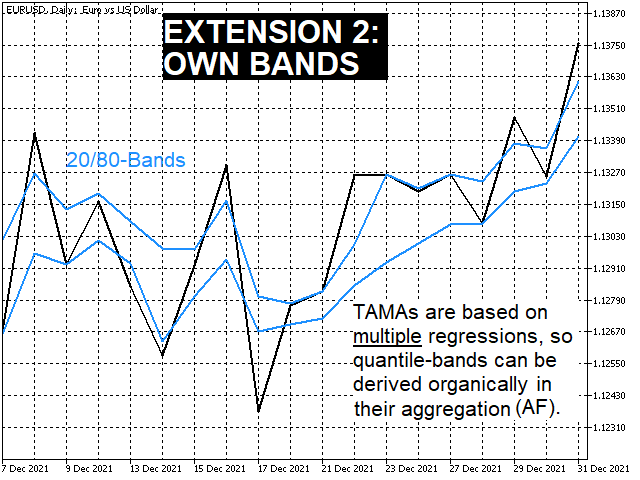
- Because of the aggregation of multiple regressions, TAMAs can also be used as a quantile-based bands indicator. (screen shot 6)
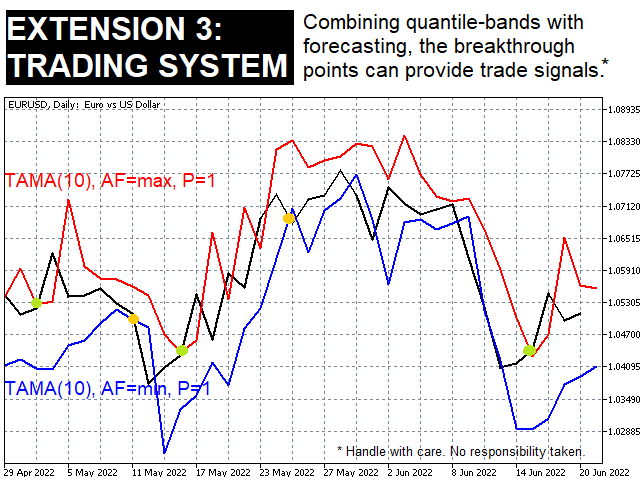
The bands generated this way are usually much narrower than Bollinger bands (in the fundamental work* factor 1:2.5), but still contain almost as many values (in the fundamental work* approx. 75%)! - By combining these approaches, possible trading signals can also be derived directly from TAMAs. (screen shot 7)
Input parameters:
| Name | Symbol | Domain | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | n | Integer > 0 | 20 | Period of the base MA |
| Base MA | w | Predefined value (enum) | HMA | Type of the base MA (SMA, WMA, EMA oder HMA) |
| Trend Adaption | TA | Boolean | true | Switch for the "TA" in TAMA; if 0, result like base MA |
| Prognosis | P | Integer >= 0 | 0 | Whether or by how many days into the future a forecast should be made |
| Aggregation function | AF | -1 for mean or real number between 0 and 1 (incl.) for corresponding Q quantile (0=min, 1=max) | -1 | Type of aggregation for the various regressions. |
Caution: P>0 has an effect for each trading day, not just the latest!
Background:
The calculation of TAMAs is based on multiple, dynamic linear regressions formed within an n-period window based on price, weighted and finally aggregated.
* Fundamental work: Patrick Winter (2022): Trend-Adaptive Moving Averages (TAMA). Contribution to the VTAD Award 2022; available online at the VTAD.
The author of the TAMA procedure, Dr. Patrick Winter, holds a doctorate in business informatics and has more than ten years of scientifically sound experience in the development of indicators. He is a multiple VTAD award winner and has been widely published in academic journals as well as the IFTA Journal.