Diagonal
A diagonal is a motive pattern yet not an impulse, as it has two corrective characteristics. As with an impulse, no reactionary subwave fully retraces the preceding actionary subwave, and the third subwave is never the shortest. However, a diagonal is the only five-wave structure in the direction of the main trend within which wave four almost always moves into the price territory of (i.e., overlaps) wave one and within which all the waves are "threes," producing an overall count of 3-3-3-3-3. On rare occasions, a diagonal may end in a truncation, although in our experience such truncations occur only by the slimmest of margins. This pattern substitutes for an impulse at two specific locations in the wave structure.
Ending Diagonal
An ending diagonal is a special type of wave that occurs primarily in the fifth wave position at times when the preceding move has gone "too far too fast," as Elliott put it. A very small percentage of ending diagonals appear in the C wave position of A-B-C formations. In double or triple threes (to be covered in Lesson 9), they appear only as the final "C" wave. In all cases, they are found at the termination points of larger patterns, indicating exhaustion of the larger movement.
Ending diagonals take a wedge shape within two converging lines, with each subwave, including waves 1, 3 and 5, subdividing into a "three," which is otherwise a corrective wave phenomenon. The ending diagonal is illustrated in Figures 1-15 and 1-16 and shown in its typical position in larger impulse waves.
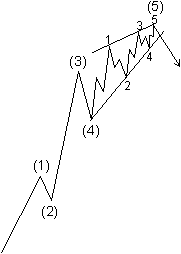
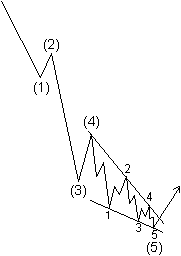
Figure 1-15 Figure 1-16
We have found one case in which the pattern's boundary lines diverged, creating an expanding wedge rather than a contracting one. However, it is unsatisfying analytically in that its third wave was the shortest actionary wave, the entire formation was larger than normal, and another interpretation was possible, if not attractive. For these reasons, we do not include it as a valid variation.
Ending diagonals have occurred recently in Minor degree as in early 1978, in Minute degree as in February-March 1976, and in Subminuette degree as in June 1976. Figures 1-17 and 1-18 show two of these periods, illustrating one upward and one downward "real-life" formation. Figure 1-19 shows our real-life possible expanding diagonal. Notice that in each case, an important change of direction followed.

Figure 1-17
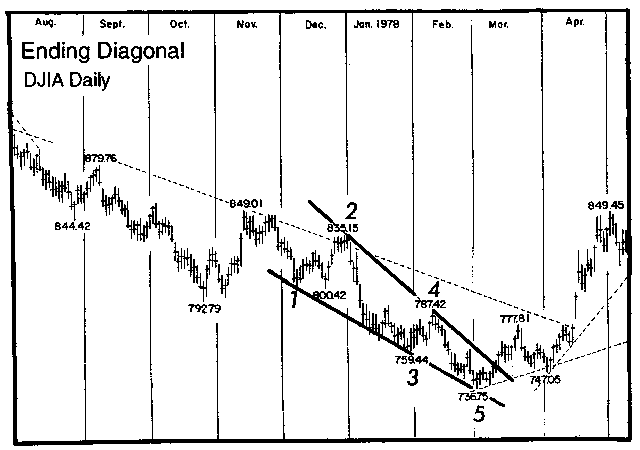
Figure 1-18
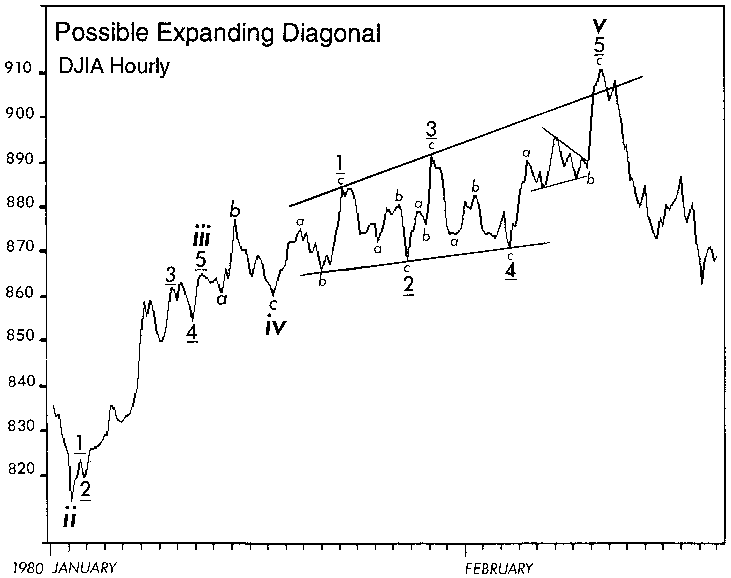
Figure 1-19
Although not so illustrated in Figures 1-15 and 1-16, fifth waves of diagonals often end in a "throw-over," i.e., a brief break of the trendline connecting the end points of waves one and three. Figures 1-17 and 1-19 show real life examples. While volume tends to diminish as a diagonal of small degree progresses, the pattern always ends with a spike of relatively high volume when a throw-over occurs. On rare occasions, the fifth subwave will fall short of its resistance trendline.
A rising diagonal is bearish and is usually followed by a sharp decline retracing at least back to the level where it began. A falling diagonal by the same token is bullish, usually giving rise to an upward thrust.
Fifth wave extensions, truncated fifths and ending diagonal all imply the same thing: dramatic reversal ahead. At some turning points, twoof these phenomena have occurred together at different degrees, compounding the violence of the next move in the opposite direction.
END OF LESSON 3 - PART 1.