Sebastiaan de Boorder / Profil
- Bilgiler
|
12+ yıl
deneyim
|
0
ürünler
|
0
demo sürümleri
|
|
0
işler
|
0
sinyaller
|
0
aboneler
|
For over thousands of years man has been trying to predict his future. He has always failed-and his failures are buried in the dust of history. Legendary fortune tellers, prophets, oracles, medicine men, astrologers, numerologists, mystics, charlatans, and seers, all claimed possession of supernatural and occult powers that enabled them to see into the future. Wars were fought, kingdoms fell, and civilizations were altered as a result of their pronouncements and predictions.
We are not without their counterparts today. They invade our homes through the media of television, radio, internet, smartphones, and the press, claiming hidden and mysterious powers that enable them to solve murders, foretell earthquakes, and blueprint our days in advance. They play on latent superstitions within all of us, piously predicting the next political assassination, the next airline tragedy, the next Hollywood divorce.
But, working quietly behind the scenes, thousands of scientists in fields as unrelated as history, botany, anthropology, mammalogy, terrestrial magnetism, sociology, and economics, to name only a few, are accumulating facts and figures that promise to make this age-old dream of foretelling the future at least a partia !!
OUR MISSION: FIND UNIVERSAL CYCLES AND THE MYSTERIOUS FORCES THAT TRIGGER EVENTS ON FINANCIAL MARKETS
( Knowledge is wonderful; Science is amazing. But wisdom is power )
We are not without their counterparts today. They invade our homes through the media of television, radio, internet, smartphones, and the press, claiming hidden and mysterious powers that enable them to solve murders, foretell earthquakes, and blueprint our days in advance. They play on latent superstitions within all of us, piously predicting the next political assassination, the next airline tragedy, the next Hollywood divorce.
But, working quietly behind the scenes, thousands of scientists in fields as unrelated as history, botany, anthropology, mammalogy, terrestrial magnetism, sociology, and economics, to name only a few, are accumulating facts and figures that promise to make this age-old dream of foretelling the future at least a partia !!
OUR MISSION: FIND UNIVERSAL CYCLES AND THE MYSTERIOUS FORCES THAT TRIGGER EVENTS ON FINANCIAL MARKETS
( Knowledge is wonderful; Science is amazing. But wisdom is power )
Arkadaşlar
927
İstekler
Giden
Sebastiaan de Boorder
The Stock Markets Of The 10 Largest Global Economies Are All Crashing:
You would think that the simultaneous crashing of all of the largest stock markets around the world would be very big news. But so far the mainstream media in the United States is treating it like it isn’t really a big deal. Over the last sixty days, we have witnessed the most significant global stock market decline since the fall of 2008, and yet most people still seem to think that this is just a temporary “bump in the road” and that the bull market will soon resume. Hopefully they are right. When the Dow Jones Industrial Average plummeted 777 points on September 29th, 2008 everyone freaked out and rightly so. But a stock market crash doesn’t have to be limited to a single day. Since the peak of the market earlier this year, the Dow is down almost three times as much as that 777 point crash back in 2008. Over the last sixty days, we have seen the 8th largest single day stock market crash in U.S. history on a point basis and the 10th largest single day stock market crash in U.S. history on a point basis. You would think that this would be enough to wake people up, but most Americans still don’t seem very alarmed. And of course what has happened to U.S. stocks so far is quite mild compared to what has been going on in the rest of the world.
Right now, stock market wealth is being wiped out all over the planet, and none of the largest global economies have been exempt from this. The following is a summary of what we have seen in recent days…
#1 The United States – The Dow Jones Industrial Average is down more than 2000 points since the peak of the market. Last month we saw stocks decline by more than 500 points on consecutive trading days for the first time ever, and there has not been this much turmoil in U.S. markets since the fall of 2008.
#2 China – The Shanghai Composite Index has plummeted nearly 40 percent since hitting a peak earlier this year. The Chinese economy is steadily slowing down, and we just learned that China’s manufacturing index has hit a 78 month low.
#3 Japan – The Nikkei has experienced extremely violent moves recently, and it is now down more than 3000 points from the peak that was hit earlier in 2015. The Japanese economy and the Japanese financial system are both basket cases at this point, and it isn’t going to take much to push Japan into a full-blown financial collapse.
#4 Germany – Almost one-fourth of the value of German stocks has already been wiped out, and this crash threatens to get much worse. The Volkswagen emissions scandal is making headlines all over the globe, and don’t forget to watch for massive trouble at Germany’s biggest bank.
#5 The United Kingdom – British stocks are down about 16 percent from the peak of the market, and the UK economy is definitely on shaky ground.
#6 France – French stocks have declined nearly 18 percent, and it has become exceedingly apparent that France is on the exact same path that Greece has already gone down.
#7 Brazil – Brazil is the epicenter of the South American financial crisis of 2015. Stocks in Brazil have plunged more than 12,000 points since the peak, and the nation has already officially entered a new recession.
#8 Italy – Watch Italy. Italian stocks are already down 15 percent, and look for the Italian economy to make very big headlines in the months ahead.
#9 India – Stocks in India have now dropped close to 4000 points, and analysts are deeply concerned about this major exporting nation as global trade continues to contract.
#10 Russia – Even though the price of oil has crashed, Russia is actually doing better than almost everyone else on this list. Russian stocks have fallen by about 10 percent so far, and if the price of oil stays this low the Russian financial system will continue to suffer.
What we are witnessing now is the continuation of a cycle of financial downturns that has happened every seven years. The following is a summary of how this cycle has played out over the past 50 years…
It started in 1966 with a 20 percent stock market crash.
Seven years later, the market lost another 45 percent (1973-74).
Seven years later was the beginning of the “hard recession” (1980).
Seven years later was the Black Monday crash of 1987.
Seven years later was the bond market crash of 1994.
Seven years later was 9/11 and the 2001 tech bubble collapse.
Seven years later was the 2008 global financial collapse.
2015: What’s next?
You would think that the simultaneous crashing of all of the largest stock markets around the world would be very big news. But so far the mainstream media in the United States is treating it like it isn’t really a big deal. Over the last sixty days, we have witnessed the most significant global stock market decline since the fall of 2008, and yet most people still seem to think that this is just a temporary “bump in the road” and that the bull market will soon resume. Hopefully they are right. When the Dow Jones Industrial Average plummeted 777 points on September 29th, 2008 everyone freaked out and rightly so. But a stock market crash doesn’t have to be limited to a single day. Since the peak of the market earlier this year, the Dow is down almost three times as much as that 777 point crash back in 2008. Over the last sixty days, we have seen the 8th largest single day stock market crash in U.S. history on a point basis and the 10th largest single day stock market crash in U.S. history on a point basis. You would think that this would be enough to wake people up, but most Americans still don’t seem very alarmed. And of course what has happened to U.S. stocks so far is quite mild compared to what has been going on in the rest of the world.
Right now, stock market wealth is being wiped out all over the planet, and none of the largest global economies have been exempt from this. The following is a summary of what we have seen in recent days…
#1 The United States – The Dow Jones Industrial Average is down more than 2000 points since the peak of the market. Last month we saw stocks decline by more than 500 points on consecutive trading days for the first time ever, and there has not been this much turmoil in U.S. markets since the fall of 2008.
#2 China – The Shanghai Composite Index has plummeted nearly 40 percent since hitting a peak earlier this year. The Chinese economy is steadily slowing down, and we just learned that China’s manufacturing index has hit a 78 month low.
#3 Japan – The Nikkei has experienced extremely violent moves recently, and it is now down more than 3000 points from the peak that was hit earlier in 2015. The Japanese economy and the Japanese financial system are both basket cases at this point, and it isn’t going to take much to push Japan into a full-blown financial collapse.
#4 Germany – Almost one-fourth of the value of German stocks has already been wiped out, and this crash threatens to get much worse. The Volkswagen emissions scandal is making headlines all over the globe, and don’t forget to watch for massive trouble at Germany’s biggest bank.
#5 The United Kingdom – British stocks are down about 16 percent from the peak of the market, and the UK economy is definitely on shaky ground.
#6 France – French stocks have declined nearly 18 percent, and it has become exceedingly apparent that France is on the exact same path that Greece has already gone down.
#7 Brazil – Brazil is the epicenter of the South American financial crisis of 2015. Stocks in Brazil have plunged more than 12,000 points since the peak, and the nation has already officially entered a new recession.
#8 Italy – Watch Italy. Italian stocks are already down 15 percent, and look for the Italian economy to make very big headlines in the months ahead.
#9 India – Stocks in India have now dropped close to 4000 points, and analysts are deeply concerned about this major exporting nation as global trade continues to contract.
#10 Russia – Even though the price of oil has crashed, Russia is actually doing better than almost everyone else on this list. Russian stocks have fallen by about 10 percent so far, and if the price of oil stays this low the Russian financial system will continue to suffer.
What we are witnessing now is the continuation of a cycle of financial downturns that has happened every seven years. The following is a summary of how this cycle has played out over the past 50 years…
It started in 1966 with a 20 percent stock market crash.
Seven years later, the market lost another 45 percent (1973-74).
Seven years later was the beginning of the “hard recession” (1980).
Seven years later was the Black Monday crash of 1987.
Seven years later was the bond market crash of 1994.
Seven years later was 9/11 and the 2001 tech bubble collapse.
Seven years later was the 2008 global financial collapse.
2015: What’s next?

Sebastiaan de Boorder



Sometimes we wonder how people actually live . When we look at for example the Dow Jones on Wall Street , we see a very rosy picture .
The stock market continues to rise and that should mean that it goes very well with the economy , or not?
Here are the statistics on the development of the Dow Jones over the past decade. (chart below)
Then you see that after the financial crisis in 2008, the stock market in early 2009 is at an all time low and then as a sort of comet enters the air.
According to the chart below , the market capitalization of companies has more than doubled since 2009 and this is now gradually at historical highs .
If the companies in that period became worth much more than you must also still be found in the real economy. That should do it according to these fantastic statistics.
The reverse appears to be the case!
This statistic indicates the question for global shipping of goods . When economies are doing well, so there is much produced and there is also a high demand for transport.
Below (right) is the Baltic Dry Index .
As you can see this chart collapsed in late 2008 at a furious pace to record lows, but struggled somewhat on again.
From the middle of last year, he goes in a straight line down to the lowest point ever .
Which means that there is little or no demand for transport by ship and worldwide economies produce much less or just lie entirely at their hole, in stark contrast to what market prices we want to emulate.
This includes all fits quite nice because the first bulk cargo carriers such as the Danish Copenhagen Ship, have filed for bankruptcy.
The CEO of Copenhagen Ship also said , "We have reached a point where there is nothing more to do ." And this is just one of the many shipping companies or have failed or teetering on the edge of it.
Is there one good economist in this world who can explain me why the value of companies on the stock market to rise to idiotic heights , while the global shipping has fallen ?
The stock market continues to rise and that should mean that it goes very well with the economy , or not?
Here are the statistics on the development of the Dow Jones over the past decade. (chart below)
Then you see that after the financial crisis in 2008, the stock market in early 2009 is at an all time low and then as a sort of comet enters the air.
According to the chart below , the market capitalization of companies has more than doubled since 2009 and this is now gradually at historical highs .
If the companies in that period became worth much more than you must also still be found in the real economy. That should do it according to these fantastic statistics.
The reverse appears to be the case!
This statistic indicates the question for global shipping of goods . When economies are doing well, so there is much produced and there is also a high demand for transport.
Below (right) is the Baltic Dry Index .
As you can see this chart collapsed in late 2008 at a furious pace to record lows, but struggled somewhat on again.
From the middle of last year, he goes in a straight line down to the lowest point ever .
Which means that there is little or no demand for transport by ship and worldwide economies produce much less or just lie entirely at their hole, in stark contrast to what market prices we want to emulate.
This includes all fits quite nice because the first bulk cargo carriers such as the Danish Copenhagen Ship, have filed for bankruptcy.
The CEO of Copenhagen Ship also said , "We have reached a point where there is nothing more to do ." And this is just one of the many shipping companies or have failed or teetering on the edge of it.
Is there one good economist in this world who can explain me why the value of companies on the stock market to rise to idiotic heights , while the global shipping has fallen ?

Tüm yorumları göster (4)
Matthew Todorovski
2015.02.07
The US Government is hijacked by a shadow government hell-bent on destroying the US dollar and economy. They must do this in order to remove the one major obstacle to their objectives of creating a New World Order. Their modus operandi is "order out of chaos", and they do this by perpetuating chaos through manufactured wars, controlled financial disasters and mass misinformation. It is not conspiracy theory - it is conspiracy facts.
Matthew Todorovski
2015.02.07
Daniel is correct, but that is but a small part of their larger plan...
Sebastiaan de Boorder
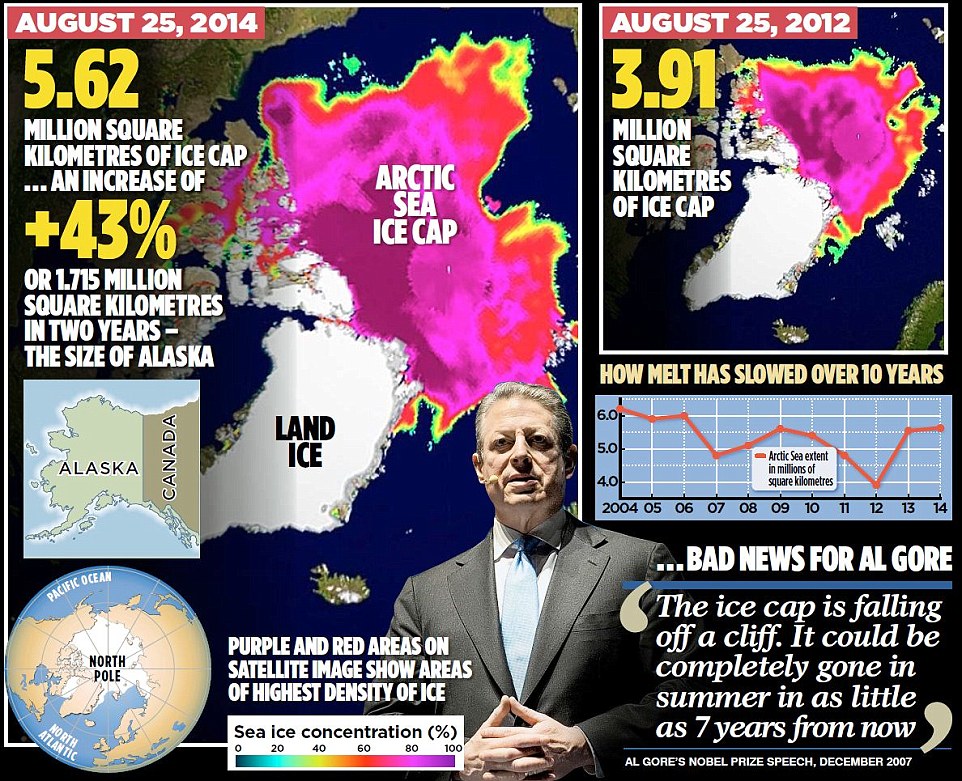



Myth of arctic meltdown:
Stunning satellite images show summer ice cap is thicker and covers 1.7million square kilometres MORE than 2 years ago...despite Al Gore's prediction it would be ICE-FREE by now!
.Seven years after former US Vice-President Al Gore's warning, Arctic ice CAP has expanded for second year in row.
.An area twice the size of .Alaska - America's biggest state - was open water two years ago and is now covered in ice
.These satellite images taken from University of Illinois's Cryosphere project show ice has become more concentrated
Stunning satellite images show summer ice cap is thicker and covers 1.7million square kilometres MORE than 2 years ago...despite Al Gore's prediction it would be ICE-FREE by now!
.Seven years after former US Vice-President Al Gore's warning, Arctic ice CAP has expanded for second year in row.
.An area twice the size of .Alaska - America's biggest state - was open water two years ago and is now covered in ice
.These satellite images taken from University of Illinois's Cryosphere project show ice has become more concentrated
Matthew Todorovski
2014.09.01
Haha global warming - what a joke! Actually, it has been shown that Earth experiences mini-Ice Ages every 200 years, and the last one was 1800-1850... so be prepared! The mini-Ice Ages are caused by the low solar activity: a quieter sun means cooler weather for Earth.
Sebastiaan de Boorder
2014.09.02
Actually we might be heading for a Grand Minimum (every 400 years) Started in 2011. This will mean cooler and drier weather for 30 to 70 years.. Ocean levels will fall not and not rise. We will survive, but food supply will be a major problem. One positive thing for humanity, there is less war during Ice Ages!
Sebastiaan de Boorder



The August SUPERMOON is supposed to be the closet to Earth.
Supermoons are actually a new or full moon which occurs when the moon is closer to the Earth than usual.
“The scientific term for the phenomenon is ‘perigee moon.’ Full Moons vary in size because of the oval shape of the Moon’s ORBIT. The Moon follows an elliptical path around Earth with one side (‘perigee’) about 50,000 km closer than the other (‘apogee’),”
“Full Moons that occur on the perigee SIDE of the Moon’s orbit seem extra big and bright.”
Because of how close the supermoon is, it can appear as much as 14 percent larger in the sky and 30 percent brighter to our eyes than normal moons. 'moon illusion'
Another one is coming up soon–on August 10. That full moon is called the Full Buck Moon. It’s supposed to be the closest to the Earth out of the five supermoons this year.
The remaining one is scheduled for September 9.
The full moon dates:
September 8, Full Harvest Moon, 9:38 p.m. EDT
October 8, Full Hunter’s Moon, 6:51 a.m.
November 6, Full Beaver Moon, 5:23 p.m.
December 6, Full Cold Moon, 7:27 a.m.
2015
For next year, there will be another six supermoons–on January 20, February 18, March 20, August 29, September 28, October 27. All of these are news moons.
Full moons are slated for January 5, February 3, March 5, April 4, May 4, June 2, July 2, July 31, August 14, September 13, October 13, November 11, and December 11.
There is extensive psychological and biological literature demonstrating that the lunar cycle can heavily influence our moods.
A full moon increases our tendency to feel depressed and pessimistic, and there is a higher rate of suicide around full moons.
This may reflect the fear and tension surrounding increased nocturnal predator action, historically, or psychological issues from sleep deprivation in night light.
So investors may feel more inclined to stay out of the stock MARKET at or near that time, or to sell out of positions: emotions trumping objectivity. A correlation between stock market returns and lunar phases is indeed found by Dichev, Yuan and Hickey in three separate studies.
This indicator shows Lunar Phases : http://www.cronossolutions.com/LunarPhases_By_Nikolay_Panev
Source: the epoch times
Supermoons are actually a new or full moon which occurs when the moon is closer to the Earth than usual.
“The scientific term for the phenomenon is ‘perigee moon.’ Full Moons vary in size because of the oval shape of the Moon’s ORBIT. The Moon follows an elliptical path around Earth with one side (‘perigee’) about 50,000 km closer than the other (‘apogee’),”
“Full Moons that occur on the perigee SIDE of the Moon’s orbit seem extra big and bright.”
Because of how close the supermoon is, it can appear as much as 14 percent larger in the sky and 30 percent brighter to our eyes than normal moons. 'moon illusion'
Another one is coming up soon–on August 10. That full moon is called the Full Buck Moon. It’s supposed to be the closest to the Earth out of the five supermoons this year.
The remaining one is scheduled for September 9.
The full moon dates:
September 8, Full Harvest Moon, 9:38 p.m. EDT
October 8, Full Hunter’s Moon, 6:51 a.m.
November 6, Full Beaver Moon, 5:23 p.m.
December 6, Full Cold Moon, 7:27 a.m.
2015
For next year, there will be another six supermoons–on January 20, February 18, March 20, August 29, September 28, October 27. All of these are news moons.
Full moons are slated for January 5, February 3, March 5, April 4, May 4, June 2, July 2, July 31, August 14, September 13, October 13, November 11, and December 11.
There is extensive psychological and biological literature demonstrating that the lunar cycle can heavily influence our moods.
A full moon increases our tendency to feel depressed and pessimistic, and there is a higher rate of suicide around full moons.
This may reflect the fear and tension surrounding increased nocturnal predator action, historically, or psychological issues from sleep deprivation in night light.
So investors may feel more inclined to stay out of the stock MARKET at or near that time, or to sell out of positions: emotions trumping objectivity. A correlation between stock market returns and lunar phases is indeed found by Dichev, Yuan and Hickey in three separate studies.
This indicator shows Lunar Phases : http://www.cronossolutions.com/LunarPhases_By_Nikolay_Panev
Source: the epoch times

Sebastiaan de Boorder
2015.10.12
This image is probably a composite...Or the moon is a hologram!! ;)
Sebastiaan de Boorder
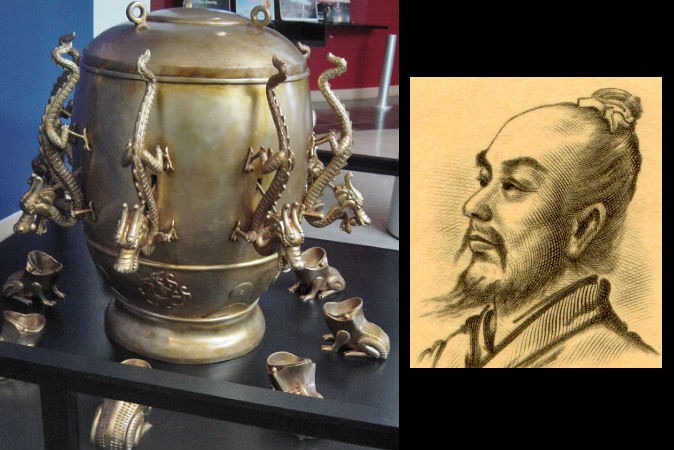


2,000-Year-Old Earthquake Detector Worked With Accuracy in China
The universe is full of mysteries that challenge our current knowledge. In "Beyond Science" Epoch Times collects stories about these strange phenomena to stimulate the imagination and open up previously undreamed of possibilities. Are they true? You decide.
In 132 A.D., Zhang Heng presented the Han court with the world’s first seismoscope. A 2005 replica was even said to detect earthquakes with the same precision as modern instruments.
Historical accounts tell of its great accuracy, though its precise design remains a mystery. The outer appearance and functioning is known for certain, but its inner workings remain open to speculation. The replicas have been built on the best guesses from such speculation.
The most common theory states that a pendulum inside the copper urn would move when an earthquake occurred, even if the quake was hundreds of miles away. The pendulum would hit a system of levers to open the mouth of one of the eight dragons on the outside of the urn. Each dragon’s mouth contained a bronze ball. This ball would roll out, landing in the mouth of a toad figurine below, making a loud clang.
A historical account described the ringing in the toad’s mouth to be so loud it could rouse the whole court from sleep, wrote Dr. Jan Pajak of the Wellington Institute of Technology in a paper prepared for the 2005 International Conference on Sensing Technology.
The dragon that had its mouth opened would be the one pointing in the direction of the earthquake. The eight dragons pointed east, west, north, south, northeast, northwest, southeast, and southwest respectively.
The invention was initially met with skepticism in its day, though Heng was already a renowned scientist, selected to be the court’s chief astronomer. In 138 A.D., a bronze ball sounded the first alarm.
It indicated that the earthquake happened west of Luoyang, the capital city. No one had felt a quake in Luoyang, so the alarm was ignored, but a few days later, a messenger from west of Luoyang arrived in the city to report that his region had experienced an earthquake. The earthquake had occurred at the same time Heng’s machine sounded the alarm. This city of Longxi, some 300 miles away, lay in ruins.
Feng Rui and Yu Yan-Xiang of the Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration, deduced in 2006 that this first earthquake detected by Heng’s machine was magnitude 7 in Longxi, with an epicenter at Tianshui on Dec. 13, 134 A.D.
The machine’s purpose was to detect earthquakes in distant regions so aid could be deployed. It worked until the death of its inventor, but apparently the device was so complex only Heng could keep up with its maintenance effectively.
The seismoscope was called Houfeng didong yi, the “instrument for measuring the seasonal winds and the movements of the Earth.” Modern attempts at replication have met with varying success, and all were built on the use of inertia, a principle integral to modern seismographs.
Dr. Pajak explains this use of intertia: “In this principle an earthquake shakes a frame of an instrument, so that this frame is displaced in relation to an inertial pendulum, while this displacement is registered as the indication of an earthquake.”
ATTEMPTS TO REPLICATE
In 1939, Japanese scientist Akitsune Imamura built a replica showing the device to be effective, according to Hong-Sen Yan in the book “Reconstruction Designs of Lost Ancient Chinese Machinery.”
However, wrote Hong-Sen, “in some circumstances the direction of an earthquake’s epicenter was found to be at right angles to the dropped ball.”
In 2005, several scientists from various disciplines at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Museum, and China Earthquake Administration declared a new replica to be the best yet.
“It represents our current utmost understanding of the ancient Didong instrument,” said Teng Jiwen, a research fellow at the Institute of Geology and Geophysics, according to a report from that time by state-run media People’s Daily.
The replica reportedly responded to the reproduced waves of four actual earthquake events in Tangshan, Yunnan, the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, and Vietnam. Tested against modern earthquake graphs, the replica was shown to be accurate and its shape fit that described in historical texts.
THE INNER WORKINGS
Hong-Sen cited a passage from a contemporary biography of Zhang Heng, the first design specification left to us in historical texts: “There is one pillar (du zhu) in the center of the interior and eight transmitting rods near the pillar.”
Transmitting rods would refer to channels through which some object would be transported, explained Hong-Sen, but nothing more specific is written about the rods.
Dr. Pajak has another theory. He wrote that the machine has been described in historical texts as containing water, as having water flow out of the dragons’ mouths like a fountain.
He hypothesized that the water flowed smoothly (as opposed to turbulently), a characteristic known as laminar flow. The shape of the chamber (parabolic) was designed to deflect vibrations coming from the earthquake zone. The deflected vibrations would focus on the inlet of the pipe in the appropriate direction, causing the water that had been washing around the metal ball to push the ball out of the dragon’s mouth.
Robert Reitherman, executive director of the Consortium of Universities for Research in Earthquake Engineering, expressed skepticism concerning the historical accounts of the machine’s accuracy in his book, “Earthquakes and Engineers: An International History.”
He wrote: “At a close distance, the whole instrument would be so severely shaken that the balls on multiple perches would have jostled loose. … At a [far] distance, ground motion from an earthquake does not leave clear footprints indicating the direction from whence those vibrations came, because the ground shakes in various directions rather chaotically by the time it reaches the instrument.”
If this machine worked as well as historical accounts describe, and if the successes of some modern replicas hint that the machine could work with such precision, it seems Heng’s genius remains out of our grasp for now.
Some of Heng’s other accomplishments include calculating pi (π) as being between 3.1466 and 3.1622, refining a time-keeping device know as an “inflow clepsydra,” and applying hydraulic motive power to rotate an astronomical instrument known as an armillary sphere.
Author: Tara MacIsaac, Epoch Times
PICTURE: A replica of an ancient Chinese seismoscope from the Eastern Han Dynasty (25-220 A.D.), and its inventor, Zhang Heng. (Wikimedia Commons)
The universe is full of mysteries that challenge our current knowledge. In "Beyond Science" Epoch Times collects stories about these strange phenomena to stimulate the imagination and open up previously undreamed of possibilities. Are they true? You decide.
In 132 A.D., Zhang Heng presented the Han court with the world’s first seismoscope. A 2005 replica was even said to detect earthquakes with the same precision as modern instruments.
Historical accounts tell of its great accuracy, though its precise design remains a mystery. The outer appearance and functioning is known for certain, but its inner workings remain open to speculation. The replicas have been built on the best guesses from such speculation.
The most common theory states that a pendulum inside the copper urn would move when an earthquake occurred, even if the quake was hundreds of miles away. The pendulum would hit a system of levers to open the mouth of one of the eight dragons on the outside of the urn. Each dragon’s mouth contained a bronze ball. This ball would roll out, landing in the mouth of a toad figurine below, making a loud clang.
A historical account described the ringing in the toad’s mouth to be so loud it could rouse the whole court from sleep, wrote Dr. Jan Pajak of the Wellington Institute of Technology in a paper prepared for the 2005 International Conference on Sensing Technology.
The dragon that had its mouth opened would be the one pointing in the direction of the earthquake. The eight dragons pointed east, west, north, south, northeast, northwest, southeast, and southwest respectively.
The invention was initially met with skepticism in its day, though Heng was already a renowned scientist, selected to be the court’s chief astronomer. In 138 A.D., a bronze ball sounded the first alarm.
It indicated that the earthquake happened west of Luoyang, the capital city. No one had felt a quake in Luoyang, so the alarm was ignored, but a few days later, a messenger from west of Luoyang arrived in the city to report that his region had experienced an earthquake. The earthquake had occurred at the same time Heng’s machine sounded the alarm. This city of Longxi, some 300 miles away, lay in ruins.
Feng Rui and Yu Yan-Xiang of the Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration, deduced in 2006 that this first earthquake detected by Heng’s machine was magnitude 7 in Longxi, with an epicenter at Tianshui on Dec. 13, 134 A.D.
The machine’s purpose was to detect earthquakes in distant regions so aid could be deployed. It worked until the death of its inventor, but apparently the device was so complex only Heng could keep up with its maintenance effectively.
The seismoscope was called Houfeng didong yi, the “instrument for measuring the seasonal winds and the movements of the Earth.” Modern attempts at replication have met with varying success, and all were built on the use of inertia, a principle integral to modern seismographs.
Dr. Pajak explains this use of intertia: “In this principle an earthquake shakes a frame of an instrument, so that this frame is displaced in relation to an inertial pendulum, while this displacement is registered as the indication of an earthquake.”
ATTEMPTS TO REPLICATE
In 1939, Japanese scientist Akitsune Imamura built a replica showing the device to be effective, according to Hong-Sen Yan in the book “Reconstruction Designs of Lost Ancient Chinese Machinery.”
However, wrote Hong-Sen, “in some circumstances the direction of an earthquake’s epicenter was found to be at right angles to the dropped ball.”
In 2005, several scientists from various disciplines at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Museum, and China Earthquake Administration declared a new replica to be the best yet.
“It represents our current utmost understanding of the ancient Didong instrument,” said Teng Jiwen, a research fellow at the Institute of Geology and Geophysics, according to a report from that time by state-run media People’s Daily.
The replica reportedly responded to the reproduced waves of four actual earthquake events in Tangshan, Yunnan, the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, and Vietnam. Tested against modern earthquake graphs, the replica was shown to be accurate and its shape fit that described in historical texts.
THE INNER WORKINGS
Hong-Sen cited a passage from a contemporary biography of Zhang Heng, the first design specification left to us in historical texts: “There is one pillar (du zhu) in the center of the interior and eight transmitting rods near the pillar.”
Transmitting rods would refer to channels through which some object would be transported, explained Hong-Sen, but nothing more specific is written about the rods.
Dr. Pajak has another theory. He wrote that the machine has been described in historical texts as containing water, as having water flow out of the dragons’ mouths like a fountain.
He hypothesized that the water flowed smoothly (as opposed to turbulently), a characteristic known as laminar flow. The shape of the chamber (parabolic) was designed to deflect vibrations coming from the earthquake zone. The deflected vibrations would focus on the inlet of the pipe in the appropriate direction, causing the water that had been washing around the metal ball to push the ball out of the dragon’s mouth.
Robert Reitherman, executive director of the Consortium of Universities for Research in Earthquake Engineering, expressed skepticism concerning the historical accounts of the machine’s accuracy in his book, “Earthquakes and Engineers: An International History.”
He wrote: “At a close distance, the whole instrument would be so severely shaken that the balls on multiple perches would have jostled loose. … At a [far] distance, ground motion from an earthquake does not leave clear footprints indicating the direction from whence those vibrations came, because the ground shakes in various directions rather chaotically by the time it reaches the instrument.”
If this machine worked as well as historical accounts describe, and if the successes of some modern replicas hint that the machine could work with such precision, it seems Heng’s genius remains out of our grasp for now.
Some of Heng’s other accomplishments include calculating pi (π) as being between 3.1466 and 3.1622, refining a time-keeping device know as an “inflow clepsydra,” and applying hydraulic motive power to rotate an astronomical instrument known as an armillary sphere.
Author: Tara MacIsaac, Epoch Times
PICTURE: A replica of an ancient Chinese seismoscope from the Eastern Han Dynasty (25-220 A.D.), and its inventor, Zhang Heng. (Wikimedia Commons)

[Silindi]
2014.07.24
Great article !
Sebastiaan de Boorder

MASSIVE 'OCEAN' DISCOVERED TOWARDS EARTH'S CORE
A reservoir of water three times the volume of all the oceans has been discovered deep beneath the Earth's surface. The finding could help explain where Earth's seas came from.
The water is hidden inside a blue rock called ringwoodite that lies 700 kilometres underground in the mantle, the layer of hot rock between Earth's surface and its core.
The huge size of the reservoir throws new light on the origin of Earth's water. Some geologists think water arrived in comets as they struck the planet, but the new discovery supports an alternative idea that the oceans gradually oozed out of the interior of the early Earth.
"It's good evidence the Earth's water came from within," says Steven Jacobsen of Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois. The hidden water could also act as a buffer for the oceans on the surface, explaining why they have stayed the same size for millions of years.
PINGING THE PLANET
Jacobsen's team used 2000 seismometers to study the seismic waves generated by more than 500 earthquakes. These waves move throughout Earth's interior, including the core, and can be detected at the surface. "They make the Earth RING like a bell for days afterwards," says Jacobsen.
By measuring the speed of the waves at different depths, the team could figure out which types of rocks the waves were passing through. The water layer revealed itself because the waves slowed down, as it takes them longer to get through soggy rock than dry rock.
Jacobsen worked out in advance what would happen to the waves if water-containing ringwoodite was present. He grew ringwoodite in his lab, and exposed samples of it to massive pressures and temperatures matching those at 700 kilometres down.
Sure enough, they found signs of wet ringwoodite in the transition zone 700 kilometres down, which divides the upper and lower regions of the mantle. At that depth, the pressures and temperatures are just right to squeeze the water out of the ringwoodite. "It's rock with water along the boundaries between the grains, almost as if they're sweating," says Jacobsen.
DAMP DOWN THERE
Jacobsen's finding supports a recent study by Graham Pearson of the University of Alberta in Edmonton, CANADA. Pearson studied a diamond from the transition zone that had been carried to the surface in a volcano, and found that it contained water-bearing ringwoodite, the first strong evidence that there was lots of water in the transition zone (Nature, doi.org/s6h).
"Since our initial report of hydrous ringwoodite, we've found another ringwoodite crystal, also containing water, so the evidence is now very strong," says Pearson.
So far, Jacobsen only has evidence that the watery rock sits beneath the US. He now wants to find out if it wraps around the entire planet.
"We should be grateful for this deep reservoir," says Jacobsen. "If it wasn't there, it would be on the surface of the Earth, and mountain TOPS would be the only land poking out."
by Andy Coghlan for http://www.newscientist.com/
Journal reference: Science, DOI: 10.1126/science.1253358
A reservoir of water three times the volume of all the oceans has been discovered deep beneath the Earth's surface. The finding could help explain where Earth's seas came from.
The water is hidden inside a blue rock called ringwoodite that lies 700 kilometres underground in the mantle, the layer of hot rock between Earth's surface and its core.
The huge size of the reservoir throws new light on the origin of Earth's water. Some geologists think water arrived in comets as they struck the planet, but the new discovery supports an alternative idea that the oceans gradually oozed out of the interior of the early Earth.
"It's good evidence the Earth's water came from within," says Steven Jacobsen of Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois. The hidden water could also act as a buffer for the oceans on the surface, explaining why they have stayed the same size for millions of years.
PINGING THE PLANET
Jacobsen's team used 2000 seismometers to study the seismic waves generated by more than 500 earthquakes. These waves move throughout Earth's interior, including the core, and can be detected at the surface. "They make the Earth RING like a bell for days afterwards," says Jacobsen.
By measuring the speed of the waves at different depths, the team could figure out which types of rocks the waves were passing through. The water layer revealed itself because the waves slowed down, as it takes them longer to get through soggy rock than dry rock.
Jacobsen worked out in advance what would happen to the waves if water-containing ringwoodite was present. He grew ringwoodite in his lab, and exposed samples of it to massive pressures and temperatures matching those at 700 kilometres down.
Sure enough, they found signs of wet ringwoodite in the transition zone 700 kilometres down, which divides the upper and lower regions of the mantle. At that depth, the pressures and temperatures are just right to squeeze the water out of the ringwoodite. "It's rock with water along the boundaries between the grains, almost as if they're sweating," says Jacobsen.
DAMP DOWN THERE
Jacobsen's finding supports a recent study by Graham Pearson of the University of Alberta in Edmonton, CANADA. Pearson studied a diamond from the transition zone that had been carried to the surface in a volcano, and found that it contained water-bearing ringwoodite, the first strong evidence that there was lots of water in the transition zone (Nature, doi.org/s6h).
"Since our initial report of hydrous ringwoodite, we've found another ringwoodite crystal, also containing water, so the evidence is now very strong," says Pearson.
So far, Jacobsen only has evidence that the watery rock sits beneath the US. He now wants to find out if it wraps around the entire planet.
"We should be grateful for this deep reservoir," says Jacobsen. "If it wasn't there, it would be on the surface of the Earth, and mountain TOPS would be the only land poking out."
by Andy Coghlan for http://www.newscientist.com/
Journal reference: Science, DOI: 10.1126/science.1253358

Sebastiaan de Boorder
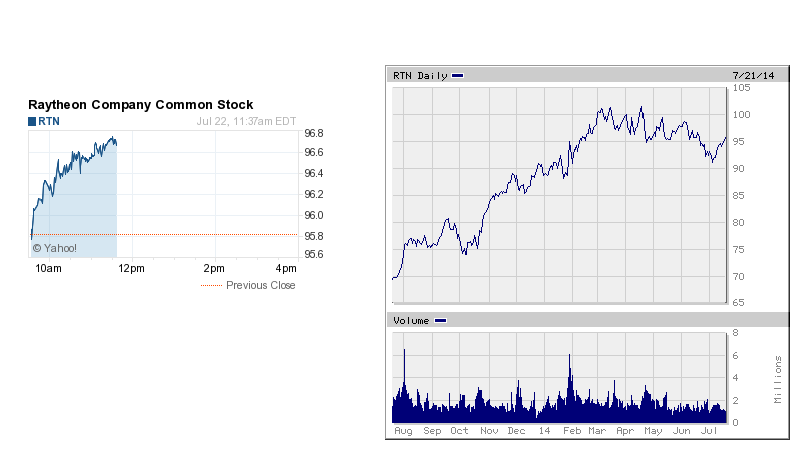
WAR TRADING PART IV.
Raytheon Company is an American defense and technology company. Raytheon gets more than 90% of their revenue from defense contracts and is the world's fifth largest defense company. They are also called the "merchant of death". As you can see, the share increased to unprecedented levels in recent months.
Raytheon Company is an American defense and technology company. Raytheon gets more than 90% of their revenue from defense contracts and is the world's fifth largest defense company. They are also called the "merchant of death". As you can see, the share increased to unprecedented levels in recent months.
Sebastiaan de Boorder

Chatty traders face criminal probe for rigging forex market
Britain’s Serious Fraud Office (SFO) is investigating the alleged use of chatrooms by FOREX traders in a conspiracy to rig exchange rates. An estimated $5.3 trillion in currencies changes hands daily.
The SFO, an independent government department that prosecutes fraud and corruption, announced the case on Monday.
"The Director of the Serious Fraud Office has today opened a criminal investigation into allegations of fraudulent conduct in the FOREIGN EXCHANGE market," the regulator's statement said.
Every day at 4:00pm, the benchmark price is determined, or ‘fixed’, and is then used across businesses as the price set for FOREIGN EXCHANGE trades, and is accepted as fair. Thus, the rate has a crucial role in the entire financial sector.
"The manipulation of the 'London 4pm Fix' doesn't just affect banks and traders, but the man in the street as well, as it is our pension and insurance FUNDS that could be swindled out of millions of pounds by this,” Mark Taylor, the dean of Warwick Business School, told the Guardian. Taylor used to trade CURRENCIES at the Bank of England, before becoming a senior economist.
"If some of the big players in the market got together and put through some very large trades - billions of dollars each - then that could affect the market, so they can charge their clients a higher rate before covering it a few minutes later to make a healthy profit. You only have to move the market a small amount for a short period, and that could be worth millions of dollars for the banks,” Taylor said.
Mark Carney, the governor of the Bank of England, has warned that rigging of CURRENCYtrades is potentially more serious than the notorious Libor scandal, which involved bankers fixing short-term interbank interest rates. In the end, banks were given more than $6 billion in fines.
The probe is on the heels of a larger world-wide investigation into benchmark manipulation in the largely unregulated foreign exchange market. Regulators in 15 countries have opened currency market rigging cases, the Guardian reports. Already dozens of individuals have been fired for manipulating currency trades.
Germany’s biggest bank, Deutsche Bank, has already dismissed currency traders over alleged wrongdoing.
The Swiss regulator has opened an investigation against Barclays, JPMorgan, Citigroup, the Royal Bank of Scotland, as well as Swiss banks UBS, Credit Suisse, Julius Baer and Zurcher Kantonalbank over rate-manipulation.
Suspicions of EXCHANGE RATE manipulation first surfaced in 2011 when UK authorities started to closely monitor currency transactions after a tip off.
Source: RT.com
Britain’s Serious Fraud Office (SFO) is investigating the alleged use of chatrooms by FOREX traders in a conspiracy to rig exchange rates. An estimated $5.3 trillion in currencies changes hands daily.
The SFO, an independent government department that prosecutes fraud and corruption, announced the case on Monday.
"The Director of the Serious Fraud Office has today opened a criminal investigation into allegations of fraudulent conduct in the FOREIGN EXCHANGE market," the regulator's statement said.
Every day at 4:00pm, the benchmark price is determined, or ‘fixed’, and is then used across businesses as the price set for FOREIGN EXCHANGE trades, and is accepted as fair. Thus, the rate has a crucial role in the entire financial sector.
"The manipulation of the 'London 4pm Fix' doesn't just affect banks and traders, but the man in the street as well, as it is our pension and insurance FUNDS that could be swindled out of millions of pounds by this,” Mark Taylor, the dean of Warwick Business School, told the Guardian. Taylor used to trade CURRENCIES at the Bank of England, before becoming a senior economist.
"If some of the big players in the market got together and put through some very large trades - billions of dollars each - then that could affect the market, so they can charge their clients a higher rate before covering it a few minutes later to make a healthy profit. You only have to move the market a small amount for a short period, and that could be worth millions of dollars for the banks,” Taylor said.
Mark Carney, the governor of the Bank of England, has warned that rigging of CURRENCYtrades is potentially more serious than the notorious Libor scandal, which involved bankers fixing short-term interbank interest rates. In the end, banks were given more than $6 billion in fines.
The probe is on the heels of a larger world-wide investigation into benchmark manipulation in the largely unregulated foreign exchange market. Regulators in 15 countries have opened currency market rigging cases, the Guardian reports. Already dozens of individuals have been fired for manipulating currency trades.
Germany’s biggest bank, Deutsche Bank, has already dismissed currency traders over alleged wrongdoing.
The Swiss regulator has opened an investigation against Barclays, JPMorgan, Citigroup, the Royal Bank of Scotland, as well as Swiss banks UBS, Credit Suisse, Julius Baer and Zurcher Kantonalbank over rate-manipulation.
Suspicions of EXCHANGE RATE manipulation first surfaced in 2011 when UK authorities started to closely monitor currency transactions after a tip off.
Source: RT.com

Sebastiaan de Boorder

IS THE UNIVERSE A BUBBLE? LET'S CHECK
Perimeter Associate Faculty member Matthew Johnson and his colleagues are working to bring the multiverse hypothesis, which to some sounds like a fanciful tale, firmly into the realm of testable science.
Never mind the big bang; in the beginning was the vacuum. The vacuum simmered with energy (variously called dark energy, vacuum energy, the inflation field, or the Higgs field). Like water in a pot, this high energy began to evaporate – bubbles formed.
Each bubble contained another vacuum, whose energy was lower, but still not nothing. This energy drove the bubbles to expand. Inevitably, some bubbles bumped into each other. It’s possible some produced secondary bubbles. Maybe the bubbles were rare and far apart; maybe they were packed close as foam.
But here’s the thing: each of these bubbles was a universe. In this picture, our universe is one bubble in a frothy sea of bubble universes.
That’s the multiverse hypothesis in a bubbly nutshell.
It’s not a bad story. It is, as scientists say, physically motivated – not just made up, but rather arising from what we think we know about cosmic inflation.
Cosmic inflation isn’t universally accepted – most cyclical models of the universe reject the idea. Nevertheless, inflation is a leading theory of the universe’s very early development, and there is some observational evidence to support it.
Inflation holds that in the instant after the big bang, the universe expanded rapidly – so rapidly that an area of space once a nanometer square ended up more than a quarter-billion light years across in just a trillionth of a trillionth of a trillionth of a second. It’s an amazing idea, but it would explain some otherwise puzzling astrophysical observations.
Inflation is thought to have been driven by an inflation field – which is vacuum energy by another name. Once you postulate that the inflation field exists, it’s hard to avoid an “in the beginning was the vacuum” kind of story. This is where the theory of inflation becomes controversial – when it starts to postulate multiple universes.
Proponents of the multiverse theory argue that it’s the next logical STEP in the inflation story. Detractors argue that it is not physics, but metaphysics – that it is not science because it cannot be tested. After all, physics lives or dies by data that can be gathered and predictions that can be checked.
That’s where Perimeter Associate Faculty member Matthew Johnson (cross-appointed at York University) comes in. Working with a small team that also includes Perimeter Faculty member Luis Lehner, Johnson is working to bring the multiverse hypothesis firmly into the realm of testable science.
“That’s what this research program is all about,” he says. “We’re trying to find out what the testable predictions of this picture would be, and then going out and looking for them.”
Specifically, Johnson has been considering the rare cases in which our bubble universe might collide with another bubble universe. He lays out the steps: “We simulate the whole universe. We start with a multiverse that has two bubbles in it, we collide the bubbles on a COMPUTER to figure out what happens, and then we stick a virtual observer in various places and ask what that observer would see from there.”
Simulating the whole universe – or more than one – seems like a tall order, but apparently that’s not so.
“Simulating the universe is easy,” says Johnson. Simulations, he explains, are not accounting for every atom, every star, or every galaxy – in fact, they ACCOUNTfor none of them.
“We’re simulating things only on the largest scales,” he says. “All I need is gravity and the stuff that makes these bubbles up. We’re now at the point where if you have a favourite model of the multiverse, I can stick it on a COMPUTER and tell you what you should see.”
That’s a small step for a computer simulation program, but a giant leap for the field of multiverse cosmology. By producing testable predictions, the multiverse model has crossed the line between appealing story and real science.
In fact, Johnson says, the program has reached the point where it can rule out certain models of the multiverse: “We’re now able to say that some models predict something that we should be able to see, and since we don’t in fact see it, we can rule those models out.”
For instance, collisions of one bubble universe with another would leave what Johnson calls “a disk on the sky” – a circular bruise in the cosmic microwave background. That the search for such a disk has so far come up empty makes certain collision-filled models less likely.
Meanwhile, the team is at work figuring out what other kinds of evidence a bubble collision might leave behind. It’s the first time, the team writes in their paper, that anyone has produced a direct quantitative set of predictions for the observable signatures of bubble collisions. And though none of those signatures has so far been found, some of them are possible to look for.
The real significance of this work is as a proof of principle: it shows that the multiverse can be testable. In other words, if we are LIVING in a bubble universe, we might actually be able to tell.
Author: Erin Bow
Perimeter Institute
Perimeter Associate Faculty member Matthew Johnson and his colleagues are working to bring the multiverse hypothesis, which to some sounds like a fanciful tale, firmly into the realm of testable science.
Never mind the big bang; in the beginning was the vacuum. The vacuum simmered with energy (variously called dark energy, vacuum energy, the inflation field, or the Higgs field). Like water in a pot, this high energy began to evaporate – bubbles formed.
Each bubble contained another vacuum, whose energy was lower, but still not nothing. This energy drove the bubbles to expand. Inevitably, some bubbles bumped into each other. It’s possible some produced secondary bubbles. Maybe the bubbles were rare and far apart; maybe they were packed close as foam.
But here’s the thing: each of these bubbles was a universe. In this picture, our universe is one bubble in a frothy sea of bubble universes.
That’s the multiverse hypothesis in a bubbly nutshell.
It’s not a bad story. It is, as scientists say, physically motivated – not just made up, but rather arising from what we think we know about cosmic inflation.
Cosmic inflation isn’t universally accepted – most cyclical models of the universe reject the idea. Nevertheless, inflation is a leading theory of the universe’s very early development, and there is some observational evidence to support it.
Inflation holds that in the instant after the big bang, the universe expanded rapidly – so rapidly that an area of space once a nanometer square ended up more than a quarter-billion light years across in just a trillionth of a trillionth of a trillionth of a second. It’s an amazing idea, but it would explain some otherwise puzzling astrophysical observations.
Inflation is thought to have been driven by an inflation field – which is vacuum energy by another name. Once you postulate that the inflation field exists, it’s hard to avoid an “in the beginning was the vacuum” kind of story. This is where the theory of inflation becomes controversial – when it starts to postulate multiple universes.
Proponents of the multiverse theory argue that it’s the next logical STEP in the inflation story. Detractors argue that it is not physics, but metaphysics – that it is not science because it cannot be tested. After all, physics lives or dies by data that can be gathered and predictions that can be checked.
That’s where Perimeter Associate Faculty member Matthew Johnson (cross-appointed at York University) comes in. Working with a small team that also includes Perimeter Faculty member Luis Lehner, Johnson is working to bring the multiverse hypothesis firmly into the realm of testable science.
“That’s what this research program is all about,” he says. “We’re trying to find out what the testable predictions of this picture would be, and then going out and looking for them.”
Specifically, Johnson has been considering the rare cases in which our bubble universe might collide with another bubble universe. He lays out the steps: “We simulate the whole universe. We start with a multiverse that has two bubbles in it, we collide the bubbles on a COMPUTER to figure out what happens, and then we stick a virtual observer in various places and ask what that observer would see from there.”
Simulating the whole universe – or more than one – seems like a tall order, but apparently that’s not so.
“Simulating the universe is easy,” says Johnson. Simulations, he explains, are not accounting for every atom, every star, or every galaxy – in fact, they ACCOUNTfor none of them.
“We’re simulating things only on the largest scales,” he says. “All I need is gravity and the stuff that makes these bubbles up. We’re now at the point where if you have a favourite model of the multiverse, I can stick it on a COMPUTER and tell you what you should see.”
That’s a small step for a computer simulation program, but a giant leap for the field of multiverse cosmology. By producing testable predictions, the multiverse model has crossed the line between appealing story and real science.
In fact, Johnson says, the program has reached the point where it can rule out certain models of the multiverse: “We’re now able to say that some models predict something that we should be able to see, and since we don’t in fact see it, we can rule those models out.”
For instance, collisions of one bubble universe with another would leave what Johnson calls “a disk on the sky” – a circular bruise in the cosmic microwave background. That the search for such a disk has so far come up empty makes certain collision-filled models less likely.
Meanwhile, the team is at work figuring out what other kinds of evidence a bubble collision might leave behind. It’s the first time, the team writes in their paper, that anyone has produced a direct quantitative set of predictions for the observable signatures of bubble collisions. And though none of those signatures has so far been found, some of them are possible to look for.
The real significance of this work is as a proof of principle: it shows that the multiverse can be testable. In other words, if we are LIVING in a bubble universe, we might actually be able to tell.
Author: Erin Bow
Perimeter Institute

Sebastiaan de Boorder

Major Arctic Sea Ice Story Lurking, But Is Anyone Watching?
“For the first time in over a decade, the Arctic sea ice anomaly in the SUMMER is forecast to be near or ABOVE normal,”
said meteorologist Joe Bastardi.
“Once it flips, this red herring of climate panic will be gone. Global and Southern Hemisphere anomalies are already unmentionable since the former is well ABOVE normal and the latter is routinely busting daily records.
“It should be obvious as to who is the boss here, and with the warm Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO) in its waning years, the Arctic sea ice hysteria will wind up where so many agenda driven items do – on the ash heap of history.
“This, if correct, is going to be a huge story. It would be the first SUMMER where Arctic sea ice returned to near normal, indicative of the increase in multiyear ice and what a turn to the colder AMO in the future means!”
“This same kind of evolution through the fall and into the winter would lead to another harsh winter for the U.S. and many other countries ”
Source: http://iceagenow.info/
“For the first time in over a decade, the Arctic sea ice anomaly in the SUMMER is forecast to be near or ABOVE normal,”
said meteorologist Joe Bastardi.
“Once it flips, this red herring of climate panic will be gone. Global and Southern Hemisphere anomalies are already unmentionable since the former is well ABOVE normal and the latter is routinely busting daily records.
“It should be obvious as to who is the boss here, and with the warm Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO) in its waning years, the Arctic sea ice hysteria will wind up where so many agenda driven items do – on the ash heap of history.
“This, if correct, is going to be a huge story. It would be the first SUMMER where Arctic sea ice returned to near normal, indicative of the increase in multiyear ice and what a turn to the colder AMO in the future means!”
“This same kind of evolution through the fall and into the winter would lead to another harsh winter for the U.S. and many other countries ”
Source: http://iceagenow.info/

Sebastiaan de Boorder
Why nobody can explain the 'moon illusion'
A huge-looking moon at the horizon isn't actually bigger, closer or even distorted by the atmosphere. It's just a lunar illusion that has defied explanation for millennia.
When this month's Harvest Moon arrives, it will perform an optical illusion that has baffled onlookers since Aristotle. As with many moonrises — but especially full moons — it will look bizarrely large when it's near the horizon, then seem to shrink as it ascends.
This is the "moon illusion," and it's all in your head. The moon isn't actually changing sizes, and while its distance from Earth does change slightly over time — producing an occasional "Supermoon," which really does appear up to 14 percent larger than usual — that happens too slowly to produce such a dramatic transformation within a single night.
Early attempts to explain the moon illusion blamed the atmosphere, assuming the moon's image is magnified by airborne dust near Earth's surface. Dust particles are known to affect the color of sunsets and sunrises, after all, and can even cast an orange hue on full moons. But scientists later realized atmospheric distortion isn't the culprit; if anything, suspended dust should make the moon look slightly smaller when it's low in the sky.
If you want proof the moon illusion is purely psychological, just hold a ruler up to the moon when it's near the horizon and again when it's high in the sky. The lower moon may have seemed significantly larger, but a ruler will reveal its diameter hasn't changed. Cameras can also expose the moon's mendacity: This multiple-exposure image, for example, tracks the rocky satellite's consistent size as it rises over Seattle.
So what's going on? When we look at the moon, rays of reflected sunlight produce a roughly 0.15 millimeter-wide image on our retinas. "High moons and low moons make the same-sized spot," NASA Science's Tony Phillips writes in an explainer about the moon illusion, "yet the brain insists one is bigger than the other."
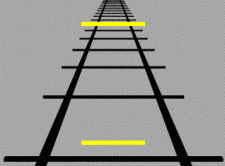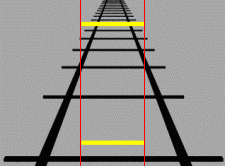
ponzo illusionVisual artists have long used perspective to portray 3-D space on a 2-D canvas, and psychologist Mario Ponzo showed a century ago how our brains can misjudge an object's true size based on its background. Known as the "Ponzo illusion," this is caused by our knowledge that distant objects appear smaller than they actually are. In the animated GIF below, the upper yellow bar seems wider than the lower one because it's "farther away" on the 2-D railroad tracks, prompting our brains to compensate for an expected distortion. Much like a high and low moon, however, they're both the same width, as the vertical red lines illustrate.
Surface features like trees and buildings might mimic this effect with the moon, along with another trick called the "Ebbinghaus illusion," which can make objects seem artificially large by juxtaposing them with smaller objects. But there's a problem with those theories, too. Pilots and sailors often see the moon illusion even when the horizon is virtually empty, suggesting foreground objects alone don't produce the phenomenon.
flat sky and Plenty of other explanations have been floated over the years, including the "flattened sky" model and a size illusion known as "oculomotor micropsia." Although many of these theories are plausible — and more than one may offer the answer — science has yet to fully explain the millennia-old mystery.
Source: http://www.mnn.com/
A huge-looking moon at the horizon isn't actually bigger, closer or even distorted by the atmosphere. It's just a lunar illusion that has defied explanation for millennia.
When this month's Harvest Moon arrives, it will perform an optical illusion that has baffled onlookers since Aristotle. As with many moonrises — but especially full moons — it will look bizarrely large when it's near the horizon, then seem to shrink as it ascends.
This is the "moon illusion," and it's all in your head. The moon isn't actually changing sizes, and while its distance from Earth does change slightly over time — producing an occasional "Supermoon," which really does appear up to 14 percent larger than usual — that happens too slowly to produce such a dramatic transformation within a single night.
Early attempts to explain the moon illusion blamed the atmosphere, assuming the moon's image is magnified by airborne dust near Earth's surface. Dust particles are known to affect the color of sunsets and sunrises, after all, and can even cast an orange hue on full moons. But scientists later realized atmospheric distortion isn't the culprit; if anything, suspended dust should make the moon look slightly smaller when it's low in the sky.
If you want proof the moon illusion is purely psychological, just hold a ruler up to the moon when it's near the horizon and again when it's high in the sky. The lower moon may have seemed significantly larger, but a ruler will reveal its diameter hasn't changed. Cameras can also expose the moon's mendacity: This multiple-exposure image, for example, tracks the rocky satellite's consistent size as it rises over Seattle.
So what's going on? When we look at the moon, rays of reflected sunlight produce a roughly 0.15 millimeter-wide image on our retinas. "High moons and low moons make the same-sized spot," NASA Science's Tony Phillips writes in an explainer about the moon illusion, "yet the brain insists one is bigger than the other."
ponzo illusionVisual artists have long used perspective to portray 3-D space on a 2-D canvas, and psychologist Mario Ponzo showed a century ago how our brains can misjudge an object's true size based on its background. Known as the "Ponzo illusion," this is caused by our knowledge that distant objects appear smaller than they actually are. In the animated GIF below, the upper yellow bar seems wider than the lower one because it's "farther away" on the 2-D railroad tracks, prompting our brains to compensate for an expected distortion. Much like a high and low moon, however, they're both the same width, as the vertical red lines illustrate.
Surface features like trees and buildings might mimic this effect with the moon, along with another trick called the "Ebbinghaus illusion," which can make objects seem artificially large by juxtaposing them with smaller objects. But there's a problem with those theories, too. Pilots and sailors often see the moon illusion even when the horizon is virtually empty, suggesting foreground objects alone don't produce the phenomenon.
flat sky and Plenty of other explanations have been floated over the years, including the "flattened sky" model and a size illusion known as "oculomotor micropsia." Although many of these theories are plausible — and more than one may offer the answer — science has yet to fully explain the millennia-old mystery.
Source: http://www.mnn.com/

Sebastiaan de Boorder
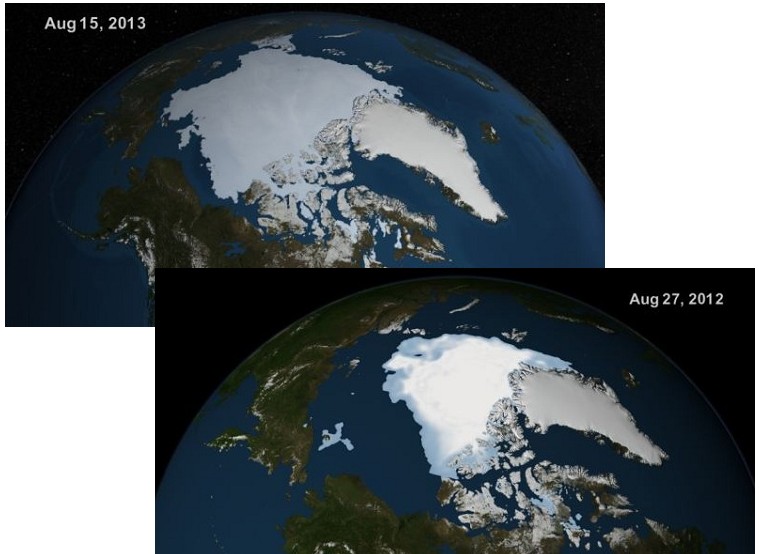

Global warming? Arctic Ice cap grows by 60 percent..
As a result of a cold Arctic summer compared with the same period last year nearly an additional 1.5 million square kilometers of ocean are covered with ice , an increase of 60 percent.
Six years ago the British public broadcaster BBC warned that even the North Pole in the summer of 2013 could well be free of ice.
Misguided.
The Northwest Passage from the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean has been blocked throughout the year .
Over 20 yachts got stuck and a cruise ship that wanted to take the route was forced to return.
Some scientists believe that the earth will continue to cool the coming years. If so computer predictions of catastrophic warming have deceived mankind in a dangerous way .
Data released last year showed that the earth did not become warmer the last 16 years . Between early 1997 and August 2012 , the global temperature has not increased .
Based on previous climate models , many governments have invested billions of euros in 'green' measures to counter Global warming.
The forecasters seem to be WRONG !
Cyclic.
There is increasing evidence that the Arctic ice levels are cyclic.
Source: http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-2415191/Global-cooling-Arctic-ice-caps-grows-60-global-warming-predictions.html
As a result of a cold Arctic summer compared with the same period last year nearly an additional 1.5 million square kilometers of ocean are covered with ice , an increase of 60 percent.
Six years ago the British public broadcaster BBC warned that even the North Pole in the summer of 2013 could well be free of ice.
Misguided.
The Northwest Passage from the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean has been blocked throughout the year .
Over 20 yachts got stuck and a cruise ship that wanted to take the route was forced to return.
Some scientists believe that the earth will continue to cool the coming years. If so computer predictions of catastrophic warming have deceived mankind in a dangerous way .
Data released last year showed that the earth did not become warmer the last 16 years . Between early 1997 and August 2012 , the global temperature has not increased .
Based on previous climate models , many governments have invested billions of euros in 'green' measures to counter Global warming.
The forecasters seem to be WRONG !
Cyclic.
There is increasing evidence that the Arctic ice levels are cyclic.
Source: http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-2415191/Global-cooling-Arctic-ice-caps-grows-60-global-warming-predictions.html

Sebastiaan de Boorder
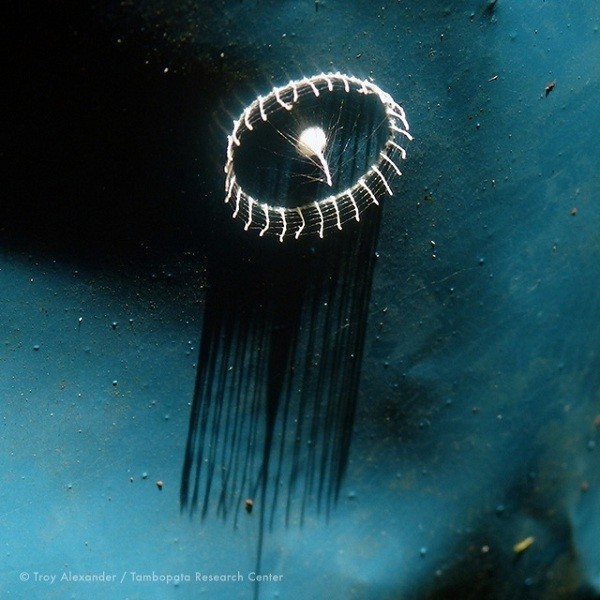

DESIGN BY MOTHER NATURE.
Mysterious tower-shaped web discovered in Peruvian Amazon.
In the Peruvian Amazon a mysterious structure has been discovered, which seems to consist of a spire surrounded by a white fence. Scientists are baffled.
The phenomenon was recorded on June 7th for the first time by Troy Alexander, a student at the Georgia Institute of Technology.
He discovered the bizarre formation under a blue stairs piece at a research center in southeastern Peru. Alexander also found these fences on tree trunks in the forest.
To date, no one can explain the structures. Also biologist Phil Torres from the Peruvian Tambopata province, has no idea what they are.
Entomologist William Eberhard said not to know what animal the formations made or what they are. Norm Platnick, curator at the spinning of the American Museum of Natural History Department, added: "I have seen the picture, but have no idea what animal responsible for this."
Source: Wired.com
Mysterious tower-shaped web discovered in Peruvian Amazon.
In the Peruvian Amazon a mysterious structure has been discovered, which seems to consist of a spire surrounded by a white fence. Scientists are baffled.
The phenomenon was recorded on June 7th for the first time by Troy Alexander, a student at the Georgia Institute of Technology.
He discovered the bizarre formation under a blue stairs piece at a research center in southeastern Peru. Alexander also found these fences on tree trunks in the forest.
To date, no one can explain the structures. Also biologist Phil Torres from the Peruvian Tambopata province, has no idea what they are.
Entomologist William Eberhard said not to know what animal the formations made or what they are. Norm Platnick, curator at the spinning of the American Museum of Natural History Department, added: "I have seen the picture, but have no idea what animal responsible for this."
Source: Wired.com

Sebastiaan de Boorder
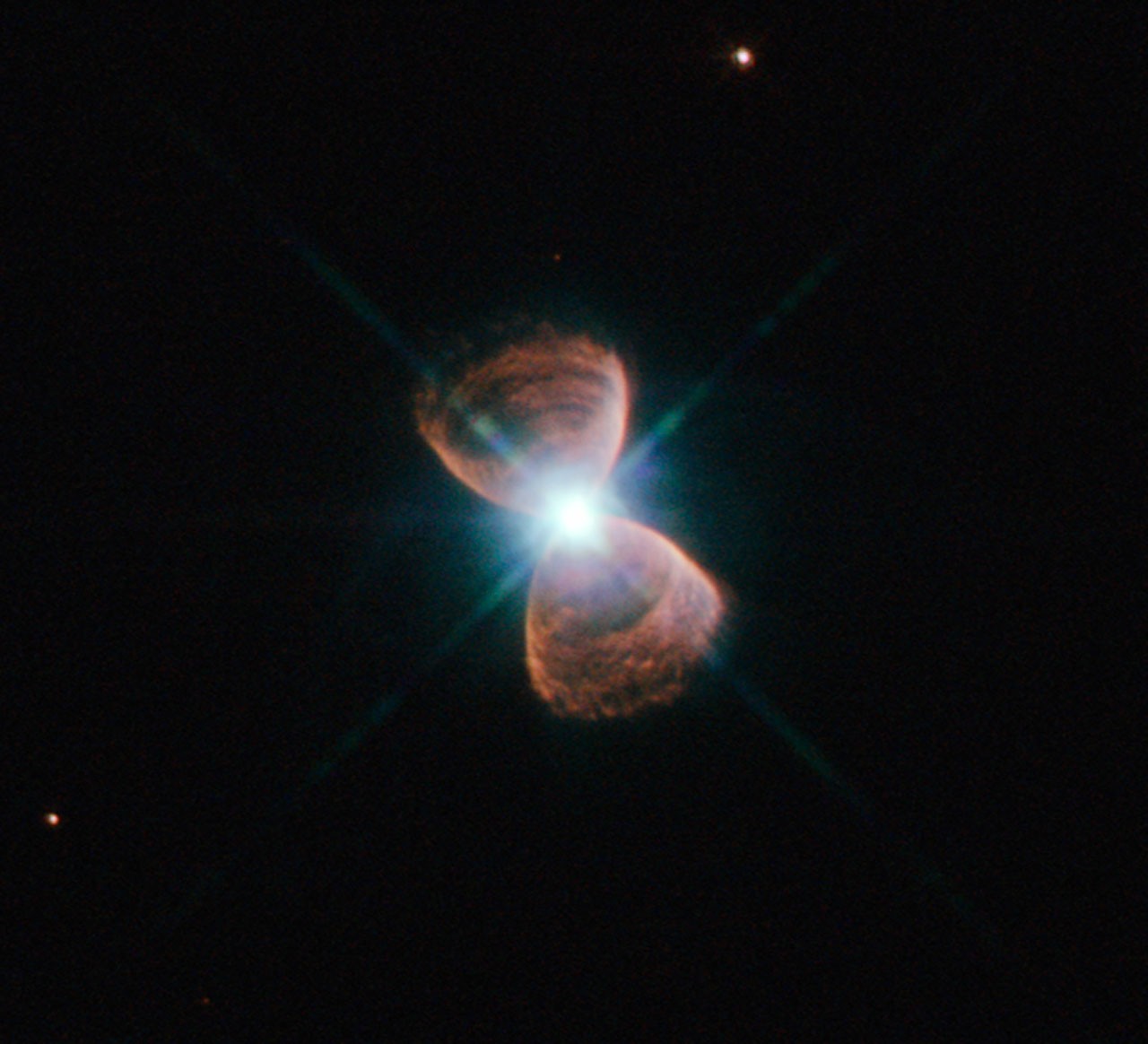

PLANETARY NEBULAE HAVE BIZARRE PREFERRED DIRECTION.
Astronomers got an unexpected surprise when they examined more than 100 planetary nebulae in the bulge of the Milky Way.
The axis of rotation of sprays are in the form of a butterfly or hourglass and are found to be in the plane of the galaxy parallel.
A planetary nebula is an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas stars in space. often a large amount of very complex shapes are found.
Towards the plane of the Milky Way we see mainly bipolar nebulae.
BOWLING ALLEY
Such nebulae have been formed in other places and have different properties, so it is a mystery why they have the same spatial orientation, as the pins at a bowling alley.
Researchers suspect that there is something bizarre going on with solar systems in the central bulge of our galaxy. The direction in which they rotate contradicts the interstellar clouds in which they are formed, which is quite remarkable
MAGNETIC FIELDS
It seems that the bulge exerts a greater influence on our galaxy than previously thought. Astronomers suspect that the orderly conduct of the planetary nebulae may be caused by the presence of strong magnetic fields at the time of the creation of the bulge.
Because nebulae that are closer to the earth have no preferred direction, magnetic fields should be less strong than they are now in our area.
Source : http://www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic1316/ and http://www.eso.org/public/news/eso1338/
Astronomers got an unexpected surprise when they examined more than 100 planetary nebulae in the bulge of the Milky Way.
The axis of rotation of sprays are in the form of a butterfly or hourglass and are found to be in the plane of the galaxy parallel.
A planetary nebula is an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas stars in space. often a large amount of very complex shapes are found.
Towards the plane of the Milky Way we see mainly bipolar nebulae.
BOWLING ALLEY
Such nebulae have been formed in other places and have different properties, so it is a mystery why they have the same spatial orientation, as the pins at a bowling alley.
Researchers suspect that there is something bizarre going on with solar systems in the central bulge of our galaxy. The direction in which they rotate contradicts the interstellar clouds in which they are formed, which is quite remarkable
MAGNETIC FIELDS
It seems that the bulge exerts a greater influence on our galaxy than previously thought. Astronomers suspect that the orderly conduct of the planetary nebulae may be caused by the presence of strong magnetic fields at the time of the creation of the bulge.
Because nebulae that are closer to the earth have no preferred direction, magnetic fields should be less strong than they are now in our area.
Source : http://www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic1316/ and http://www.eso.org/public/news/eso1338/

Sebastiaan de Boorder
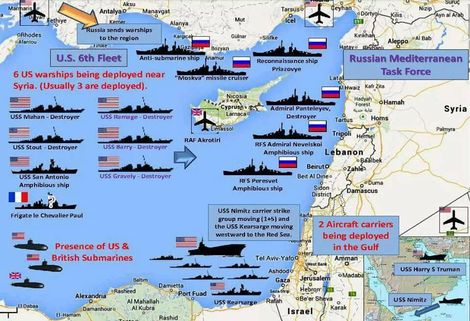
WAR TRADING PART III .
If we are trading War, we should look and know what we are trading..
This reminds me of a game i played when i was a kid!
If we are trading War, we should look and know what we are trading..
This reminds me of a game i played when i was a kid!

Sebastiaan de Boorder
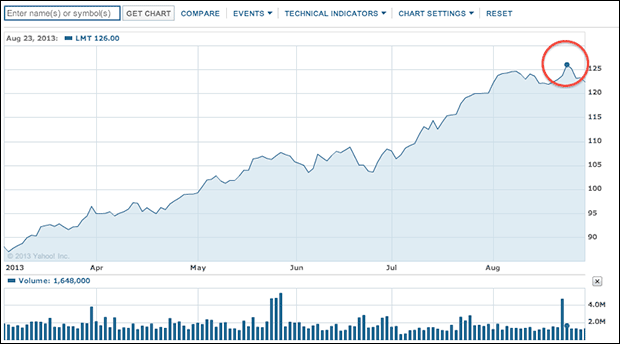
WAR TRADING PART DEUX.
We could have bought Lockheed Martin,
Lockheed Martin is the largest defense company in the world!
The company builds aircraft, naval vessels, land vehicles and spacecraft.
Their products are used throughout the world, but mainly by the U.S. Army.
In 2003, sales of Lockheed Martin was 80% dependent on the U.S. Department of Defense and other U.S. government agencies.
Again the same story for the shares.
´Sad sick little world!
We could have bought Lockheed Martin,
Lockheed Martin is the largest defense company in the world!
The company builds aircraft, naval vessels, land vehicles and spacecraft.
Their products are used throughout the world, but mainly by the U.S. Army.
In 2003, sales of Lockheed Martin was 80% dependent on the U.S. Department of Defense and other U.S. government agencies.
Again the same story for the shares.
´Sad sick little world!

Sebastiaan de Boorder

WAR TRADING.
Raytheon Company is an American defense and technology company. Raytheon gets more than 90% of their revenue from defense contracts and is the world's fifth largest defense company. They are also called the "merchant of death". As you can see, the share increased to unprecedented levels in recent months.
Raytheon Company is an American defense and technology company. Raytheon gets more than 90% of their revenue from defense contracts and is the world's fifth largest defense company. They are also called the "merchant of death". As you can see, the share increased to unprecedented levels in recent months.

Sebastiaan de Boorder


THE GOLD RUSH..
1.
The element symbol for gold is Au. The symbol comes from the old Latin name for gold, aurum, which means "shining dawn" or "glow of sunrise". The word "gold" comes from the Germanic languages, originating from the Proto-Germanic gulþ and Proto-Indo-European ghel, meaning "yellow/green". The pure element has been known since ancient times.
2.
Gold and copper were the first metals to be discovered by humans around 5000 B.C. and are the only two non-white-colored metals.
3.
Gold is so rare that the world pours more steel in an hour than it has poured gold since the beginning of recorded history.
4.
Gold has been discovered on every continent on earth.
5.
Gold melts at 1064.43° Centigrade. It can conduct both heat and electricity and it never rusts.
6.
Gold is extremely ductile. A single ounce of gold (about 28 grams) can be stretched into a gold thread 5 miles (8 kilometers) long.
7.
Gold threads can even be used as embroidery thread.
8.
In 1933, Franklin Roosevelt signed Executive Order 6102 which outlawed U.S. citizens from hoarding gold. Owning gold (except for jewelers, dentists, electricians, and other industry workers) was punishable by fine up to $10,000 and/or ten years in prison
9.
In 1599, a Spanish governor in Ecuador taxed the Jivaro tribe so excessively that they executed him by pouring molten gold down his throat. This form of execution was also practiced by the Romans and the Spanish Inquisition.
10.
The value of gold has been used as the standard for many currencies. After WWII, the United States created the Bretton Woods System, which set the value of the U.S. dollar to 1/35th of a troy ounce (888.671 mg) of gold. This system was abandoned in 1971 when there was no longer enough gold to cover all the paper money in circulation.
11.
The “troy ounce” of gold comes from the French town of Troyes, which first created a system of weights in the Middle Ages used for precious metals and gems. One troy ounce is 480 grains. A grain is exactly 64.79892 mg.
12.
The world’s largest stockpile of gold can be found five stories underground inside the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s vault and it holds 25% of the world's gold reserve (540,000 gold bars). While it contains more gold than Fort Knox, most of it belongs to foreign governments.
13. ??
Question : Is our gold still inside the Federal Reserve Bank? Germany does not get access to their own gold..
IMAGE RT.COM
1.
The element symbol for gold is Au. The symbol comes from the old Latin name for gold, aurum, which means "shining dawn" or "glow of sunrise". The word "gold" comes from the Germanic languages, originating from the Proto-Germanic gulþ and Proto-Indo-European ghel, meaning "yellow/green". The pure element has been known since ancient times.
2.
Gold and copper were the first metals to be discovered by humans around 5000 B.C. and are the only two non-white-colored metals.
3.
Gold is so rare that the world pours more steel in an hour than it has poured gold since the beginning of recorded history.
4.
Gold has been discovered on every continent on earth.
5.
Gold melts at 1064.43° Centigrade. It can conduct both heat and electricity and it never rusts.
6.
Gold is extremely ductile. A single ounce of gold (about 28 grams) can be stretched into a gold thread 5 miles (8 kilometers) long.
7.
Gold threads can even be used as embroidery thread.
8.
In 1933, Franklin Roosevelt signed Executive Order 6102 which outlawed U.S. citizens from hoarding gold. Owning gold (except for jewelers, dentists, electricians, and other industry workers) was punishable by fine up to $10,000 and/or ten years in prison
9.
In 1599, a Spanish governor in Ecuador taxed the Jivaro tribe so excessively that they executed him by pouring molten gold down his throat. This form of execution was also practiced by the Romans and the Spanish Inquisition.
10.
The value of gold has been used as the standard for many currencies. After WWII, the United States created the Bretton Woods System, which set the value of the U.S. dollar to 1/35th of a troy ounce (888.671 mg) of gold. This system was abandoned in 1971 when there was no longer enough gold to cover all the paper money in circulation.
11.
The “troy ounce” of gold comes from the French town of Troyes, which first created a system of weights in the Middle Ages used for precious metals and gems. One troy ounce is 480 grains. A grain is exactly 64.79892 mg.
12.
The world’s largest stockpile of gold can be found five stories underground inside the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s vault and it holds 25% of the world's gold reserve (540,000 gold bars). While it contains more gold than Fort Knox, most of it belongs to foreign governments.
13. ??
Question : Is our gold still inside the Federal Reserve Bank? Germany does not get access to their own gold..
IMAGE RT.COM

Sebastiaan de Boorder




China is experiencing its coldest winter in decades
BEIJING — Ice swimmers were taking their shocking plunges in north China through the thickest ice in years, but most Chinese nationwide are shivering through the coldest weather in nearly three decades.
Freezing weather has sent temperatures diving to a national average of 25 degrees Fahrenheit since Nov. 20, the lowest average temperature in 28 years, says the China Meteorological Administration.
In China's frozen northeast, where the city of Harbin hosts a popular snow and ice festival each winter, temperatures over the same period averaged minus-5 degrees, a 43-year low, according to the CMA.
And a new cold front will hit south China this week, the CMA said, as temperatures in several regions will be several degrees lower than the average of normal years. The CMA said ice had covered 10,500 square miles of the sea surface, the most expansive since 2008 when authorities began to collect ice data, and it said the ice coverage will likely continue to grow.
One million people in normally temperate south China have been going through unusually cold weather in recent days, the state-run Xinhua news agency reported Tuesday. Thousands of travelers have endured long delays as fog and frozen runways paralyzed airports. Hundreds of irate passengers berated staff at Kunming's airport last week, according to pictures on the Caixin magazine website.
Some trains have also been halted and several highways temporarily closed due to snow and ice.
In north China's Inner Mongolia, record-low temperatures and heavy snow have left two people dead and affected 770,000 others, said Xinhua. More than 260,000 people were in need of emergency aid.
In eastern Shandong province, more than 1,000 ships are stuck because of thick sea ice on Laizhou Bay. The government fretted over damage to late-season crops such as winter wheat. Prices for vegetable have jumped 55% in the past 10 weeks, reported the People's Daily newspaper.
The super-low temperatures are rare but will continue for some time, said Zhang Lansheng, 85, one of China's earliest environment and climate experts. Compared to early 2008, when south China suffered a snow and ice "disaster" that caused widespread power outages and affected more than 100 million people, China now boasts more experience and disaster readiness, he said.
"But we need to increase the accuracy of weather forecasts, and different levels of government should improve emergency facilities and organize people to boost their ability to cope with disasters."
The weather has also exposed a decades-old debate about the lack of heating in south China. A line drawn in the 1950s split China into a northern half that built and still enjoys heavily subsidized public heating, and a southern half that shivers through winter without a public heating network and must make do with private, often less effective, heating devices.
While some officials and energy experts suggest heating the south could endanger China's energy supply, Zhang hopes southern cities with enough financial resources can build heating networks with clean energy.
"I don't think the old way to divide the heating areas is good. But it's hard to change it now, so I don't think the south will be the same as the north anytime soon."
The nation's great size means tourists can always enjoy warm days in destinations such as Hainan Island, China's "Hawaii." But some Chinese are determined to make the most of the deep chill.
At the Harbin ice festival, 16 Chinese and foreign couples braved the cold for a mass wedding celebration on Sunday.
China has no history of winter sports, but middle-class Chinese are increasingly heading to suburban ski resorts that have mushroomed in north China in recent years where ice fishermen still haul their thrashing prey up through holes sawed through thick ice.
The seven-leg China Tour de Ski, a cross-country ski race that started in frozen Jilin in China's northeast, continued as scheduled. It finishes Friday in frigid Xinjiang, on China's border with Kazakhstan, where temperatures have hit 40 below this winter.
India is also experiencing record cold, and forecasts in Israel call for 2 inches of snow, a rare occurrence. The Weather Underground reports that the northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, where New Delhi is located, has seen record cold temperatures. Temperatures in New Delhi fell to a low of 35.4 degrees on Jan. 6 and the high temperature on Jan. 2 was 49.6, the coldest daily maximum in 44 years.
Locations in Haryana State reported a low temperature of 26.7 degrees, an all-time record cold temperature.
Contributing: Sunny Yang
Source: http://www.usatoday.com/story/news/world/2013/01/08/china-cold/1817271/
BEIJING — Ice swimmers were taking their shocking plunges in north China through the thickest ice in years, but most Chinese nationwide are shivering through the coldest weather in nearly three decades.
Freezing weather has sent temperatures diving to a national average of 25 degrees Fahrenheit since Nov. 20, the lowest average temperature in 28 years, says the China Meteorological Administration.
In China's frozen northeast, where the city of Harbin hosts a popular snow and ice festival each winter, temperatures over the same period averaged minus-5 degrees, a 43-year low, according to the CMA.
And a new cold front will hit south China this week, the CMA said, as temperatures in several regions will be several degrees lower than the average of normal years. The CMA said ice had covered 10,500 square miles of the sea surface, the most expansive since 2008 when authorities began to collect ice data, and it said the ice coverage will likely continue to grow.
One million people in normally temperate south China have been going through unusually cold weather in recent days, the state-run Xinhua news agency reported Tuesday. Thousands of travelers have endured long delays as fog and frozen runways paralyzed airports. Hundreds of irate passengers berated staff at Kunming's airport last week, according to pictures on the Caixin magazine website.
Some trains have also been halted and several highways temporarily closed due to snow and ice.
In north China's Inner Mongolia, record-low temperatures and heavy snow have left two people dead and affected 770,000 others, said Xinhua. More than 260,000 people were in need of emergency aid.
In eastern Shandong province, more than 1,000 ships are stuck because of thick sea ice on Laizhou Bay. The government fretted over damage to late-season crops such as winter wheat. Prices for vegetable have jumped 55% in the past 10 weeks, reported the People's Daily newspaper.
The super-low temperatures are rare but will continue for some time, said Zhang Lansheng, 85, one of China's earliest environment and climate experts. Compared to early 2008, when south China suffered a snow and ice "disaster" that caused widespread power outages and affected more than 100 million people, China now boasts more experience and disaster readiness, he said.
"But we need to increase the accuracy of weather forecasts, and different levels of government should improve emergency facilities and organize people to boost their ability to cope with disasters."
The weather has also exposed a decades-old debate about the lack of heating in south China. A line drawn in the 1950s split China into a northern half that built and still enjoys heavily subsidized public heating, and a southern half that shivers through winter without a public heating network and must make do with private, often less effective, heating devices.
While some officials and energy experts suggest heating the south could endanger China's energy supply, Zhang hopes southern cities with enough financial resources can build heating networks with clean energy.
"I don't think the old way to divide the heating areas is good. But it's hard to change it now, so I don't think the south will be the same as the north anytime soon."
The nation's great size means tourists can always enjoy warm days in destinations such as Hainan Island, China's "Hawaii." But some Chinese are determined to make the most of the deep chill.
At the Harbin ice festival, 16 Chinese and foreign couples braved the cold for a mass wedding celebration on Sunday.
China has no history of winter sports, but middle-class Chinese are increasingly heading to suburban ski resorts that have mushroomed in north China in recent years where ice fishermen still haul their thrashing prey up through holes sawed through thick ice.
The seven-leg China Tour de Ski, a cross-country ski race that started in frozen Jilin in China's northeast, continued as scheduled. It finishes Friday in frigid Xinjiang, on China's border with Kazakhstan, where temperatures have hit 40 below this winter.
India is also experiencing record cold, and forecasts in Israel call for 2 inches of snow, a rare occurrence. The Weather Underground reports that the northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, where New Delhi is located, has seen record cold temperatures. Temperatures in New Delhi fell to a low of 35.4 degrees on Jan. 6 and the high temperature on Jan. 2 was 49.6, the coldest daily maximum in 44 years.
Locations in Haryana State reported a low temperature of 26.7 degrees, an all-time record cold temperature.
Contributing: Sunny Yang
Source: http://www.usatoday.com/story/news/world/2013/01/08/china-cold/1817271/

:
